Scurvy is a disease caused by a serious vitamin C deficiency. Not eating enough fruits and vegetables is the main cause of the disease. Left untreated, scurvy can lead to bleeding gums, loosened teeth and bleeding under your skin. Treatment for the condition includes getting plenty of vitamin C in your diet. Dietary supplements are also available.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Scurvy is a disease caused by a significant lack of vitamin C in your diet. The medical definition of scurvy is severe vitamin C (ascorbic acid) deficiency.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Vitamin C deficiency can occur due to a diet low in vitamin C. But a deficiency severe enough to cause scurvy is rare in the U.S. because most people get enough of the nutrient in their diet. The condition is a problem in countries around the world where people are malnourished.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is a very important nutrient for your body. It’s responsible for the development, growth and healing of your skin, bones and connective tissue. In addition, you need vitamin C for your blood vessels to function properly. Vitamin C helps maintain your teeth and gums. It helps your body absorb iron, which it needs to make red blood cells. Vitamin C also helps heal burns and other wounds.
Vitamin C is an antioxidant, meaning it protects your cells against damage from free radicals. Free radicals are byproducts of normal cell activity which participate in chemical reactions within cells. Some of these reactions can cause damage over your lifetime.
In the U.S., scurvy most commonly affects babies, children and older adults who don’t get enough vitamin C in their diet. Risk factors for developing the condition include:
Advertisement
The rates of vitamin C deficiency around the world vary. In the U.S., 7.1% of people may develop a deficiency. In north India, the rate is 73.9%. However, severe deficiency (scurvy) is rare.
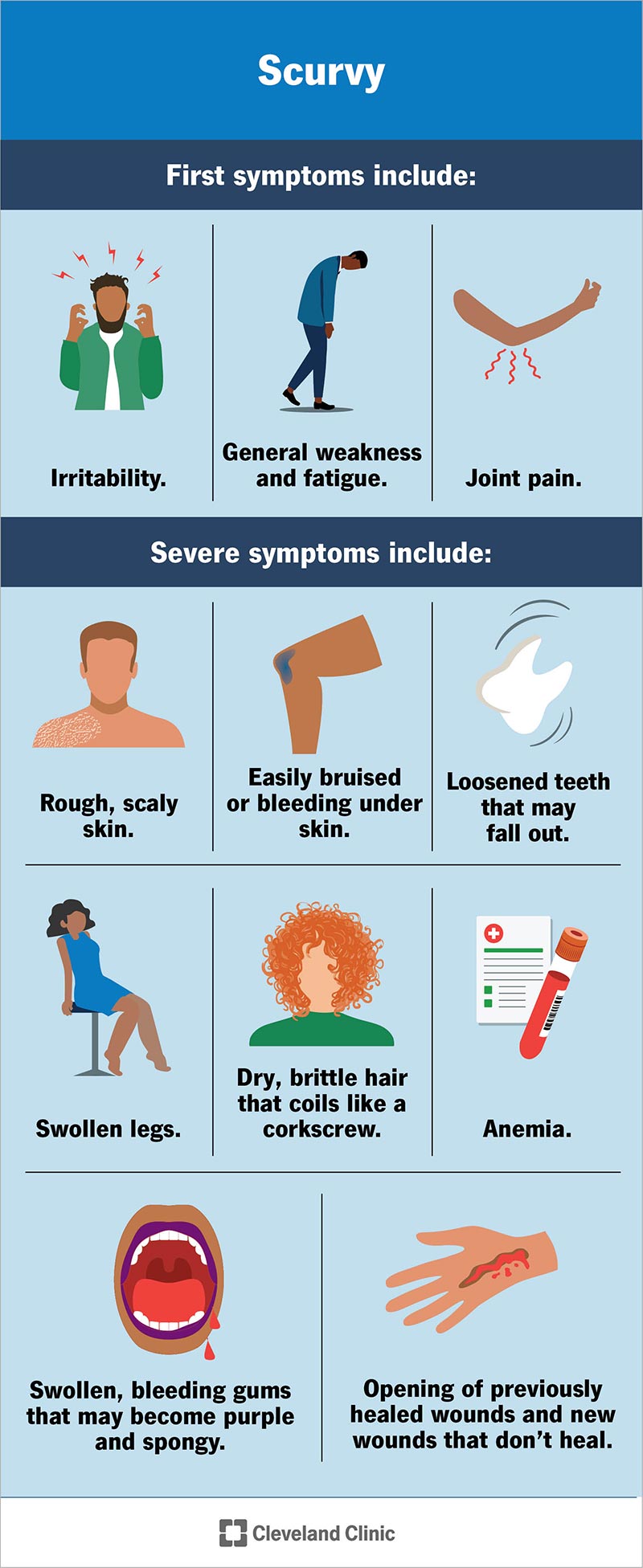
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/24318-scurvy)
Scurvy symptoms may start to develop after a few months of not getting enough vitamin C in your diet. The first symptoms may include general weakness, fatigue, irritability and joint pain.
