Staph A bacteria may cause folliculitis decalvans, a condition that causes baldness with scarring (cicatricial alopecia). Inflammation and bacteria in hair follicles cause pustules to form. Hair follicles eventually die, preventing new hair growth and causing circular bald patches. Treatments include antibiotics and photodynamic therapy.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
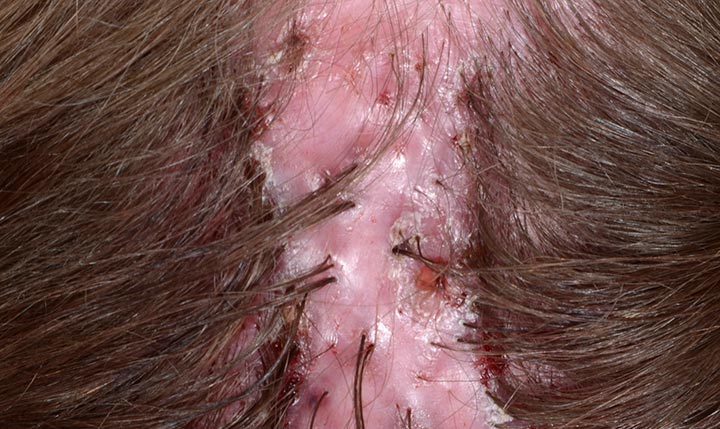
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22784-folliculitis-decalvans)
Folliculitis decalvans is a rare condition that causes ongoing (chronic) inflammation of your hair follicles and scalp. Over time, hair falls out and scarring occurs. The condition causes permanent hair loss with scarring (cicatricial alopecia).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Folliculitis is inflammation of the hair follicle. Follicles are the bulb-shaped root that anchors hair to your scalp and generates new hair. Bacteria trapped in the inflamed hair follicle can cause small pus-filled bumps called pustules to form. These red, oozing pustules look like acne.
Experts aren’t sure what causes folliculitis decalvans. A staphylococcus infection (staph infection) may be to blame. Some people seem to have an unusual reaction to Staphylococcus aureus (Staph A). This bacterium is naturally found on your skin and inside your nose.
Staph A is usually harmless. But for some people, the bacteria causes ongoing inflammation. Over time, this inflammation destroys hair follicles, preventing them from growing new hair. Eventually, hair falls out, leaving scars. This hair loss (also known as alopecia) is permanent.
Folliculitis decalvans can cause permanent hair loss in women and men. It more often affects men. It often starts during the teen years or early adulthood but can develop at any time.
Folliculitis decalvans typically affects only your scalp, causing round or oval-shaped bald spots. Rarely, hair loss occurs in other regions. It can affect your armpits, genitals, face, legs and arms.
Advertisement
Some people don’t have noticeable symptoms until they begin to lose hair. Others may have an itchy scalp that feels like dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis).
The scalp may feel tight or painful. Pustules most commonly appear on the back of your head but can occur anywhere on your scalp. You may feel scaly skin or crusts after the pustules ooze and form scabs.
Folliculitis decalvans causes hair to grow in tufts. Several strands of hair grow from the same follicle, like bristles on a toothbrush. For this reason, the condition is also called tufted folliculitis. When the follicle dies, the tufts of hair fall out, leaving a scar and bald spot.
A dermatologist, a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of skin conditions, will examine your scalp. Your provider may use a magnifying device to view the pustules more clearly.
Your provider may also:
There isn’t a cure for folliculitis decalvans. But treatments can reduce inflammation and prevent scarring and further hair loss. The condition sometimes goes into remission (no symptoms) but can return and cause a flare (active symptoms). Treatment is often an ongoing process.
Folliculitis decalvans treatments include oral:
Some studies suggest that methyl aminolevulinate photodynamic therapy (MAL-PDT) helps. This treatment uses a chemical applied to the scalp. The chemical reacts to a special light to kill bacteria and cells.
Your provider may recommend an antiseptic shampoo or a shampoo containing tar to kill bacteria on your scalp.
Hair loss from folliculitis decalvans may make you self-conscious about your appearance. This may lead to depression or anxiety. Hair loss treatments like hair grafting or scalp micropigmentation may make the bald spots less noticeable. You can also wear a wig, hairpiece or head covering. A counselor can help you take steps to foster a positive self-image.
You may want to ask your healthcare provider:
Advertisement
No, you can’t catch folliculitis decalvans from someone else. The condition sometimes affects members of the same family, but experts aren’t sure why.
No, folliculitis decalvans isn’t skin cancer. Having the condition doesn’t increase your cancer risk.
Unfortunately, hair loss from folliculitis decalvans is permanent. If you notice symptoms, seeking treatment right away may help you minimize hair loss.
Folliculitis decalvans causes bald patches and red, crusty pustules to form on the scalp. Experts aren’t sure why some people develop this condition, although Staph A bacteria may play a role. Antibiotics, steroids and other treatments can help ease inflammation and prevent more hair loss. The hair loss is permanent, but certain hair loss treatments may help. Talk to your provider if you become self-conscious about your appearance.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Losing your hair can be shocking and overwhelming. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll find the right treatment to help you feel (and look) like yourself again.
