The corpus callosum is a bundle of nerve fibers that allow your brain’s left and right hemispheres to communicate. It plays a role in how you think, remember and coordinate your movements. Conditions present at birth and acquired conditions may affect the development and function of this part of your brain.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
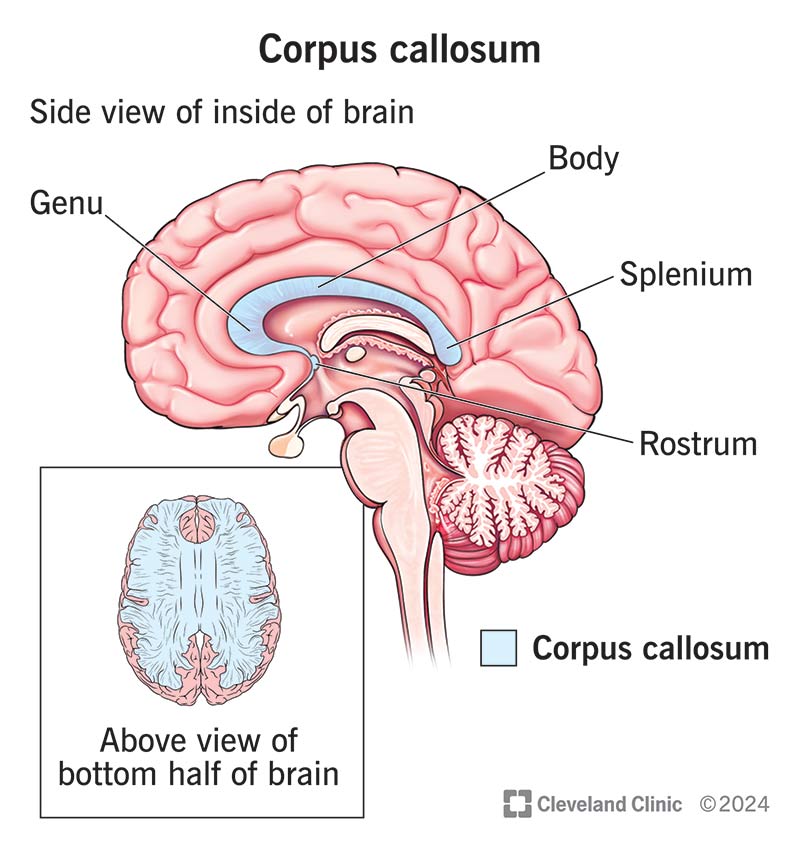
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/corpus-callosum)
The corpus callosum is a structure in the middle of your brain that connects the right and left hemispheres (sides). The structure is made up of nerve fibers. Nerve fibers help the left and right sides of your brain talk to each other by sending signals. This communication pathway allows you to coordinate many essential functions that are part of your daily routine.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The purpose of the corpus callosum is to connect the left and right hemispheres of your brain so they can communicate.
Your corpus callosum functions as a bridge. It allows nerve signals to move between the two sides of your brain. Nerve signals are like people crossing the bridge. Each person carries a message to a different location in your brain. These messages help you coordinate your:
The corpus callosum sits deep within the middle of your brain. It’s between the two hemispheres. This spot is called the longitudinal fissure.
There are four parts of the corpus callosum:
Advertisement
The corpus callosum is made up of nerve fibers — more than 200 million axons (a type of myelinated nerve fiber that sends messages outward). These nerve fibers are known as white matter. The corpus callosum is one of the largest white matter structures in your central nervous system.
The corpus callosum is about 10 centimeters (3.9 inches) long. It makes an arch or a “C” shape that faces downward (toward your torso) between the two sides of your brain with the fibers passing through it.
Corpus callosum dysfunction means that one side of your brain can’t communicate well with the other.
Dysfunction can happen with the following:
Agenesis of the corpus callosum is a congenital (present at birth) condition that happens when the corpus callosum doesn’t develop as expected. A child may have complete agenesis (severed or split hemispheres without a connection) or partial agenesis (some parts of the corpus callosum developed but not all of them). Research suggests a genetic change could cause underdevelopment of this part of your brain.
In addition, as you naturally get older, the speed of messages sent from one side of your brain to the other slows down. Your mind and body may not be able to respond or move as quickly as they used to due to how aging affects your brain.
If the left and right sides of your brain have trouble communicating with each other, you may experience the following symptoms:
Your symptoms can vary based on how much damage is on your corpus callosum. The location matters, too. For example, damage to your corpus callosum may make the following tasks more difficult:
A healthcare provider may order imaging tests to learn more about the health of your corpus callosum, like a computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These tests allow your provider to look at your brain in more detail to see if you have damage or are missing a part of this brain structure.
Treatment can help you manage symptoms related to corpus callosum dysfunction, including:
These treatment options vary based on what symptoms you experience and what causes them. A healthcare provider will give you the most accurate information on what you can expect and what treatment options are available based on your situation.
Advertisement
Your corpus callosum plays an important role in how your brain functions. You can take steps to keep it healthy by taking care of your entire body, like:
Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to keep your mind and body healthy. They may have specific suggestions catered to you and your lifestyle.
It’s hard to imagine or remember what it was like before we had phones. Now, faster than ever, we can communicate with anyone around the world at any given time. Like phones, the corpus callosum allows different parts of your brain to talk to one another. Each side sends signals (messages) to the other without you even thinking about it. This can help you ride a bicycle, remember someone’s name and follow instructions.
While certain conditions can affect how this part of your brain develops or functions, treatment options are available to help you manage symptoms of corpus callosum dysfunction. Talk to your healthcare provider to learn more about your corpus callosum and what you can do to keep it healthy.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Epilepsy and seizures can impact your life in challenging ways. Cleveland Clinic experts can help you manage them and find relief.
