Your left atrial appendage (LAA) is a small pouch of tissue that extends out from your left atrium (upper heart chamber). It’s in a groove between that chamber and the one below it. The number of lobes in your LAA varies from person to person, and so does the shape. The most common shape looks like a chicken wing.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
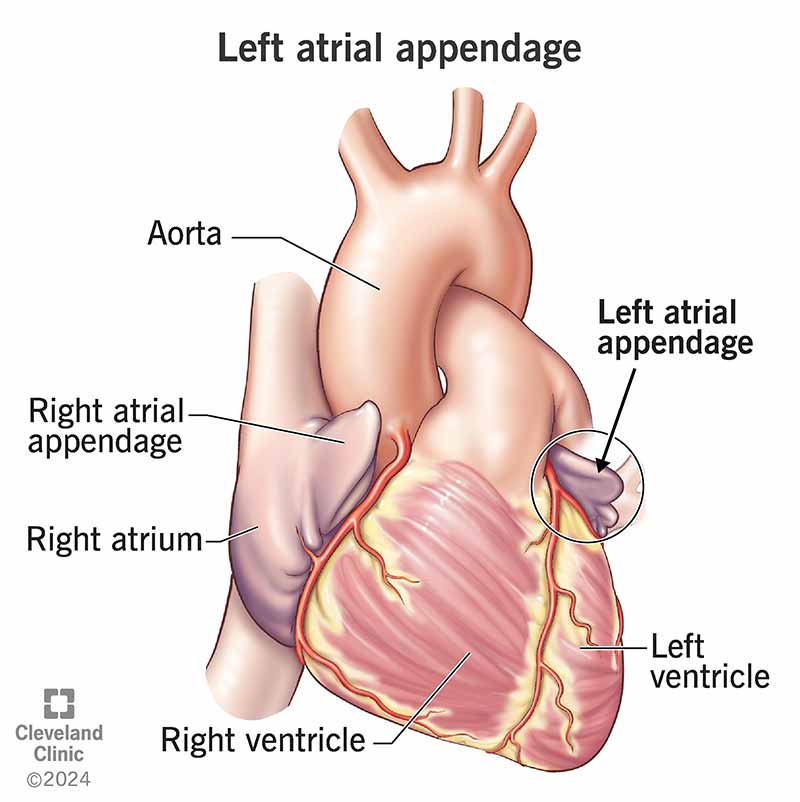
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/left-atrial-appendage)
A left atrial appendage (LAA) is a pouch of muscular tissue that sticks out of your heart. It connects to the wall of your left atrium (upper heart chamber).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
You may only hear about your left atrial appendage if your healthcare provider wants to close it off. Closing, removing or blocking it can reduce stroke risk for people with atrial fibrillation (Afib). This is because most blood clots form in the LAA in people with Afib. But don’t worry; your heart doesn’t need your LAA to do its job.
The function of your left atrial appendage is to manage the amount of blood in your heart. It does this by releasing natriuretic peptides (proteins) when blood volume is high enough to make your LAA walls stretch too much. These peptides go into your bloodstream and encourage your kidneys to get rid of more salt and water (in pee). The peptides also loosen your blood vessels. These actions can lower your blood pressure.
You may wonder what happens to your peptide levels if you have a procedure to remove or block your left atrial appendage. After three months of abnormal levels, peptide amounts tend to go back to normal.
Typically, high levels of these peptides may mean you have heart failure. With this condition, your body is trying to get rid of extra fluid because your heart can’t handle a large volume of blood.
Your left atrial appendage is in a groove between your left atrium and left ventricle. It lies on top of your left ventricle or main pulmonary artery. It runs in the same direction as your left superior pulmonary vein. Along with the rest of your heart, your LAA is inside your heart’s protective sac (pericardium).
Advertisement
Your left atrial appendage anatomy consists of an opening and a pouch of muscular tissue that contracts. Blood goes in and out of the opening and pouch.
Your left atrial appendage is about 46 mm (just under 2 inches) long but can be 27 to 60 mm (millimeters). That’s close to the short edge of a credit card. Your LAA can hold about 9 mL (about 2 teaspoons) of blood. The left atrial appendage’s opening is usually oval but can be round or other shapes in some people.
Most people have two or three lobes in their left atrial appendages. But you can have as few as one or as many as four or more lobes. Left atrial appendages usually fit one of these descriptions:
Here are some conditions that affect your LAA:
Healthcare providers can use imaging to look at your left atrial appendage. They may use:
An operation or minimally invasive procedure can treat various issues that affect your left atrial appendage.
A healthcare provider can:
Your entire heart works at its best when you take care of it. You can do this by:
Although many people have never heard of a left atrial appendage, it does serve a purpose. Still, you can do without it if it’s putting you at a risk of stroke. The thought of having a procedure on your heart may make you uneasy. But blocking your LAA can free you from taking blood thinners to prevent a stroke if you have Afib. Talk with your provider about what’s best for your situation.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When your heart rhythm is out of sync, the experts at Cleveland Clinic can find out why. We offer personalized care for all types of arrhythmias.