If left untreated, more severe symptoms may start to develop. These may include:
In babies and children, symptoms of scurvy may include:
A severe lack of vitamin C in your diet for at least three months can cause scurvy. Reasons for this deficiency include not eating enough fresh fruits and vegetables. Also, cooking destroys some of the vitamin C found in food.
Certain conditions increase your body’s vitamin C requirement. You need more vitamin C and risk deficiency if you don’t get enough while experiencing the following conditions:
No, scurvy isn’t contagious. You can only get scurvy by having a severe vitamin C deficiency.
Your healthcare provider can diagnose scurvy based on your symptoms. They’ll perform a physical examination and evaluate you based on certain risk factors for the condition.
Your healthcare provider may request a blood test to measure the amount of vitamin C in your blood. In addition, they may perform a test called a dermoscopy. With this procedure, they’ll take a sample of your affected skin or hair (biopsy) and examine it under a microscope.
Scurvy treatment is essential to avoid further complications. The condition is easily treatable by consuming more vitamin C. You should try to maintain a nutritious diet that includes one to two times your daily recommended amount of vitamin C. You can do so by adding fresh fruits and vegetables to every meal.
Your healthcare provider may also recommend taking a vitamin C supplement until you feel better. Children with scurvy can take a supplement of up to 300 milligrams (mg) daily. Adults can take between 500 mg and 1000 mg.
Advertisement
Most people feel better within 48 hours of treatment. You should be able to make a full recovery within two weeks. Some symptoms may take longer to fully clear up. Depending on the cause of your condition, your provider may refer you to a specialist for further treatment.
With immediate treatment, the symptoms of scurvy should start to pass within 24 to 48 hours. Some symptoms may take longer to go away. Dental and gum issues as well as corkscrew hairs may take weeks to months to disappear. Severe gum disease may cause permanent damage.
You can prevent scurvy by getting the recommended daily allowance of vitamin C in your diet. The best sources of the nutrient are fresh fruits and vegetables. Good sources of vitamin C include:
Speak to your healthcare provider before taking a vitamin C dietary supplement.
The amount of vitamin C you need every day depends on your age and other factors. The average daily recommended amounts of vitamin C are:
| Age/Life Stage | Recommended Daily Amount |
|---|---|
| Birth to age 6 months | 40 mg |
| Infants ages 7 to 12 months | 50 mg |
| Children ages 1 to 3 years | 15 mg |
| Children ages 4 to 8 years | 25 mg |
| Children ages 9 to 13 years | 45 mg |
| Teenage boys (14 to 18 years old) | 75 mg |
| Teenage girls (14 to 18 years old) | 65 mg |
| Men (ages 19 years and up) | 90 mg |
| Women (ages 19 years and up) | 75 mg |
| Pregnant teenagers | 80 mg |
| Pregnant adults | 85 mg |
| Breastfeeding teenagers | 115 mg |
| Breastfeeding adults | 120 mg |
| Age/Life Stage | |
| Birth to age 6 months | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 40 mg | |
| Infants ages 7 to 12 months | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 50 mg | |
| Children ages 1 to 3 years | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 15 mg | |
| Children ages 4 to 8 years | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 25 mg | |
| Children ages 9 to 13 years | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 45 mg | |
| Teenage boys (14 to 18 years old) | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 75 mg | |
| Teenage girls (14 to 18 years old) | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 65 mg | |
| Men (ages 19 years and up) | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 90 mg | |
| Women (ages 19 years and up) | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 75 mg | |
| Pregnant teenagers | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 80 mg | |
| Pregnant adults | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 85 mg | |
| Breastfeeding teenagers | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 115 mg | |
| Breastfeeding adults | |
| Recommended Daily Amount | |
| 120 mg |
If you smoke, you should add 35 milligrams to the above values to get your total daily recommended amount.
Scurvy is a disease caused by an extreme vitamin C deficiency. While a diet low in vitamin C can cause a deficiency, the condition usually doesn’t reach the level of scurvy. To avoid any risk, make sure to eat plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables with your diet. Citrus fruits such as oranges and grapefruits are great choices, but you can also get plenty of this nutrient through potatoes, tomatoes and even strawberries. If you’re experiencing any symptoms of scurvy, see your healthcare provider right away.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
