A calcaneus fracture (broken heel) is when you damage your heel bone. That can happen if you put stress on your heel bone. You may have a more serious calcaneal fracture if you’re in a vehicle accident or land on your foot after falling from a high spot. Treatment varies depending on your injury, but you may need surgery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
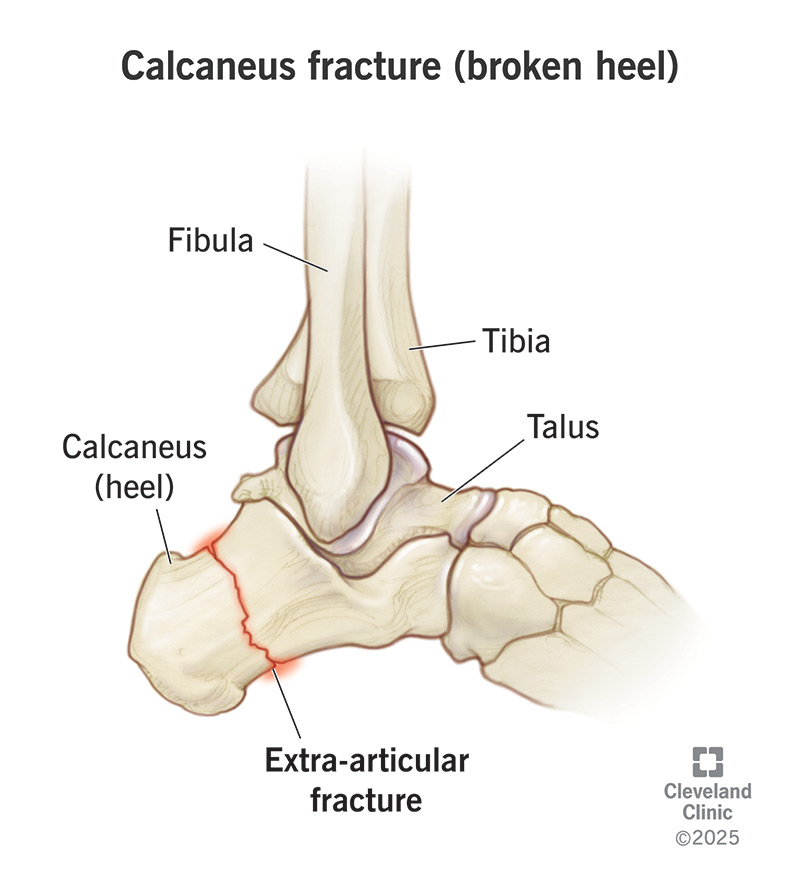
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/calcaneus-fracture-broken-heel)
A calcaneus (kal-KAY-nee-us) fracture, or calcaneal fracture, is a type of bone fracture. It happens when you break your heel bone (calcaneus). Your heel bone is the large bone at the back of your foot.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Calcaneus fractures can be severe fractures that crush your heel bone and damage a nearby joint, cartilage, ligament and tendons. Less serious fractures are calcaneus stress fractures.
Orthopedic surgeons and podiatrists are healthcare providers who specialize in diagnosing and treating broken heels.
The types of fractured heel you have depends on the amount of damage to your heel:
Advertisement
Calcaneus fractures and calcaneus stress fractures cause different symptoms. In general, calcaneus fractures cause more serious and painful symptoms than calcaneus stress fractures.
Intra-articular and extra-articular calcaneus fractures may cause the following symptoms:
Sometimes, pieces of a broken heel bone break through your skin (compound fracture). This is a medical emergency. Call 911 (or your local emergency services number) or have someone take you to the emergency room.
Calcaneal stress fractures cause heel pain that gets worse when you put pressure on your heel. For example, standing for a long time may make your heel hurt. The pain eases when you’re not being active. Stress fractures develop over time. You may notice a twinge in your heel that slowly becomes more noticeable. Other are:
All calcaneus fractures happen when you damage your heel bone. But calcaneus fractures and calcaneus stress fractures have very different causes.
