Hyperandrogenism happens when you have high amounts of androgens (a group of sex hormones) in your body. It most commonly affects females and can cause excessive hair growth, acne and irregular periods.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Hyperandrogenism happens when you have an excess amount of androgens in your body. These hormones help start puberty and play a role in reproductive health and body development.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Everyone produces androgens, but males naturally make much more than females. The most well-known androgen is testosterone. Androgens are mostly made in the testicles or the ovaries. Both sexes also make androgens in their adrenal glands. Hyperandrogenism affects about 5% to 10% of females of reproductive age. It’s less common in males.
The condition causes different symptoms based on your age and sex. It has several possible causes. There are several ways healthcare providers treat the condition.
No, but they’re related. PCOS is a common cause of hyperandrogenism in females. But it’s just one possible cause out of many. Hyperandrogenism can affect anyone, no matter their sex. PCOS only affects females.
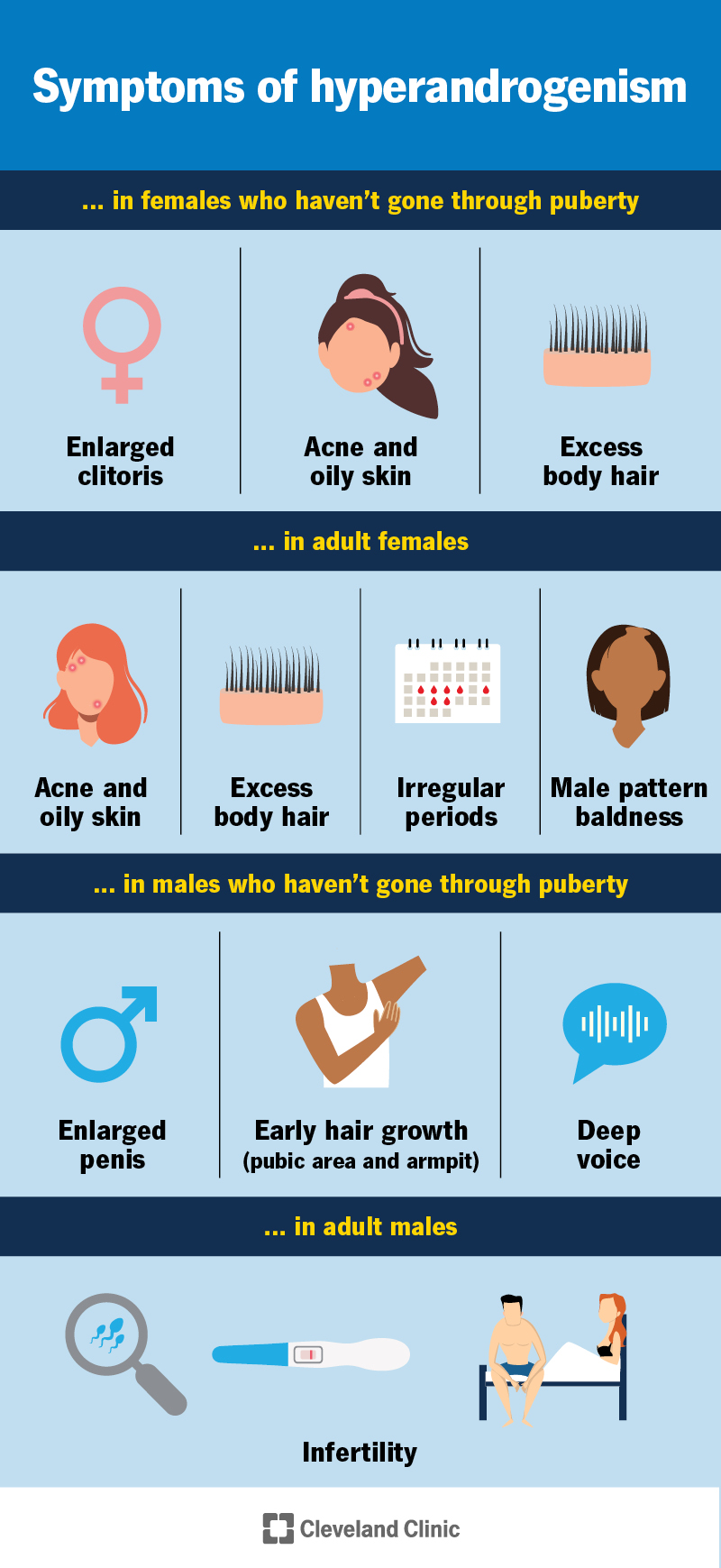
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/24639-hyperandrogenism)
Hyperandrogenism has various symptoms depending on your sex and whether or not you’ve been through puberty.
