Wound dehiscence is a complication of surgery. In wound dehiscence, your closed surgical incision (cut) opens after surgery, exposing internal tissues and possibly exposing organs. Wound dehiscence symptoms include bleeding, pain and broken sutures or stitches.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
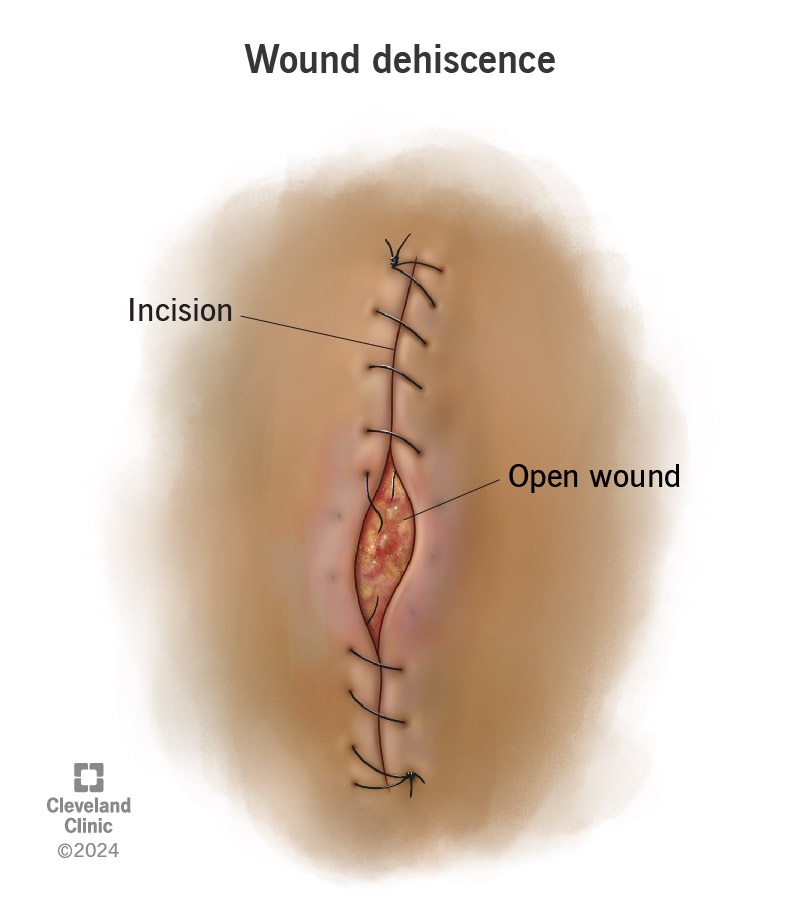
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/wound-dehiscence.jpg)
Wound dehiscence (pronounced “duh-hi-since”) is when the incision (cut) a surgeon makes opens or pulls apart after surgery. (Think of a closed zipper that separates in the middle.) The condition happens when an incision doesn’t heal as it should. Healthcare providers may also call this condition wound disruption or wound separation.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A wound dehiscence can be partial or complete:
It can be scary when an incision opens. You may wonder why it happened and what it means for your recovery. Wound dehiscence can occur for several reasons. For example, stress on the incision can affect healing. So can infection or having certain medical conditions. But healthcare providers have ways to manage wound dehiscence and get you back on the road to recovery.
The most significant symptoms are:
Wound dehiscence symptoms can develop at any time during the healing process. The healing process is complex and takes time. You probably won’t notice the initial steps in the process. Healthcare providers may call these wound healing phases. They include:
Advertisement
A surgical wound infection is the most common cause of wound dehiscence. This happens when you have incisions (cuts) in your skin. Surgical wound infections happen when bacteria get into your body through the incisions that your surgeons make. This can happen during surgery, during recovery in the hospital or while you’re recovering from surgery at home.
Sometimes, post-surgery complications like severe vomiting or coughing can also make an incision open.
Certain medical conditions or medical treatments may increase your risk for wound dehiscence. For example, anything that affects your blood or blocks its flow can slow down healing.
Medical conditions that increase wound dehiscence include:
Your healthcare team will treat underlying conditions that increase your wound dehiscence risk. They’ll do that before your surgery. But there may be times when pre-surgery treatment isn’t possible. That can be the case if you need emergency surgery for a traumatic injury or a sudden serious medical issue.
Advertisement
Medical treatments that can increase wound dehiscence risk include:
The most serious complication is evisceration. This is the medical term for when internal organs poke through an incision.
This is a rare complication that may happen if you have surgery on your abdomen. Evisceration is a medical emergency. If this happens to you, you’ll have surgery right away.
A healthcare provider will look at the incision. They may take a fluid sample from your incision. If they do, a medical pathologist will test the sample to find out what bacteria may be responsible. In some cases, they may do a computed tomography (CT) scan.
Treatment for wound dehiscence may include:
Advertisement
It can, but that depends on your specific situation. For example, your healthcare provider may not do surgery to replace broken sutures. They may instead recommend that you cover the incision to protect it from infection as the wound heals.
Healing takes time. How much time depends on your situation. In general, it may take several weeks for smaller dehiscence wounds to heal. But healing may take several months. That can happen if you need follow-up surgery for a larger incision that reopens.
You may not be able to prevent all things that can cause an incision to open. But there are some steps you can take to reduce your risk:
Advertisement
Contact your surgeon right away if the incision from your surgery opens. Even a small opening, like a single broken suture, is information your surgeon should have.
Wound dehiscence can happen anytime you have an incision (cut) in your skin from surgery, but it most often happens after abdominal or heart surgery.
After surgery, you’re probably ready to get on the road to recovery. Wound dehiscence — when an incision from surgery reopens — may feel like an unexpected and unwelcome detour. And you may wonder why you have wound dehiscence and how it will affect your recovery. Your healthcare team will be glad to explain why your incision opened. They’ll also explain treatments to get you right back on the road to getting well.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Sometimes you have surgery planned. Other times, it’s an emergency. No matter how you end up in the OR, Cleveland Clinic’s general surgery team is here for you.
