A pilon fracture (tibial plafond fracture) is a rare but severe type of bone break that affects your tibia (and, sometimes, fibula). High-impact events like car accidents are the most common cause of this type of fracture. You’ll likely experience sudden, extreme pain. Depending on the severity of the injury, treatment usually involves surgery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
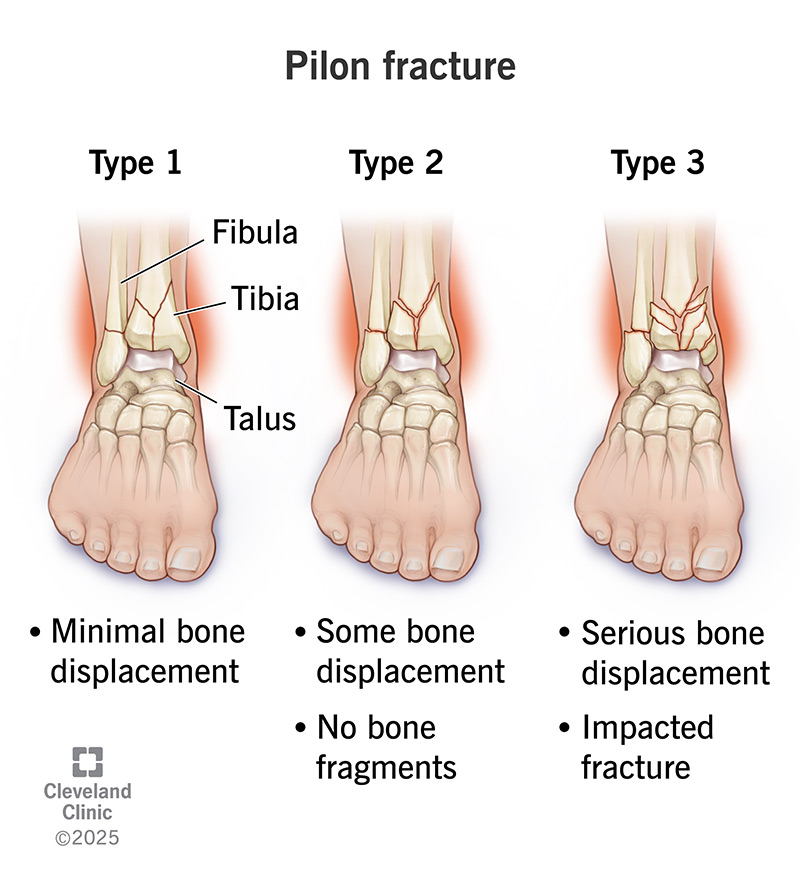
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/pilon-fracture)
A pilon fracture, or tibial plafond fracture, is a relatively rare bone break (fracture) that affects the lower end of your shinbone (tibia). In many cases, your other ankle bone (fibula) is broken, as well. Pilon fractures can be challenging to treat because they involve your ankle joint, and there’s usually damage to surrounding soft tissues like skin, muscles and ligaments.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“Pilon” is the French word for pestle, which is a tool with a rounded end that’s used to crush and grind substances. This type of bone break is called a pilon fracture because of the crushing force that often causes it. Your tibia and fibula are attached to your talus, which is the other weight-bearing bone in your ankle. Tibial plafond fractures happen when your talus is driven into your tibia with such force that your tibia (and often your fibula) breaks at your ankle joint.
Healthcare providers can classify pilon fractures (tibial plafond fractures) in a couple of different ways.
Under the Ruedi-Allgower classification system, providers categorize pilon fractures into the following types:
Advertisement
Under the AO/OTA classification system, providers categorize pilon fractures as:
Then, they subclassify the fracture based on the degree of comminution.
Tibial plafond fractures are often severe injuries that can cause intense pain in your lower leg and ankle. The injury can be extremely uncomfortable and affect your ability to walk.
Other pilon fracture symptoms may include:
Most pilon fractures happen when your talus is driven into your tibia and fibula with such force that your leg bone(s) breaks at your ankle joint. There are a few situations or conditions that can cause tibial plafond fractures, including:
Anyone can experience a pilon fracture at any age, but certain people are more likely to have one:
Your risk of complications from a tibial plafond fracture depends on how severe the fracture is and whether you had other injuries. Complications may include:
An orthopedic surgeon will do a physical exam of your leg and ankle and ask you about your symptoms. They’ll need to see an X-ray to diagnose a pilon fracture (tibial plafond fracture). They may request additional imaging tests to learn more about your injury.
Imaging tests that your provider may use to diagnose a tibial plafond fracture include:
Treatment for a tibial plafond fracture depends on several factors, including:
If you have a tibial plafond fracture that isn’t displaced and your bones are still aligned properly, you may not need surgery. Nonsurgical treatment for pilon fractures may include:
Advertisement
If you have a pilon fracture that’s displaced and the bones aren’t aligned properly, you’ll likely need surgery. Depending on the severity of your fracture and whether you have other injuries, your orthopedic surgeon may delay your surgery until the swelling around your ankle has settled. They need to make sure you’re healthy enough to have the surgery to minimize risks, like an infection. Types of pilon fracture surgeries include:
Advertisement
The length of time it takes for a tibial plafond fracture to heal depends on the severity and whether you had other injuries. Most pilon fractures require surgery. It usually takes three to six months for the fracture to heal completely after surgery. But it often takes a year or more to fully recover from the injury.
If you’re experiencing signs and symptoms of a pilon fracture, see a healthcare provider right away. If you can’t get to urgent care or an emergency room on your own, call 911 or your local emergency number for help.
If you had surgery to fix the pilon fracture and are experiencing signs of infection — like redness, pus or warmth at your surgical site — go to the nearest hospital as soon as possible.
Despite advances in imaging technology and surgical approaches, pilon fractures are challenging to treat. This is because pilon fractures often cause damage to the ankle joint surface itself and the surrounding soft tissues, like muscles and ligaments. It can take a year or more to fully recover from the injury, and long-term ankle arthritis, stiffness and swelling are common following a pilon fracture.
Some risk factors for getting a pilon fracture include:
Advertisement
Depending on your age and lifestyle, there are a few things you can do to try and prevent getting a pilon fracture, including:
A pilon fracture (tibial plafond fracture) is a painful injury. Whether you experience a mild fracture or severe injury, you can expect it to take a while to heal. Depending on the severity of your condition and if you had other injuries, you may develop complications, too. Don’t be afraid to ask your healthcare team about your injury and treatment plan. You can lean on them and get support along the way to your recovery.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
From sudden injuries to chronic conditions, Cleveland Clinic’s orthopaedic providers can guide you through testing, treatment and beyond.