You can have symptoms of hyperandrogenism even if your androgen levels look normal in a blood test. It’s also possible to have high androgen levels in your blood but not notice symptoms.
If these symptoms develop rapidly and suddenly, it’s important to see your healthcare provider as soon as possible. In this case, the cause is often an androgen-secreting tumor.
Symptoms of hyperandrogenism in females who haven’t gone through puberty include:
Advertisement
Symptoms of hyperandrogenism in males who haven’t gone through puberty include:
Symptoms of hyperandrogenism in adult females include:
In adult males, the effects of hyperandrogenism depend on where the hormones come from — your adrenal glands or an outside source like anabolic steroid injections. High levels of adrenal androgens usually don’t cause obvious symptoms. But they can affect how the testicles work and may lead to infertility.
Hyperandrogenism happens when any of the organs or hormones that produce or release androgens aren’t working right. Possible causes include:
With PCOS, high levels of luteinizing hormone and insulin cause your ovaries to make more androgens. High insulin levels (hyperinsulinemia) prevent your liver from making a protein called SHBG. Without SHBG, you have more testosterone in your blood. This results in increased levels of free testosterone in your blood.
Approximately 80% to 90% of females with hyperandrogenism have PCOS.
CAH is a group of genetic conditions affecting your adrenal glands.
A genetic change causes the body to have low levels of certain enzymes needed to make important hormones. When these enzymes are low, the adrenal glands can make too much testosterone.
Some people have a milder form of this condition with just a partial enzyme shortage.
Cushing disease is a type of Cushing syndrome. It happens when your body has too much cortisol.
Cushing disease happens when a noncancerous tumor in your pituitary gland makes too much ACTH, a hormone that tells your body to produce cortisol. This extra ACTH also makes your adrenal glands release more androgens.
Certain adrenal tumors and tumors in your ovaries or testicles can produce and release androgens. Hyperandrogenism from these kinds of tumors is rare, but is often very severe and sudden. This causes higher-than-normal androgen levels in your body.
Hyperandrogenism due to ovarian or adrenal tumors is rare. See your provider right away if you have sudden symptoms of hyperandrogenism.
Certain medications can cause hyperandrogenism:
Advertisement
Hyperandrogenism can affect both children and adults. But it more commonly affects females of reproductive age.
Since PCOS is one of the most common causes in females, reducing your risk of PCOS can help. There isn’t one proven way to do this, but maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly can help.
Another risk factor for hyperandrogenism is obesity, which can increase insulin resistance.
Left untreated, hyperandrogenism can lead to complications like:
Your healthcare provider will perform a physical exam to check for signs of the condition, like excessive body hair growth.
They’ll also ask you several questions about your medical history, including:
If your provider suspects hyperandrogenism, they’ll order blood tests to measure certain hormone levels:
Advertisement
Your provider may order additional blood tests to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms. They may also order the following imaging tests:
Providers treat hyperandrogenism by lowering the amount of androgens in the body. This can usually be accomplished by blocking the effects of androgens or by preventing your ovaries or adrenals from producing them.
Many people see their provider to help with symptoms like excess hair growth, acne or irregular periods.
The medical treatment depends on its cause. For example:
Surgery can be a treatment for ovarian, testicular or adrenal tumors. Sometimes, stopping a medication or switching to a different medication can help (if medication is the cause).
Advertisement
You can also seek treatment that improves your symptoms:
It’s not completely reversible, but you can manage the symptoms it causes.
If you’re taking medication, you’ll likely need to see your healthcare provider regularly to make sure your treatment is working.
The outlook for hyperandrogenism is good. Treatment is usually lifelong. But with the right care and treatment, you can manage its effects. Work closely with your healthcare provider. It may take several tries to find the right combination of treatments that work for you.
The signs and symptoms of hyperandrogenism can affect your self-esteem and mental health. It’s important to see a psychologist if you’re experiencing stress and/or depression due to these symptoms.
Hyperandrogenism can be tough to deal with, especially when it affects things like your skin, hair or how you feel about your body. It’s okay to feel frustrated. Talk to your provider about your symptoms and don’t be afraid to ask questions. Treatment is available to help you. With your provider’s help, you can find ways to manage the condition.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Hormonal conditions can be tricky to find and complicated to treat. The experts in endocrinology at Cleveland Clinic are here to provide the best care.
