You might need ankle surgery if you’ve seriously injured your ankle, or if you have a condition that causes chronic pain, like arthritis. Ankle surgery can fix structural problems and remove and replace damaged tissues to relieve your pain. There are many different types of procedures.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
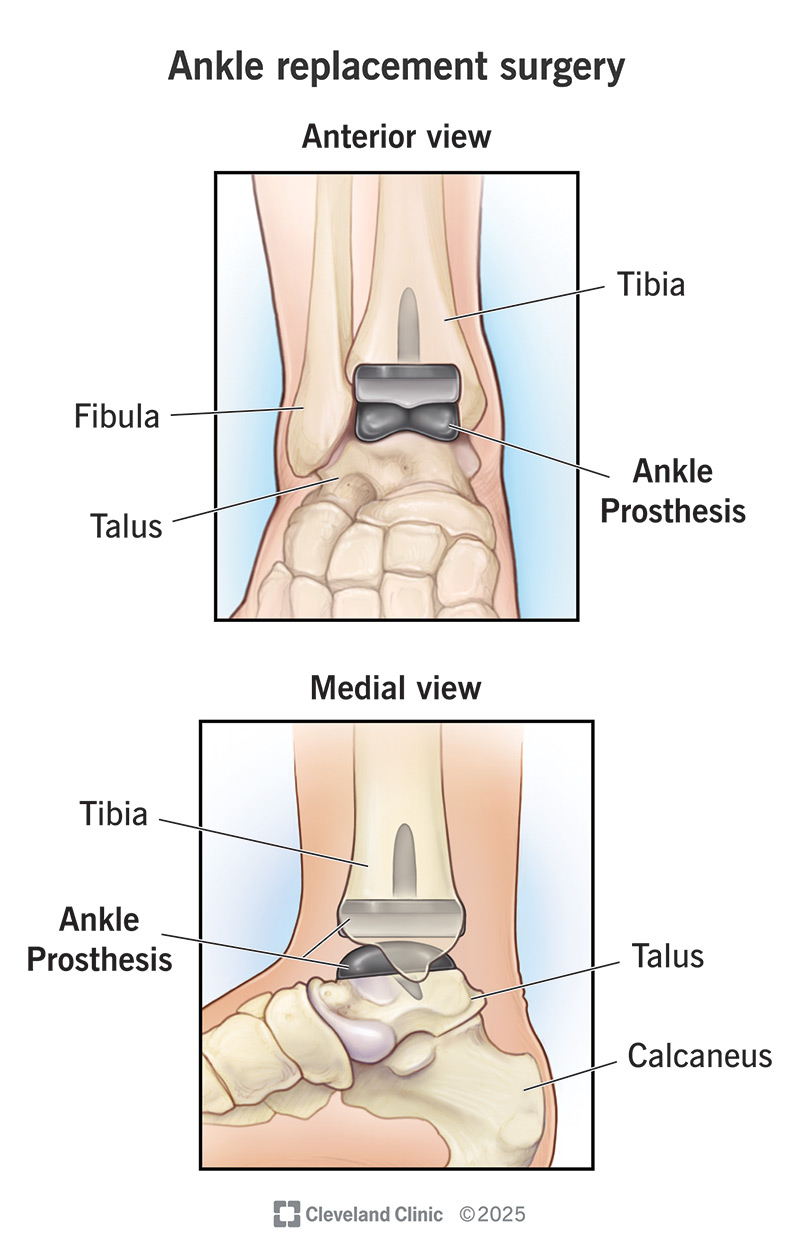
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/ankle-surgery)
Ankle surgery is any surgical procedure that treats an injury or condition in your ankle. Your ankle joint is the connection point between several bones. Cartilage and ligaments hold these bones together, while muscles and tendons help them move. Ankle pain and ankle injuries may affect any of these parts. You might need ankle surgery if other treatments can’t relieve your pain or repair the damage to your ankle.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
You might need ankle surgery to treat:
Many ankle injuries can heal without surgery, and many chronic ankle conditions are manageable with other treatments. But sometimes, they’re not and they don’t. Your provider might recommend surgery if you have ongoing difficulties using your ankle, or if they expect your condition to worsen without it.
Often, surgeons can operate on your ankle using minimally invasive surgery techniques. One type of minimally invasive ankle surgery is called ankle arthroscopy. This means that surgeons make small cuts and operate using an arthroscope, a small tube with a camera at the end that allows them to see inside your joint. Arthroscopy works for many ankle procedures, but for some, open surgery is more practical.
