Subcutaneous fat is fat that you can pinch. It’s found just under your skin. Some subcutaneous fat is good for your body and helps protect it. But too much body fat overall can lead to serious health issues including heart disease, diabetes, stroke and more. The best way to lose excess subcutaneous fat is with a healthy diet and regular exercise.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
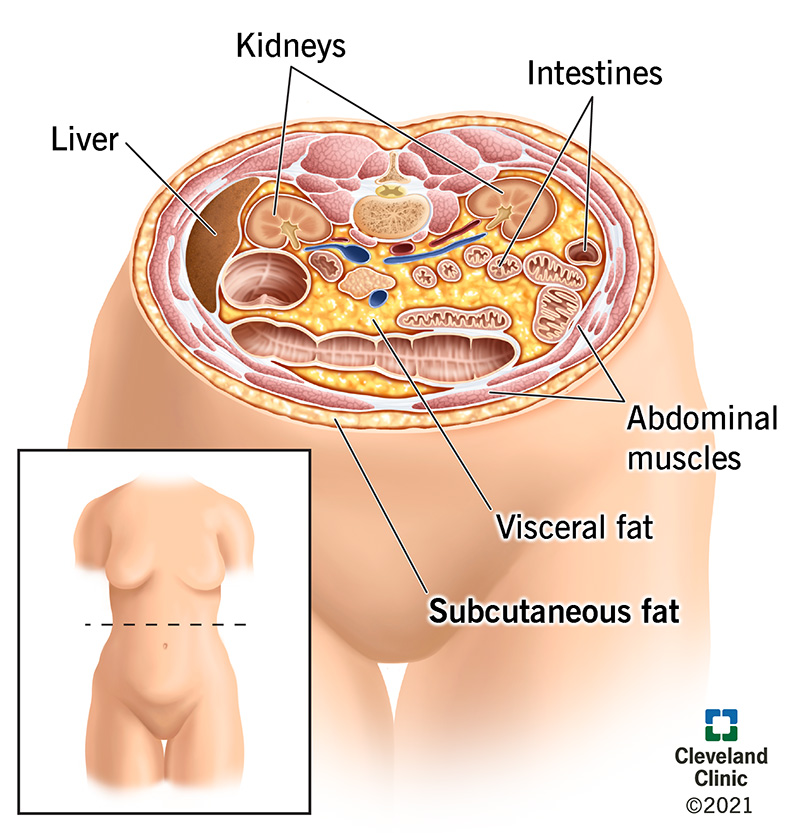
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/23968-subcutaneous-fat)
Subcutaneous fat is a type of fat that’s stored just beneath your skin. Your skin is made up of three layers – the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous fat. Subcutaneous fat is the deepest layer of your skin. It serves many functions. Subcutaneous fat:
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Visceral fat is fat that lies deep within your abdominal organs and can’t be seen from the outside. It surrounds your stomach, liver, intestines and other important organs. Subcutaneous fat is different. Subcutaneous fat is the fat just under your skin. It’s the kind that you can grab and pinch between your fingers. Subcutaneous fat collects mainly around your hips, butt, thighs and belly.
Genetics determine the amount of subcutaneous fat you start with – everyone has some. Environmental factors play an important role in how much subcutaneous fat you develop over time.
A non-healthy diet with high amounts of fatty foods and an inactive lifestyle are the main environmental factors that can contribute to an increase in subcutaneous fat. You may also have more subcutaneous fat if you have low muscle mass and don’t do any aerobic activity. If you have diabetes or are insulin resistant, you may have higher levels of subcutaneous fat as well.
Advertisement
Some subcutaneous fat is good for your body. It protects your body, serves as an energy reserve and has many other functions. However, too much subcutaneous fat can be unhealthy. If you have too much subcutaneous fat, it’s often a sign that you have too much visceral fat. Too much visceral fat can lead to serious health issues such as:
For most people, subcutaneous fat makes up about 90% of their body fat. The remaining 10% makes up visceral fat. There are several ways you can measure your body fat at home:
The best way to lose subcutaneous fat is by maintaining a healthy lifestyle. You can lower your subcutaneous fat level by focusing on a fat-burning diet and exercise plan. In addition, getting enough sleep and keeping stress at bay are important for losing subcutaneous fat.
Advertisement
It’s important to see your healthcare provider regularly. They can track your body fat percentage, including your subcutaneous fat. If you measure your body fat at home and your measurements are higher than recommended, make an appointment to see your provider. They can talk to you about your health risks and recommend a diet and exercise plan that’ll work for you.
Subcutaneous fat is fat that’s found under your skin. Too much subcutaneous fat can be a sign that you have too much visceral fat. Visceral fat lies deep within your abdominal cavity and surrounds your organs. Too much fat can have harmful effects on your health. By maintaining a healthy diet and keeping up with regular exercise, you can burn calories and shed the subcutaneous fat your body is storing. If you suspect you may have too much subcutaneous fat, talk to your healthcare provider. They can talk to you about your health risks and recommend a diet and exercise plan that’ll work for you.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
