Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT or biventricular pacing) is a procedure to implant a special type of pacemaker. This helps most people who have this procedure get both of their heart ventricles to contract at the same time. It can help people with heart failure have a better quality of life.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
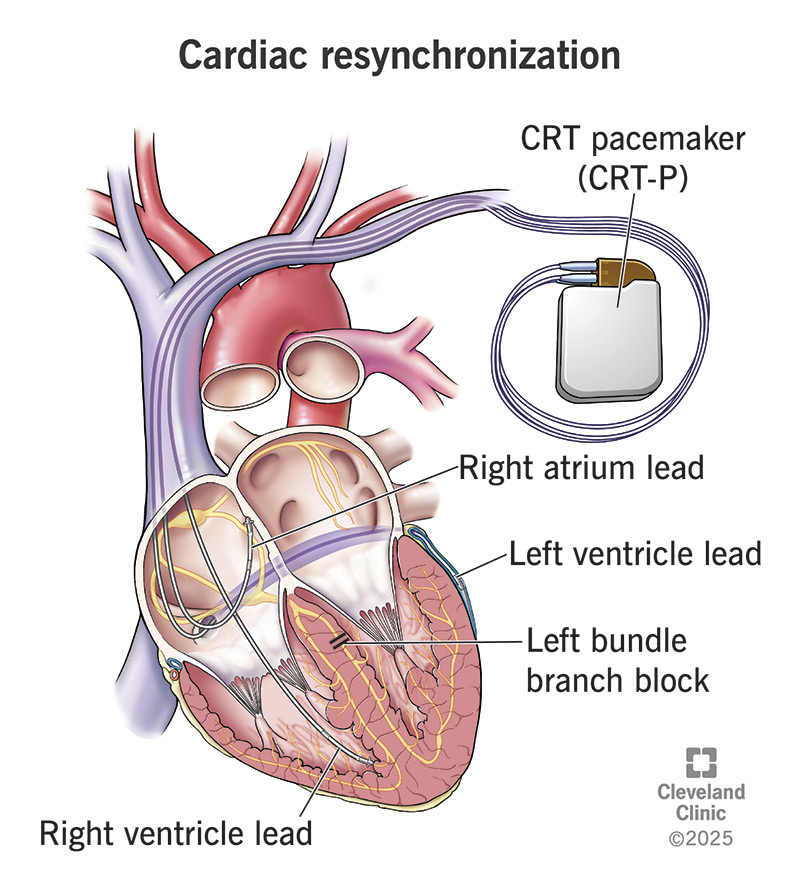
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22936-cardiac-resynchronization-therapy)
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (also called CRT or biventricular pacing) is a procedure that makes your ventricles beat together. You may need this if you have heart failure and your ventricles beat out of sync. When both ventricles (lower heart chambers) beat at the same time, it’s easier for your heart to pump blood.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
In CRT, your healthcare provider puts a biventricular pacemaker in your chest. This is a pacemaker with an extra wire. Your cardiologist may suggest this option after you try medicine and lifestyle changes.
Heart resynchronization therapy is fairly common. People with a heart rhythm problem, like left bundle branch block, may have it. But it still comes with risks.
Unlike other pacemakers that have one or two wires or leads, a CRT pacemaker (CRT-P) has three. One lead goes to each of your ventricles. The third goes to your right atrium, one of your heart’s upper chambers. (Your heart has two ventricles and two atria.)
With a cardiac resynchronization therapy device, three leads can send a signal. This makes your heart chambers work together and corrects your heart rhythm. Signals come from electrodes that a provider places in your heart muscle.
Your healthcare provider will:
During cardiac resynchronization therapy, your healthcare provider will:
Advertisement
This biventricular pacing procedure takes several hours.
CRT treatment may give you these benefits:
Possible complications of cardiac resynchronization therapy include:
After you receive a cardiac resynchronization therapy device:
After heart resynchronization therapy, you can go back to your normal activities in a few days. You shouldn’t drive or lift heavy things for a week or so.
Your CRT pacemaker should last for several years. It should improve your quality of life. Cardiac rehab can help you handle more physical activity after this procedure.
Contact your provider if you get a fever weeks or months after getting a CRT pacemaker. It could mean you have an infection around your device.
You’ll have a follow-up visit a month after you get your CRT pacemaker. Then, you’ll see your provider once or twice a year.
Your provider will check your pacemaker remotely from their office. But they’ll still need to see you at times. They need to be sure your device, battery and wires are in good shape. They can also do testing to see if the device is helping your heart work better.
The success rate for the procedure itself is high. But researchers estimate that CRT doesn’t help 2 to 3 out of 10 people who receive it.
An ICD (defibrillator) gets a fast rhythm back to normal. It helps people who have dangerous heart rhythms in their ventricles.
Cardiac resynchronization therapy uses a biventricular pacemaker (CRT-P) to make your ventricles work together.
Advertisement
Many people may need a biventricular pacemaker with an ICD (CRT-D) to correct all of these issues.
It’s normal to have questions about cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). Talk with your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of this procedure. Be sure to follow all instructions your provider gives you about your device so you can gain the most benefit from it.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic can diagnose and treat heart failure of any kind, at any stage, with advanced therapies and compassionate care.
