Carotid artery dissection happens when there is a tear or separation in the layers of one of the two carotid arteries in your neck. Dissection can occur spontaneously or after a neck injury. The condition can heal itself over time but may cause life-threatening complications like a stroke or bleeding in the brain.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
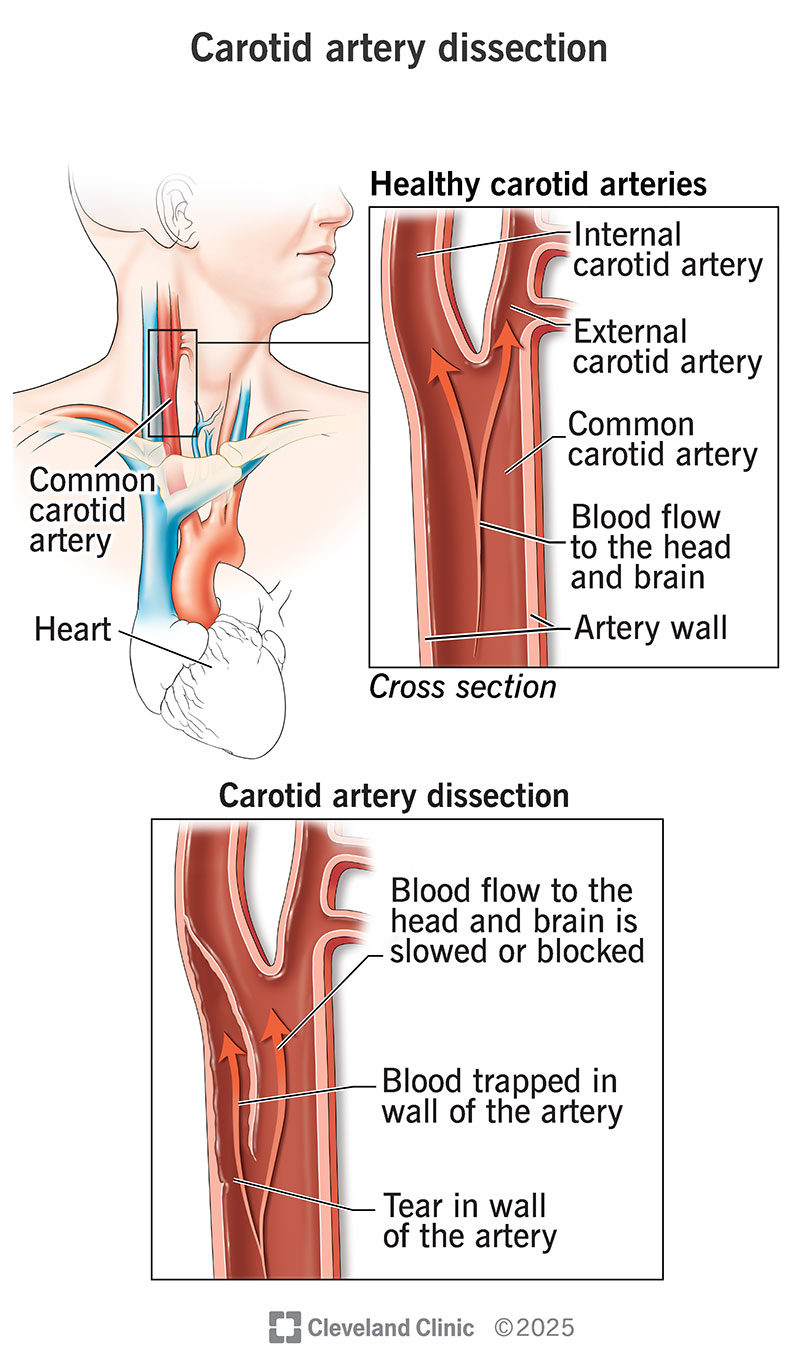
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22697-carotid-artery-dissection)
A carotid artery dissection is a tear in the wall of your carotid arteries, which supply blood to your brain. This rare tear in the artery’s layers allows blood to flow between the layers. Blood stays in your artery, but can flow more slowly or stop flowing to your brain. You may even have a complete blockage in your carotid artery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
When you don’t have enough blood flowing to your brain, you can have a stroke. This can happen even if you’re in your 40s, 30s or younger.
Because of the risk of stroke, you should seek treatment right away.
Carotid artery dissection symptoms vary widely, from none at all to sudden stroke. Sometimes, pain (often around your eye) is the only symptom. Others may include:
The cause of this condition is often unknown. But major or minor trauma to your neck can create a tear in your artery wall. Known causes of this condition include:
Carotid dissection can happen to anyone at any age. But it’s more common in people in their 40s or 50s. Risk factors include:
Advertisement
If you have a condition that puts you at risk of carotid artery dissection, following your healthcare provider’s instructions can help. Your provider may be able to prevent dissection or detect it early.
A healthy lifestyle can help manage your blood pressure and minimize the risk of carotid artery dissection. Tips include:
A carotid dissection can make your artery narrow and cause a blood clot. You can have serious complications, like:
Because symptoms vary so widely, dissection of a carotid artery can be difficult to diagnose. But a timely diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications or death.
For diagnosis, a healthcare provider may perform or order the following:
Your healthcare provider will recommend treatment depending on several factors, like other medical conditions you have and the cause of dissection. They’ll also consider whether you’ve had a stroke or are bleeding.
Carotid artery dissection treatment to lower your stroke risk may include:
You should seek medical care right away for any signs of dissection of your carotid artery. This is especially important if you have any of the associated conditions or if you’ve recently injured your neck.
You can expect to have follow-up visits after treatment for this condition. Repeating imaging scans weeks or months later helps a provider see if the tear is healing. They’ll also want to know if the medicine you’re taking is working.
Questions to ask your provider may include:
Advertisement
The prognosis (outlook) with this condition varies widely, depending on its cause and severity. Some people don’t need treatment. But others have serious, life-threatening complications. There’s a high risk of stroke. The outlook depends on whether you get a diagnosis before you have stroke symptoms.
A carotid artery dissection may heal itself over time. Your healthcare provider might monitor it to determine whether it’s getting worse and to detect any possible complications early. In one study, 6 out of 10 people with a dissection got full blood flow back in their carotid arteries. This is more likely if you have mild symptoms.
A carotid artery dissection doesn’t usually happen again after treatment.
A problem with an artery that sends blood to your brain can make anyone anxious. If you have signs of carotid artery dissection, seek medical attention. Prompt diagnosis and treatment help prevent a stroke. Don’t hesitate to speak up and ask questions if you’d like more information from your healthcare providers.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When the carotid arteries in your neck are blocked, you’re at risk for a stroke. Cleveland Clinic’s experts are world renowned in treating this condition.
