Mpox, formerly called monkeypox, is a disease similar to smallpox caused by a virus. It causes flu-like symptoms such as fever and chills, and a rash that can take weeks to clear. There’s no proven treatment for mpox, but it usually goes away on its own. Healthcare experts recommend getting vaccinated if you’re at higher risk for mpox.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
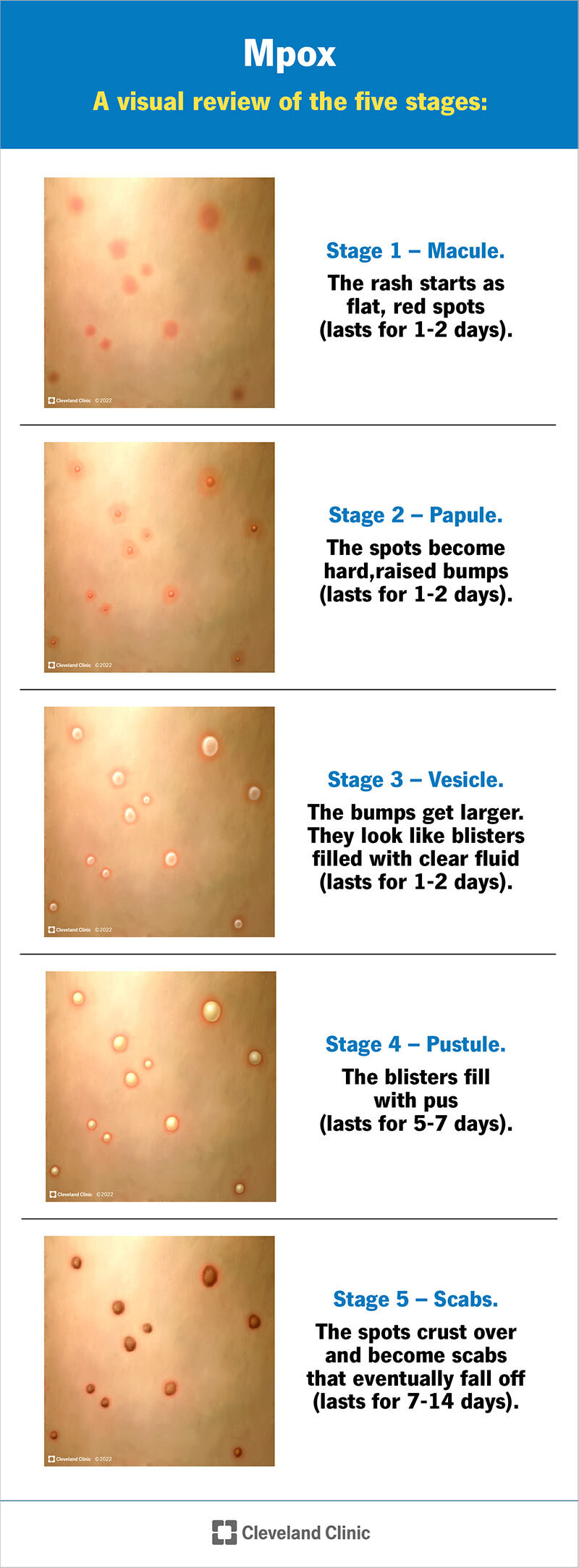
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/mpox)
Mpox (previously known as monkeypox) is a disease caused by a virus. It usually causes a rash and flu-like symptoms. The rash is similar to the one caused by a related virus, smallpox.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Cases of mpox happen regularly (it’s endemic) in parts of Africa. But outbreaks sometimes happen in other places around the world. An outbreak is an increase in cases, or a larger-than-expected number of cases.
There are two known subtypes of mpox:
Since 2023, there’s been an outbreak of clade I mpox in Central and East Africa.
Since 2022, there’s been an ongoing outbreak of clade II mpox affecting countries around the world. There were 1,700 reported cases in the U.S. in 2023. In total, there’ve been over 102,000 reported cases of clade II mpox worldwide since 2022.
The last outbreak in the U.S. before this was in 2003. Forty-seven people in six states were infected with mpox from pet prairie dogs. It wasn’t spread from person to person.
Symptoms of mpox include:
Not everyone with mpox develops all the symptoms. Different ways you might experience symptoms include:
Advertisement
The rash caused by mpox can appear as sores on your mouth, face, hands, feet, penis, vagina or anus (butthole). Some people have a widespread rash, but others only a have few bumps or blisters.