For example, intra-articular and extra-articular calcaneus fractures often happen because you have a traumatic injury from:
These types of fractures can happen during a crash because you push your foot down on the floorboard, brake or accelerator. Force from the crash can crush your heel bone.
Any motion you do over and over can cause a calcaneus stress fracture. The condition often affects people who walk, jog or run a lot. You may get a calcaneus stress fracture if you play sports that involve a lot of running back and forth, like basketball, soccer or tennis.
Calcaneus fractures and calcaneus stress fractures are very different injuries that may lead to different types of complications.
Intra-articular and extra-articular calcaneus fractures and treatment may cause the following complications:
Advertisement
Without treatment, malunion and foot deformity may cause ankle pain and ankle arthritis.
Calcaneus stress fracture complications are less serious than complications from a calcaneus fracture and treatment. Complications may include:
Doctors take different steps to diagnose calcaneus fractures. You may work with a podiatrist to find out why you have heel pain that comes and goes. Orthopaedic surgeons, trauma surgeons or podiatrists with special training in hindfoot and ankle surgery typically diagnose and treat more severe fractures.
Most calcaneal fractures are traumatic injuries. That’s why you may receive your diagnosis and initial treatment in an emergency room. A surgeon will ask how the injury happened. They’ll examine your foot and ankle. Then, they’ll do imaging tests. The surgeon may do more tests to look for issues that a fall or vehicle crash can cause.
Studies show people with calcaneal fractures often have spinal compression fractures and tibial plateau fractures (a broken bone in your knee).
A podiatrist or sports medicine physician may diagnose a calcaneus stress fracture. They’ll ask about your symptoms and how long you’ve had them. They may ask about your daily routine and activities.
Advertisement
They’ll examine your heel and ankle. They may also check if you can feel sensations on the bottom of your foot.
Your healthcare providers may do imaging tests like:
Your treatment will depend on the type of fracture. In general, surgery is treatment for calcaneus fractures where pieces of your bone are out of place, damage your subtalar joint or move enough to form a gap.
If you need surgery, your orthopedic or podiatric surgeon will do an open reduction and internal fixation. Your surgeon will make an incision (cut) in your heel. They’ll realign the broken bones. Then, they’ll place screws or plates on the bones to keep them in place while they heal.
You may need more than one surgery to repair a severe calcaneus fracture. You may also need physical therapy if your injury and surgery make it hard for you to move your foot. Physical therapy supports healing, too.
You won’t need surgery for a calcaneus stress fracture. You also won’t need it for a fracture that doesn’t affect your subtalar joint or one where your bone doesn’t move enough to create a gap. Your provider may recommend the RICE method to treat these kinds of fractures. RICE stands for:
Advertisement
Your provider may place your foot in a boot if you have a stress fracture. They may put a splint or cast on your foot and ankle to treat a calcaneus fracture. The cast or splint will protect your heel and keep damaged bones in place while they heal. You’ll also receive physical therapy.
That depends on your situation. For example, you may need several surgeries and other kinds of treatment if you have a severe calcaneus fracture that damages your subtalar joint. In that case, it may be months or years before you completely recover.
Most people heal from a calcaneal stress fracture within a few months. During healing, you’ll likely wear a boot and limit weightbearing on your heel. After treatment, you may need physical therapy. Therapy will improve your strength and prevent further injury.
It takes time to recover from a calcaneus fracture (broken heel). That’s true if your heel injury is a stress fracture or you do serious damage to your heel bone in a fall or vehicle accident. Intra-articular fractures are severe injuries and can sometimes cause permanent damage and even be life-changing.
A stress fracture in your heel may put you on the sidelines for a few months. And a severely broken heel can take months or even years to recover from. Your healthcare team will understand if you’re wondering what to expect. They’ll do everything they can to help you heal. And they’ll be with you every step of the way as you work to recover.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
From sudden injuries to chronic conditions, Cleveland Clinic’s orthopaedic providers can guide you through testing, treatment and beyond.
