Pneumonitis is inflammation in your lung tissue. Causes include irritants such as chemicals, allergens and certain treatments for other conditions. Healthcare providers can treat pneumonitis, but long-term inflammation can cause irreversible lung damage.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
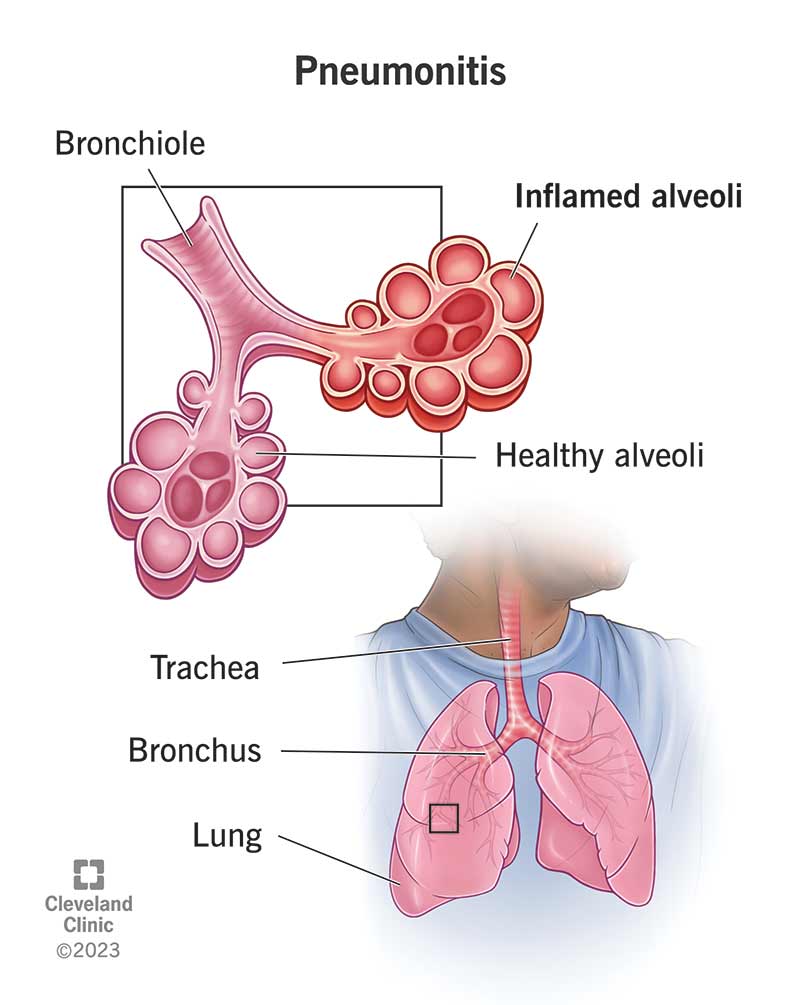
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/24810-pneumonitis)
Pneumonitis (noo-MOHN-eye-tus) is general inflammation in your lungs that can affect how well you breathe and cause other bodily symptoms. It occurs when a foreign substance (irritant) inflames the small air sacs in your lungs (alveoli).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
There are different types of pneumonitis inflammation. They include:
Yes, pneumonitis is serious. Long-term exposure to irritants that cause pneumonitis may cause permanent lung damage.
There are different types of pneumonitis according to their cause. These include:
Early signs of pneumonitis include common cold-like symptoms, including:
Advertisement
Other symptoms may include:
Chronic pneumonitis symptoms may include:
There are many different possible pneumonitis causes. Common causes include:
No, pneumonitis isn’t contagious. However, some viruses or bacteria that may cause pneumonitis are contagious.
Anyone can get pneumonitis. However, you may be more likely to get pneumonitis if you work:
Using a humidifier in your home or spending time in hot tubs also increases your risk of getting pneumonitis. These devices give off a mist that you breathe in. Without regular cleaning, molds and bacteria can grow, and you may breathe them in through the mist.
Long-term exposure to irritants that cause pneumonitis may cause serious, irreversible lung damage. These may include:
A healthcare provider can diagnose pneumonitis. They’ll examine your symptoms, review your medical history and conduct a physical examination. During the physical exam, they’ll listen to your lungs with a stethoscope (auscultation). They’ll also order tests to help confirm their diagnosis.
To help confirm pneumonitis, a healthcare provider may order the following tests:
Advertisement
If you have pneumonitis, the best way to treat it is to avoid its cause. Your provider may also recommend the following medications or treatments:
Advertisement
It depends on what’s causing your pneumonitis and its severity. It may take several months for your lungs to heal. In some cases, lung damage may be permanent.
With early diagnosis and treatment, the outlook for pneumonitis is good. If you have acute pneumonitis, your symptoms may go away within a few days after removing the irritant from your environment.
Subacute cases of pneumonitis fall between acute and chronic. They usually occur due to long-term exposure to low levels of irritants. Your symptoms may last a few months, and you typically need medication or therapy.
Chronic pneumonitis damage is usually permanent. However, medication and therapy can help reduce the severity of your symptoms.
Milder cases of pneumonitis may go away within a few days or months once you and a healthcare provider identify the irritant and take the proper steps to avoid it.
Severe cases of pneumonitis usually don’t go away.
It depends. With proper diagnosis and treatment, you can fully recover from acute and subacute cases of pneumonitis. You usually can’t make a full recovery from severe cases of pneumonitis. However, medication and therapy can help make your symptoms more manageable.
The best way to lower your risk of developing pneumonitis is to avoid substances that cause lung inflammation. If you must be around potential irritants, you may be able to reduce your exposure by:
Advertisement
If you have pneumonitis, you and your healthcare provider will work together to reduce exposure to what’s causing pneumonitis. Be sure to take all prescribed medications and perform all breathing exercises as directed by your provider.
See your healthcare provider if you have symptoms of pneumonitis or if your symptoms don’t improve with treatment.
Call 911 or your local emergency number or get to an emergency room immediately if you feel like you can’t get enough air into your lungs.
Pneumonitis is inflammation in your lung tissues without an infection. The inflammation affects the walls of your alveoli, but it doesn’t cause fluid or pus to build up. Pneumonitis can cause a dry cough.
Pneumonia is a bacterial, viral or fungal infection in your lungs. It’s a type of pneumonitis that causes inflammation and fluid or pus to build up in your lung tissues. This can cause a cough that brings up yellow, green or bloody mucus (wet cough).
Pneumonitis causes inflammation in your lung tissues. Long-term exposure to whatever is causing pneumonitis can cause severe lung damage. It’s a good idea to see a healthcare provider at the first sign of symptoms to help prevent irreversible damage. They can order tests to determine the severity of your pneumonitis and work with you to reduce your symptoms and improve your breathing.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Breathing issues can affect your life in many ways. Cleveland Clinic’s respiratory therapy program treats your symptoms so you can feel better day to day.
