Urosepsis is a type of sepsis that begins in your urinary tract. It happens when a urinary tract infection (UTI) goes untreated and spreads to your kidneys. Urosepsis can be a medical emergency. Antibiotics, IV fluid and other medications can treat it before it progresses.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Urosepsis is when a urinary tract infection (UTI) leads to sepsis. Sepsis occurs when your body has a life-threatening response to an infection. It’s a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment because it can lead to tissue damage, organ failure or death. Many different conditions can cause sepsis.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The urinary tract consists of your:
Urosepsis typically happens because a bacterial infection from your lower urinary tract (bladder and urethra) spreads to your kidneys (pyelonephritis). You can also get a UTI from a fungal infection or without ever having symptoms of a UTI, but this is rare.
A UTI is an infection in your urinary tract. It most often happens when bacteria from your genital area enter your urethra. This can happen in a number of ways, like wiping yourself from back to front or from sexual activity. You can also get a UTI when bacteria normally found in your urinary tract multiply to an unhealthy level.
A healthcare provider treats UTIs with antibiotics. UTIs that go untreated or don’t fully resolve can spread to your kidneys and cause urosepsis.
UTIs are common and affect about 20% of women at least once in their lives. Men and children can also get UTIs, but they’re less common. Healthcare providers treat up to 10 million people for UTIs each year in the United States.
Advertisement
Urosepsis is one of the most common causes of sepsis. Up to 30% of all sepsis cases begin in the urinary tract.
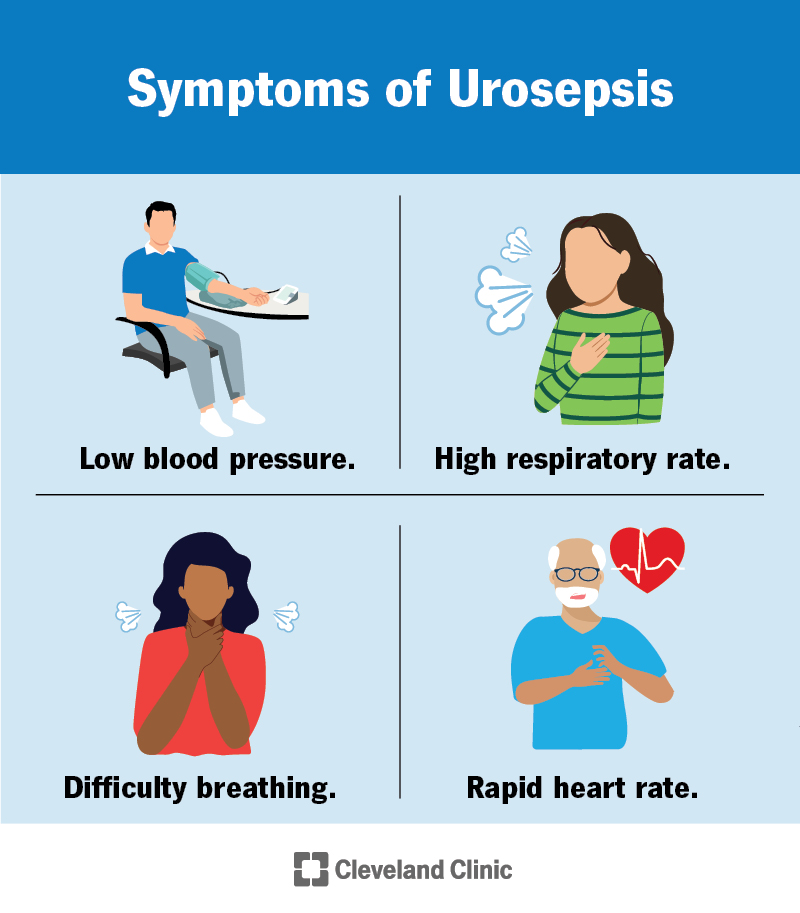
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/25008-urosepsis)
Symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the infection. Once an infection progresses to sepsis, you may have the following symptoms:
It’s important not to let infections go untreated. If you have symptoms of a UTI, get help from a healthcare provider.
