Swimmer’s ear (also called otitis externa) is an ear infection in your ear canal, the pathway between your outer ear and your middle ear. Swimmer’s ear may be a bacterial or fungal infection. Healthcare providers treat swimmer’s ear with ear drops that eliminate the infection.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
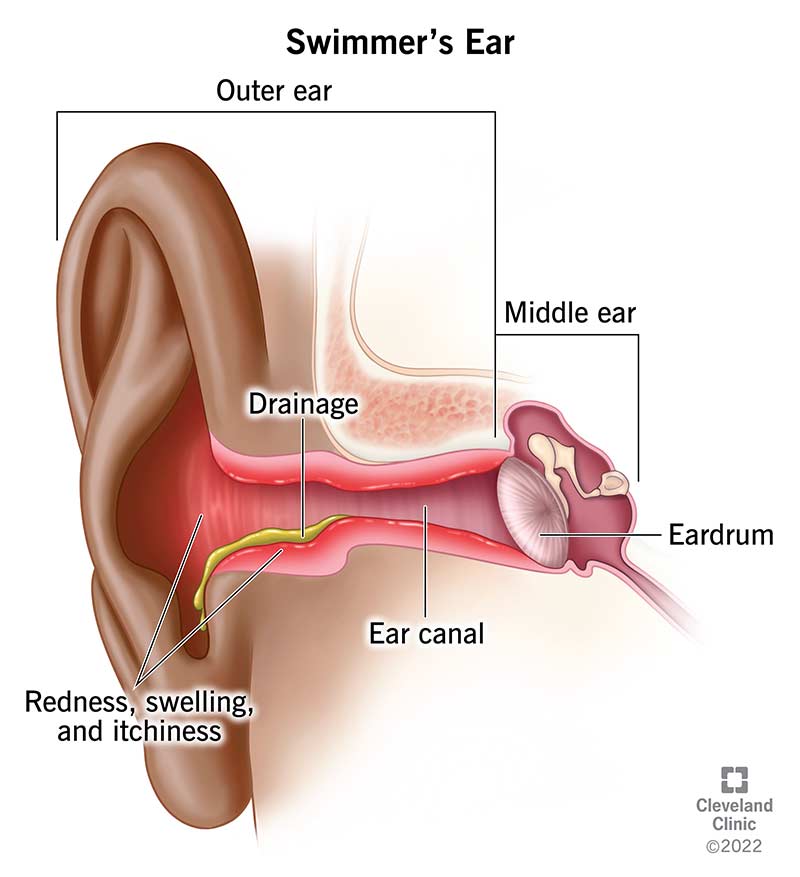
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/8381-swimmers-ear)
Swimmer’s ear (otitis externa) is an ear canal infection. Your ear canal is the pathway between your outer ear and your middle ear. Swimmer’s ear can be a bacterial infection or fungal infection.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
We call it “swimmer’s ear” because avid swimmers commonly experience it. But anyone can get it — especially during the warmer months when many people spend more time in the water.
Left untreated, swimmer’s ear may muffle your hearing. In some cases, it can even cause temporary hearing loss. Most of the time, treatment solves any infection-related hearing issues. Healthcare providers treat swimmer’s ear with ear drops.
Swimmer’s ear is common. About 10% of people in the U.S. will have it at some point. Swimmer’s ear can affect anyone. But kids between the ages of 7 and 14 are most likely to get it.
Swimmer’s ear symptoms can be mild or severe and may include:
Many things can cause swimmer’s ear, but activity that traps water in your ear canal is the most common cause. Bacteria and fungi thrive in warm, moist places. So, water pooling in your ear canal is the perfect environment for bacteria and fungi to settle in, start multiplying and eventually cause infection.
Advertisement
It’s much more common to get swimmer’s ear from a bacterium than a fungus. In rare cases, a combination of pathogens (germs that make you sick) can cause swimmer’s ear. Bacteria that can cause swimmer’s ear include Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Fungi that can cause the condition include Candida and Aspergillus.
You’re more likely to develop swimmer’s ear if you:
Swimmer’s ear complications are rare, especially if you treat your symptoms quickly. But they can still happen. Possible issues include:
A provider will examine your ears for redness, swelling or other signs of damage. If you have drainage coming from your ears, providers may take a sample of the fluid to determine what caused the infection. This is valuable information because bacterial infections and fungal infections require different treatments.
Advertisement
It’s easy to confuse swimmer’s ear with a middle ear infection — another common childhood condition. Typically, kids with a middle ear infection have pain that gets worse when laying down. They might also develop vomiting, diarrhea or a decreased appetite.
These two conditions require different treatments. What works for swimmer’s ear won’t work for a middle ear infection, and vice versa. That’s why it’s so important to see your healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis.
In most cases, healthcare providers prescribe ear drops to eliminate the infection. Depending on your situation, your provider might recommend these medications for otitis externa:
You can also take over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers like acetaminophen (Tylenol®) or ibuprofen (Advil®) to ease any discomfort.
Swimmer’s ear usually isn’t serious when you get treatment. In most cases, you can expect the infection to go away in about a week. Without treatment, complications — like the spread of infection — can occur. These complications usually require stronger antibiotics or antifungals.
Advertisement
No, it won’t. Swimmer’s ear is an infection in your ear canal that won’t go away unless you treat it. Left untreated, a swimmer’s ear infection may spread to the base of your skull, your brain or your cranial nerves.
Because infection can spread beyond your outer ear, it’s important to schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider whenever you notice symptoms. The sooner you treat it, the better.
Yes, keeping your ears dry is the most effective way to prevent swimmer’s ear.
To further reduce your risk, follow these otitis externa self-care tips:
Schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider if you develop any swimmer’s ear symptoms like ear pain, drainage, itchiness or muffled hearing.
If a healthcare provider has already prescribed ear drops for a swimmer’s ear infection, call them if you still have symptoms 10 days later. You might need a stronger medication.
Advertisement
Before you hit the pool, lake or beach, take extra care to protect your ears. If you notice ear pain or itchiness after being in the water, let your healthcare provider know. They can prescribe ear drops that can get rid of your symptoms in about a week. Swimmer’s ear usually isn’t serious if you treat it early.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Need care fast? Cleveland Clinic’s Express Care and Urgent Care locations treat everything from sprains to sinus infections — no appointment needed.
