Commonly referred to as the “birth control shot,” Depo-Provera® is an injectable form of birth control. It’s a shot of progestin that you get every three months, most commonly in your arm or butt. You don’t have to take a daily pill, and it’s very effective when you take it as scheduled.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
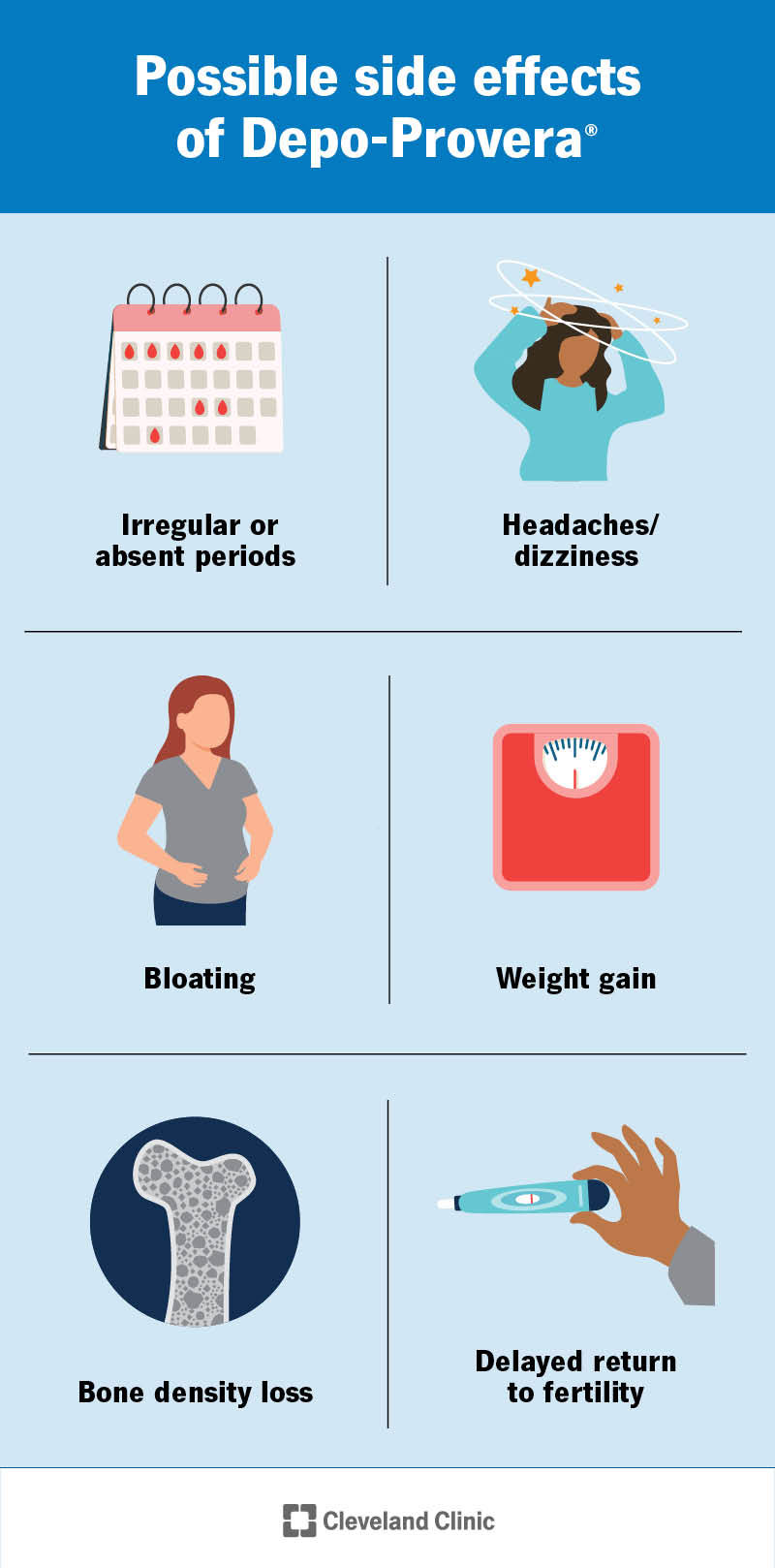
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/4086-depo-provera-birth-control-shot)
Depo-Provera® (medroxyprogesterone acetate) is a type of birth control that comes as an injectable shot. It’s sometimes called the “Depo shot” or “birth control shot.” Your healthcare provider injects it into your arm or buttocks. There is also a version of Depo that you can inject at home on your own. Depo-Provera protects against pregnancy for up to 14 weeks — though you typically need to receive one shot every 12 weeks.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
With perfect use, it can be 99% effective at preventing pregnancy. But we’re all human, and sometimes, people forget or miss their shot. So, its average effectiveness is about 96%. That means 4 in 100 users will get pregnant each year.