Some signs of infection in your urinary tract include:
The most common cause of urosepsis is an untreated or undertreated UTI. This happens when bacteria enter your lower urinary tract and spread through the rest of your urinary system. The bacteria multiply, and your immune system doesn’t fight it off.
A UTI can also develop when bacteria normally found in your urinary tract multiply to an unhealthy level.
Left untreated, the infection continues to spread through your urethra, bladder and, ultimately, your kidneys. This can lead to sepsis.
Sepsis is your body’s dangerous reaction to an infection. When you have an infection, your immune system works to try to fight it. But sometimes, your immune system stops fighting the infection and starts damaging your normal tissues and organs, leading to widespread inflammation throughout your body.
Urosepsis, and all forms of sepsis, can be divided into three stages: sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock. Septic shock is the last and most dangerous stage of sepsis.
Women and older adults are more at risk for developing urosepsis. Having a urinary catheter can also increase your risk for urosepsis because it can carry bacteria.
The main risk factor for urosepsis is having a UTI. Other risk factors for urosepsis include:
Advertisement
Urosepsis is serious. It’s important to get prompt treatment to avoid complications. These complications include:
A healthcare provider diagnoses urosepsis after reviewing your health history, evaluating your symptoms and ordering blood tests. Some blood tests could include:
Providers will request several additional tests to identify your infection and any organ damage. These tests may include:
Antibiotics are the first line of defense for urosepsis and must be given quickly and promptly to get rid of the bacteria causing the infection. Healthcare providers use broad-spectrum antibiotics, which can treat several common bacteria. These are given through an IV (intravenous or in a vein) because they can get into your bloodstream faster. Getting antibiotics as soon as you get a diagnosis can improve your outcome.
Advertisement
IV fluids are a second treatment for sepsis. Your provider also gives fluids through a vein in your hand or arm. Typically, these fluids contain minerals like sodium. IV fluids keep your blood pressure from dropping too low and can help treat organ damage from urosepsis.
If fluids don’t increase your blood pressure, you may receive medication like vasopressin (Pitressin®) to raise it. You may receive corticosteroids if fluids and medication haven’t increased your blood pressure to a stable level.
Some people need supplemental oxygen through a face mask or nasal cannula. A breathing tube may be placed in your windpipe (trachea) to connect you to a breathing machine (ventilator) if you can’t breathe well on your own.
When caught early, most people with mild urosepsis have a good chance of survival. Studies vary, but on average, approximately 70% of people who have sepsis survive if they receive treatment.
Talk to a healthcare provider if you have any symptoms of a UTI. This is the best way to prevent urosepsis. Trying to prevent a UTI can also help. Some tips for preventing a UTI include:
Advertisement
Don’t use products such as spermicides, douches, deodorant sprays or scented soaps.
Contact a healthcare provider if you have symptoms of a UTI or continue to have symptoms of a UTI after treatment. This is the most common cause of urosepsis. Symptoms of a UTI include:
Go to your nearest emergency room if you experience symptoms like:
Urosepsis is a type of sepsis. It just means that the sepsis began in your urinary system.
Urosepsis is a type of sepsis that begins in your urinary tract. A UTI is an infection of your urinary tract that can lead to urosepsis if left untreated.
Urosepsis is a serious complication of a UTI. A UTI is a very common infection that mainly affects your urethra and bladder. Knowing the signs of a UTI and getting prompt treatment for a UTI are the best ways to prevent urosepsis. Changes in your pee are often the first symptom of a UTI. Good bathroom hygiene, such as wiping from front to back, and peeing after sex, are two ways to lower your UTI risk.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have a condition that’s affecting your urinary system, you want expert advice. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll work to create a treatment plan that’s right for you.