Mpox rash can go through several stages over two to four weeks:
An infection with monkeypox virus (Orthopoxvirus monkeypox) causes mpox. Viruses are small pieces of genetic information in a protective coating. The virus that causes mpox is a pox virus, and a member of the genus Orthopoxvirus.
Mpox can spread through:
Specific situations that can spread mpox include:
Anyone can get mpox. The global outbreak appears to be disproportionately affecting men who have sex with men (MSM). On the other hand, in the clade I outbreak in the Democratic Republic of Congo, children under 15 years old make up more than half the cases.
In the U.S., you might be at a higher risk of exposure if:
Advertisement
You might be more likely to get severely ill with mpox if you:
Babies younger than 1 year old are also at a higher risk for severe illness.
Complications caused by mpox can include:
To diagnose mpox, your healthcare provider will swab two to three sores (lesions). They’ll send the samples to a lab for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing. They may also do blood tests.
It’s important to let your provider know if you may have been exposed to mpox. Your provider might test you for other illness that cause a rash, like measles or chickenpox.
There aren’t any approved antiviral treatments for mpox. If you’re very sick or if you’re pregnant, your provider might treat you with antiviral drugs, like tecovirimat (TPOXX) or cidofovir/brincidofovir. Vaccinia immune globulin (VIG-IV), a type of antibody treatment, is also sometimes an option.
Advertisement
These drugs are approved to treat other viral infections (like smallpox) and could benefit some people. But researchers are still studying how well they work for mpox.
Mpox normally takes about two to four weeks to run its course. Your provider will monitor you until the rash resolves.
Clade II mpox — the subtype causing a global outbreak — is rarely fatal. The fatality (death) rate for clade I has historically been around 10%. But during recent outbreaks, it’s been less than 3.3%.
The best way to reduce your risk of mpox is to get vaccinated if you’re at a higher risk of exposure. It’s important to get vaccinated before, or as soon as possible after, exposure.
In addition to vaccines, other ways to help prevent the spread of mpox include:
Advertisement
You can have mpox and not know it. Even if you don’t show many signs of infection, it’s possible that you can still spread it to others through prolonged, close contact.
If you have mpox symptoms, you can take care of yourself at home with:
You can also reduce the risk of spreading mpox and take care of others by:
Talk to your healthcare provider if you:
If you’re pregnant, let your pregnancy care provider know right away if you’ve been exposed to mpox or have symptoms. They can help you reduce your risk of severe illness and passing mpox to the fetus during pregnancy and birth.
Go to the emergency room or call 911 (or your local emergency services number) if you experience:
It might be helpful to ask your healthcare provider:
The World Health Organization (WHO) changed the name to mpox in November 2022. This aligns it with the WHO’s current recommendations for naming diseases in a way that avoids stigmas. The virus that causes mpox is still called monkeypox virus.
Although they both cause skin rashes, different viruses cause mpox and chickenpox. Mpox is an orthopoxvirus, while chickenpox is a herpes virus. Both viruses can spread through skin-to-skin or prolonged face-to-face contact, but chickenpox is very contagious and spreads more easily than mpox. People with mpox are more likely to have swollen lymph nodes than people with chickenpox.
The rashes act differently, too. While the chickenpox rash can appear in waves, mpox sores develop at the same time. Chickenpox symptoms — including the rash — tend to get better within two weeks, while it takes two to four weeks for mpox to resolve.
Smallpox and mpox are both part of the Orthopoxvirus genus, so they’re caused by similar but distinct viruses. Thanks to effective vaccines, smallpox was eradicated (is no longer a circulating disease) by 1980. Smallpox was very contagious and spread more easily than mpox. Mpox symptoms are similar to smallpox, but milder.
News of a disease outbreak — and even the word “outbreak” — can cause a lot of anxiety and fear. Especially if, like many of us, you’d never heard of mpox until 2022, it might feel like one more thing to add to your list of concerns.
But research into similar viruses, like smallpox, has been going on for decades. Because of this, healthcare providers have been able to quickly implement vaccines and other measures to reduce the spread of mpox. If you think you’re at a higher risk for exposure to mpox, there are ways to reduce your risk. Talk to a healthcare provider if you have any concerns.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Have a virus, fungus or bacteria? Some of these “bugs” won’t go away on their own. Cleveland Clinic’s infectious disease experts are here to help.