The Depo-Provera shot contains progestin. Progestin prevents you from ovulating (releasing an egg). Without an egg, pregnancy can’t happen. It also thickens your cervical mucus, which makes it hard for sperm to swim through your cervix.
You receive the shot every three months. Other than making sure you stick to the shot schedule, you don’t need to do anything else to prevent pregnancy.
This type of birth control is prescription only. In most cases, you get the injection at your healthcare provider’s office.
There is another brand of the birth control shot that you can do at home. This shot is called Depo-subQ Provera 104. This version goes into your skin, not into your muscle. The shot comes in a ready-to-use syringe. Your provider can teach you how to give yourself this shot before you start doing it on your own.
You can start Depo-Provera on any day of your menstrual cycle, as long as you aren’t pregnant. Your provider may have you take a pregnancy test before getting the shot.
Advertisement
You must receive another shot once every three months (12 weeks). It’s important to stick with the schedule for your shot. If you’re late or miss a shot, you can get pregnant. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best timing for your shots and the risks of missing one.
You’re immediately protected after receiving the first Depo shot if you get it during your menstrual period. If you get the shot at another time during your cycle, you may need to wait a week to 10 days before having intercourse without a condom to prevent pregnancy.
The birth control shot may not be safe if you have:
Talk to your healthcare provider about your complete medical history when considering this type of birth control.
If you’re considering Depo-Provera while breastfeeding, talk to your healthcare provider about the risks. As a little bit of the medicine gets into your breast milk, it’s generally recommended to wait until your baby is at least 6 weeks old before starting the shots.
Depo-Provera can cause side effects like:
Changes in your menstrual cycle are the most common side effect. After a year of use, about 55% of users will stop getting their periods. It’s not medically necessary to have a period every month to be healthy.
Talk to your healthcare provider about the risks of Depo based on your health history.
Weight gain is one of the side effects of Depo-Provera. In one study, users gained about 5 pounds after one year of use. But not everyone will gain weight.
If you have concerns about gaining weight while taking birth control, talk to your healthcare provider about your options.
Yes, but it takes about 10 months on average to conceive after your last injection.
(Remember, you can also become pregnant if you miss a dose of the birth control shot or if you get it late.)
Some of the advantages of the birth control shot are:
Disadvantages of the shot can include:
Advertisement
You can stay on Depo-Provera for about two years. It can weaken your bones, which increases your risk of osteoporosis. Your healthcare provider may recommend switching to a different type of birth control or having a bone density test if you wish to keep using it after two years.
It’s important to find the right birth control that fits your lifestyle and goals. Talk to your healthcare provider about factors like how often you want to take birth control and your plans for any future pregnancies. Certain options, like the birth control shot (Depo-Provera), are good for people who don’t want to take a daily contraceptive. But you do have to stick to a schedule for your shots when you take Depo-Provera. Talk to your provider about the pros and cons of the birth control shot to decide if it’s the right option for you.
Advertisement
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Your birth control needs to work for you. At Cleveland Clinic, we help you find the right birth control option to fit your goals and lifestyle.
