Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), also known as heart bypass surgery, is a procedure to restore blood flow to areas of your heart. Artery blockages can cut off blood flow, causing heart attacks or heart attack-like symptoms. CABG restores blood flow by using blood vessels from other parts of your body to create a detour around blockages.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
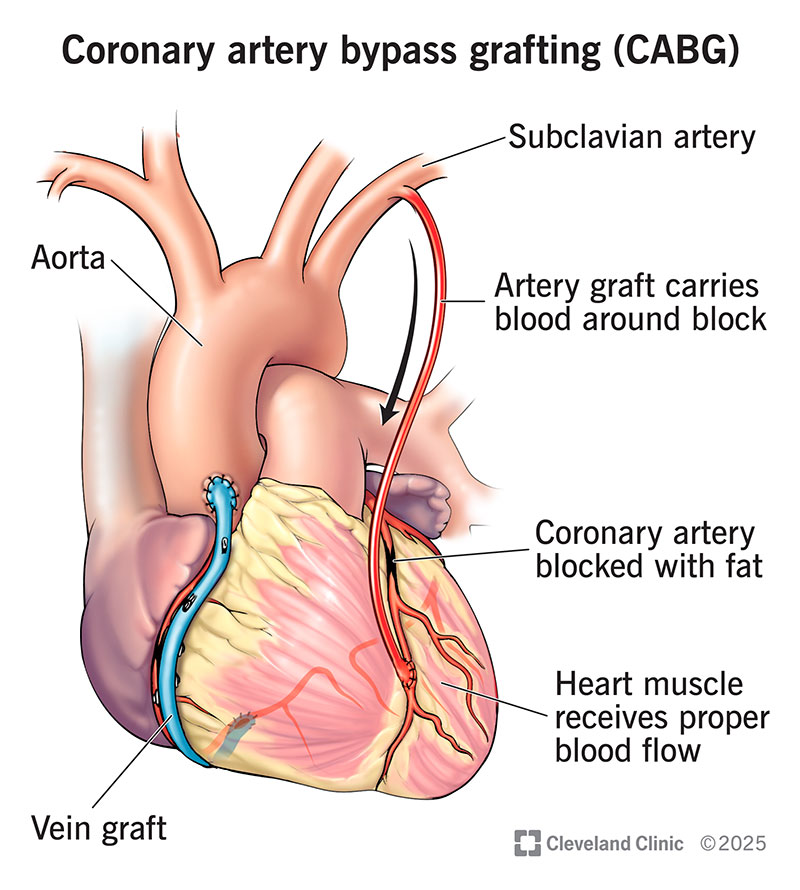
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is an open-heart surgery to restore blood flow to areas of your heart. You need this when your heart can’t get enough blood from arteries that wrap around it. When blood supply is low due to artery blockages, heart muscle cells start to die.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
CABG creates a bypass for blood to reach areas of your heart that need more blood. A bypass is like a detour for your blood to get around an obstacle. Surgeons take a blood vessel from your leg, arm or chest. They use it to make the detour around the blockage.
You may need multiple bypasses if you have more than one blocked artery. These are double (2), triple (3) and quadruple (4) bypasses.
Bypass surgery can improve your heart function and how you feel. It’s for people who have coronary artery disease. This can mean you’ve had a heart attack or you’re at risk for one. CABG also treats chest pain (angina) or silent myocardial ischemia. This is a lack of blood flow to your heart muscle, but with no symptoms.
These problems happen because of a buildup of fatty residue called plaque in arteries. Plaque (atheroma) makes arteries in your heart narrow and stiff. If plaque breaks open, blood clots can form there and make blockages in those arteries. Those blockages cause ischemia in parts of your heart. This can lead to a heart attack.
Coronary artery bypass surgery is the most common heart surgery in the world. The average age for people who have CABG surgery is around 66 years old. Most of the people who undergo it are male.
Advertisement
CABG is major surgery. Before heart bypass surgery, you’ll need to have several tests. These help your healthcare provider see if it’s safe for you to have this surgery and decide whether you need it.
Tests may include, but aren’t limited to, the following:
Your healthcare provider will discuss what medications you’re taking before the surgery. They’ll also tell you which ones to keep taking and which ones you should stop. You’ll need to fast (stop eating and drinking) several hours before surgery.
During coronary artery bypass grafting, a healthcare provider will:
Different ways to do a CABG procedure include:
CABG is a complicated procedure that takes three to six hours to complete. The actual time it takes depends on the specific type of CABG surgery, how many bypasses you need and more.
CABG has several advantages. These include:
Advertisement
Heart bypass surgery is a major surgery, which means it can have risks and complications. Most of these are uncommon and avoidable or treatable. But it’s important to understand them. Possible risks include:
After surgery, you’ll go to the hospital’s intensive care unit. When a provider feels you’re ready, you’ll move to a regular medical-surgical room in the hospital.
The average hospital stay for heart bypass surgery is between five and seven days. The stay is longer for people who had CABG because of a heart attack. It’s shorter for those who didn’t.
Most people who have CABG will need six weeks to recover. During that time, it’s best to avoid anything that might put too much stress on your heart and cuts.
Your healthcare provider is the best person to tell you how long it will take to recover and what you should expect. They’ll also tell you when you can drive, go back to work or be physically active.
CABG surgery can restore blood flow. But the issues that caused you to need CABG can still happen again. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance on improving your lifestyle. This includes what you eat and how much physical activity you get. Improving your habits can help you avoid more issues in the future.
Advertisement
A cardiac rehab program can make a huge difference in your overall recovery and how you feel after bypass surgery. Medical professionals who monitor cardiac rehab can help catch any potential problems or warning signs sooner rather than later.
During your recovery, be sure to take medicines as instructed and speak with a counselor if you feel anxious or depressed.
You should see your provider for follow-up visits to check your heart function, remove stitches or staples, and make sure your wounds are healing well.
You should go to the hospital right away if you have any of the following:
Many studies have linked CABG with improved long-term outcomes, including better survival odds. This advantage often grows when advanced bypass techniques are used, with lasting results. In clinical trials, CABG relieves angina symptoms in 8 out of 10 people.
Some people need another bypass eight to 10 years after bypass surgery because of another blockage. But you may be able to prevent this by reducing your LDL cholesterol, avoiding tobacco products and taking one aspirin a day. Also, the use of more arterial grafts instead of veins may reduce the need for future procedures.
Advertisement
Some people are still doing well for 20 years or more after bypass surgery. The life expectancy after bypass surgery was 18 years in one study.
Coronary artery bypass grafting is a surgery that can make a big difference in how you feel and your overall length and quality of life. It’s also a major procedure, and it’s normal to worry or feel anxious about it. Talking to your healthcare provider is important. They can provide you with information and resources that can help you better understand what’s happening. They can also guide you on what you can do to help yourself have the best possible outcome.
When you need treatment for coronary artery disease, you want expert care. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll create a treatment plan that’s personalized to you.

Last reviewed on 08/22/2025.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.