A kidney biopsy is a procedure in which a healthcare provider removes a small tissue sample from your kidney to check its health and diagnose conditions. They may use a small needle to take the sample or remove it during surgery. Risks are minimal but may include bleeding, pain at the biopsy site and infection. You should get your results within a few days.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
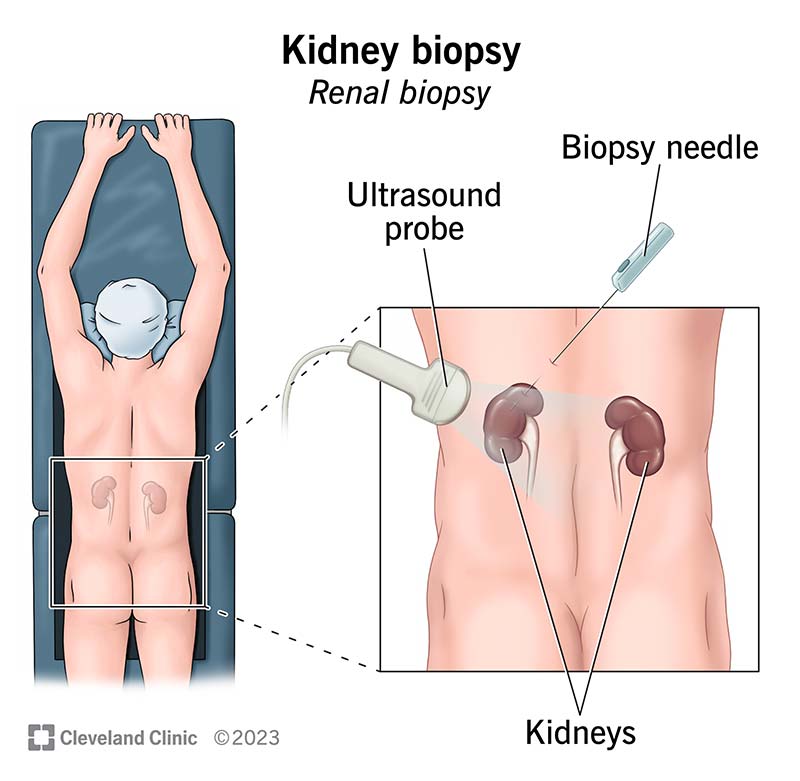
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/kidney-biopsy)
A kidney biopsy is a procedure in which a medical provider removes a small sample of your kidney tissue to examine it for signs of disease. In most cases, they’ll use a biopsy needle to remove the tissue sample. But sometimes, they’ll take the sample during surgery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Another name for a kidney biopsy is a renal biopsy.
A healthcare provider may recommend a kidney biopsy to identify symptoms that may affect your kidneys that imaging, blood or urine (pee) tests can’t reveal, such as:
A kidney biopsy can also help a provider determine how well a transplanted kidney is working and monitor the progression of chronic kidney disease.
A provider may also recommend a kidney biopsy if you have:
A kidney biopsy is a relatively safe procedure. It’s usually minimally invasive, and it shouldn’t take long to recover. A healthcare provider can tell you more about what to expect.
You’ll meet with a healthcare provider before a kidney biopsy. They’ll review your health history and perform a physical examination. They may also order a blood test and pee test. If these tests reveal you have an infection, you may need to treat it before the procedure.
Tell the provider about all prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) medications you’re taking, including herbal supplements. Aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and certain herbal supplements can increase your risk of bleeding. You may need to stop taking certain medications up to one week before a kidney biopsy.
Advertisement
In some cases, you may receive specific directions on when to stop eating and drinking before the procedure. You’ll also receive instructions about which medications to continue and which to stop before the procedure.
Healthcare providers perform most kidney biopsies with sedation. A provider will give you general anesthesia or moderate sedation. With general anesthesia, you’re asleep and won’t feel pain. With moderate sedation, you’re awake but very relaxed and won’t feel pain.
A special team of healthcare providers will perform a kidney biopsy. The team usually includes:
Providers usually perform kidney biopsies in a hospital. In most cases, they’ll instruct you to lie on your stomach on a surgical table so they can perform the procedure through your back. But if you have a transplanted kidney, you’ll lie on your back because they perform the procedure through your belly (lower abdomen). The provider will numb the area and give you moderate sedation or general anesthesia so you won’t feel pain.
The radiologist or nephrologist will take the sample through one of these approaches:
A kidney biopsy usually takes about an hour.
You’ll be numb during a kidney biopsy, so you shouldn’t feel pain or discomfort. After a percutaneous biopsy, you may feel sore for a few days. An open biopsy is usually more painful afterward. Most people start to feel better within a week.
After a kidney biopsy, you’ll move to a recovery room, where healthcare providers will observe you. Observation can last anywhere from a few hours to overnight. They’ll check your vital signs, conduct blood tests and monitor your pee. They’ll also make sure you can drink fluids and pee comfortably. In most cases, you can go home to rest once your providers determine you’re healthy enough and no longer require monitoring or tests.
Advertisement
The providers will then send your sample to a lab for examination and testing. A pathologist will process the sample and observe it under a microscope. They’ll then compile their findings into a report and send it to your provider. You should get the results of your kidney biopsy from your provider within a few days. In urgent cases, you may get the results within a day.
You may need up to a day of bed rest after a kidney biopsy to help reduce your risk of bleeding and promote healing. A healthcare provider will tell you exactly how much bed rest you need.
The medications that healthcare providers use during a kidney biopsy can stay in your body for up to a day and make you feel drowsy. You must have a family member or friend drive you home.
The main benefit of a kidney biopsy is that it can reveal conditions that affect your kidneys. It can also tell healthcare providers how well a donated kidney is working after a kidney transplant.
Kidney biopsy risks are small, but complications can occur. You may experience bleeding after the procedure, including blood in your pee (hematuria). Healthcare providers will monitor you for a few hours to ensure you don’t have severe bleeding, which may require further treatment.
Advertisement
Other kidney biopsy risks may include:
Percutaneous biopsy pain usually starts to go away within a few days, while open biopsy pain may take a week or longer. A healthcare provider may prescribe pain relievers or recommend over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It’s important to remember that your body is unique, and your recovery time may be different than others. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions to encourage healing.
You should avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities (including sports) for one to two weeks. Talk to a healthcare provider before resuming any activity.
You should be able to return to work or school a day or two after a percutaneous kidney biopsy. An open biopsy may require you to stay home for at least a week.
Call a healthcare provider or go to the nearest emergency room if you have:
Advertisement
You may want to ask your provider:
A kidney biopsy is a procedure in which a healthcare provider removes tissue from your kidney to check its health. It can be stressful to hear that you need a kidney biopsy, especially while you wait for results. Talk to a healthcare provider. They understand your feelings and are available to answer any questions you may have.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have a condition that’s affecting your kidneys, you want experts by your side. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll work with you to craft a personalized treatment plan.
