The membranous urethra is the shortest, middle section of the male urethra. Also known as the intermediate urethra, it ends right above your penis. This part of your urethra has muscular tissue around it, so it helps you hold in your pee. Blockages, inflammation, infection and cancer (rarely) can affect your membranous urethra.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
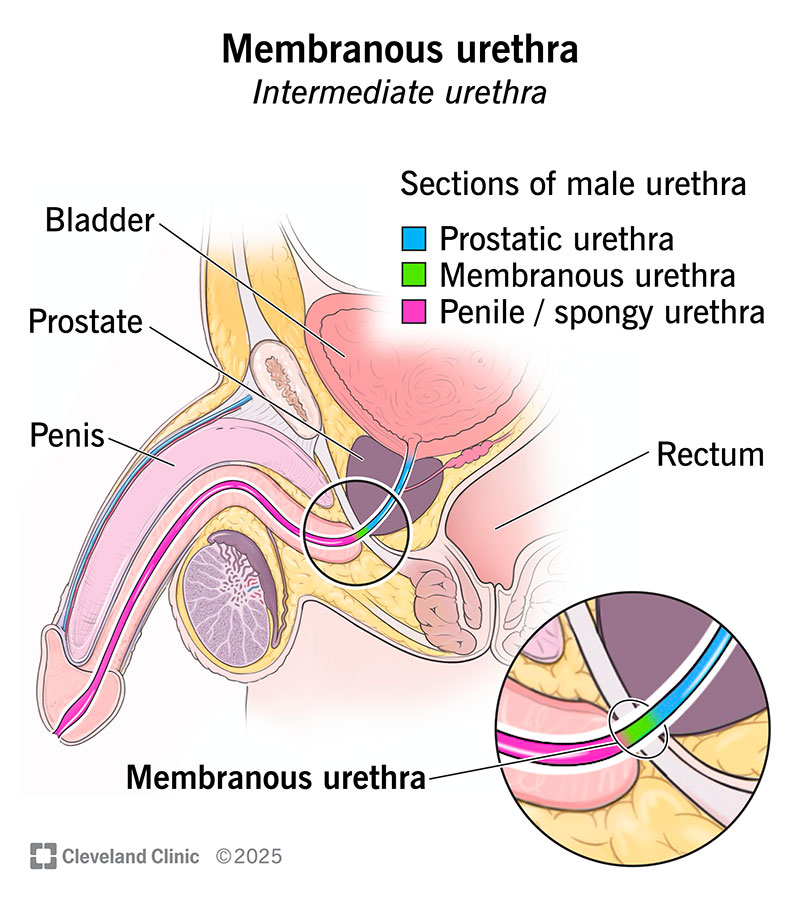
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/membranous-urethra)
The membranous urethra is part of the male urethra. A female urethra doesn’t have one.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The urethra is a tube that empties urine (pee) from your bladder. In men, it also carries semen as part of the male reproductive system.
The urethra starts at the bottom of your bladder. It ends at the tip of your penis. The membranous part is in the middle. Another name for it is the intermediate urethra.
It starts just below your prostate. Your membranous urethra passes through your pelvic floor and ends above the base of your penis at the perineum as it exits the pelvis. There, the membranous part of your urethra becomes your penile, or spongy, urethra. That extends down through the length of your penis.
Your membranous urethra has three layers. They are the:
The whole urethra looks a bit like an “S” turned on its side. The membranous urethra is the first curve of the “S.”
Advertisement
The urethra is about 8 inches long in males. But the membranous part of it is only about half an inch long. It’s the shortest section.
Some of the most common problems that affect your membranous urethra are:
You may not have any signs of a problem. Talk to your healthcare provider if you notice symptoms like:
You can care for your urethra in these ways:
The membranous part of your urethra is short. The spongy urethra is as long as your penis. The spongy urethra has some wide parts. The membranous urethra is narrow.
A fall or a medical procedure can cause a membranous urethral injury. Examples include:
It’s frustrating to make more trips to the bathroom than usual. You rely on your membranous urethra to hold in your pee. But infections, injuries, swelling and other conditions can affect the health of your penis and urethra. Talk to your healthcare provider right away if you have any problems with peeing, like pain or blockages.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