Common ankle surgery procedures include:
If you break a bone in your ankle, you might need surgery to help it heal correctly. Ankle fraction surgery uses metal plates, screws and wires to hold your bones together in the right position for healing. Sometimes, you might also need ligament repair for the same injury, to help stabilize your ankle joint.
Advertisement
You might need surgery to remove bone or tissues that have become trapped in your ankle joint, causing pain and restriction when it moves (impingement). This might be a bone spur, scar tissue, or soft tissues that have become swollen or loosened by injury or disease. Surgery removes these to restore the joint.
Ankle fusion is a procedure to treat advanced ankle arthritis. Your surgeon removes the damaged cartilage and bone tissue from your ankle joint, then brings the ends of the bones together and secures them with plates and screws. This causes the bones to grow together and the joint to fuse in position.
Ankle fusion removes the friction and inflammation that causes pain with advanced arthritis. But it makes your joint stiff. Surgeons fuse the joint at a right angle, as you would need it for standing or walking. Afterward, it can bear your weight without pain, but it won’t be as flexible as it was before.
You might need ankle reconstruction surgery if you have chronic ankle instability. This is usually a result of torn ligaments in your ankle that never fully healed. Weakened ankle ligaments leave you vulnerable to repeated ankle sprains in a vicious cycle that makes your ankle more and more unstable over time.
Lateral ankle ligament reconstruction is a surgical procedure to repair your lateral ankle ligaments — the ligaments that stabilize your ankle from the sides. The most common way is to tighten the ligaments with stitches (Brostrom procedure). In severe cases, they might need to replace one of your ligaments.
You might need ankle tendon repair surgery if you have chronic ankle tendinopathy, peroneal tendon instability or a tendon tear. Acute injuries can cause tendon tears or tendon instability. Repetitive strain injuries can cause chronic tendonitis, leading to chronic tendinosis (tendinopathy).
Tendon repair surgery might mean removing damaged layers of tendon tissue, tightening the tendon and/or repairing a tear with stitches. For severe tears, you might need a tendon transfer. This means replacing a damaged tendon with another one from a donor or from somewhere else in your body.
Total ankle replacement is a type of joint replacement surgery (arthroplasty). It removes damaged parts of your ankle joint and replaces them with prosthetic parts. Total ankle replacement is a procedure to treat ankle deformity or advanced ankle arthritis when more conservative treatments haven’t worked.
Advertisement
Like any type of surgery, ankle surgery comes with a small risk of possible complications, including:
After ankle surgery, you may need to put some time into rehabilitation. Keeping up with your physical therapy is important to restore the full use of your ankle. Otherwise, it may become stiff and weak.
Each individual procedure also comes with its own possible disadvantages and success rate. Your provider will discuss these in detail with you when you’re considering your treatment options.
You’ll have anesthesia for the procedure and pain control after surgery as needed. When you go home, you’ll have prescription or OTC (over-the-counter) pain relievers. How much pain relief you’ll need will depend on the procedure and your own sensitivity. You can discuss your options with your provider in advance.
Healthcare providers recommend ankle surgery when your ankle has become very difficult to use, either because of pain, structural problems or both — and when other treatments aren’t helping enough. In these cases, surgery can make your ankle usable again. Surgery for arthritis can relieve your pain.
Advertisement
Different ankle surgery procedures have different recovery times. But generally, you’ll spend around two to six weeks with your ankle in a cast or medical boot. It’s important to keep your ankle immobilized during this period and avoid putting weight on it. You’ll need a walking aid, like crutches, to get around. After removing the cast, you’ll spend several more weeks in physical therapy to rehabilitate your ankle.
Most people can return to their former activities after eight to 12 weeks. But it may take longer for the ankle to fully heal after surgery. Depending on the procedure, it might take six months to up to a year, in some cases. If you’re an athlete, you might need to modify how you use your ankle during this time. Your provider will tell you more about what to expect and how to take care of your ankle while it heals.
Surgery can be a stressful thing to consider, especially when it’s not an emergency. Most people want to try all the alternatives first. But some ankle conditions can only be fixed manually. Surgeons can remove what’s hurting your ankle and restore the proper form and function of the joint. If you’re willing to put your trust in a surgeon and rally through the recovery period, relief waits for you on the other side.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When you need ankle surgery, you want experts by your side to help you through it. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll be with you from start to finish.
