Your pes anserinus bursa is a thin, fluid-filled sac located on the inside of your knee joint. It cushions your joint and prevents your bones from rubbing against each other. Pes anserine bursitis occurs when inflammation affects this bursa, causing pain, swelling and tenderness. Fortunately, many nonsurgical treatment options are available.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
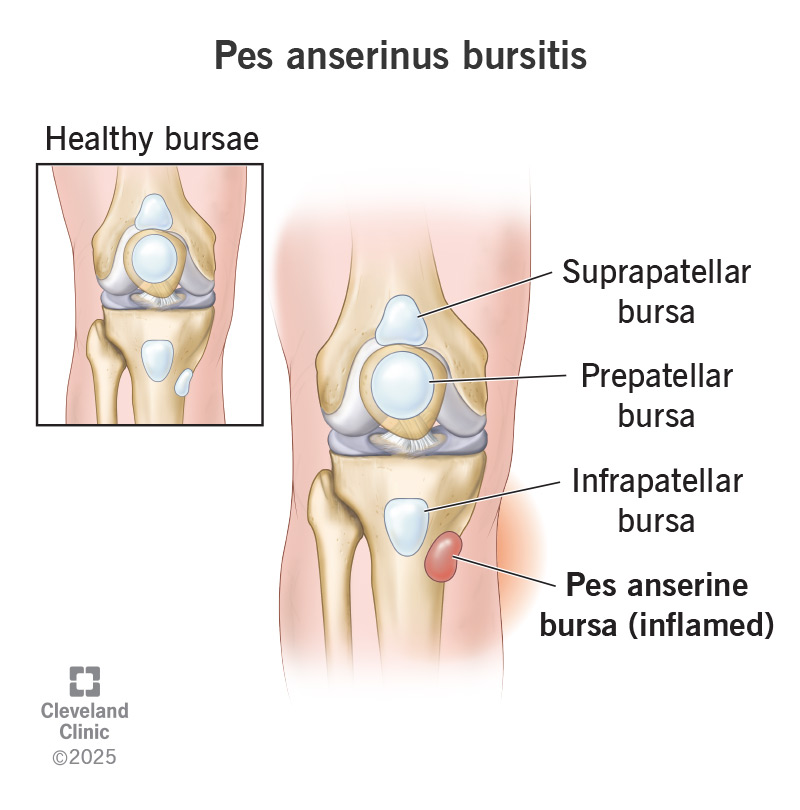
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/pes-anserinus-bursitis)
Pes anserine bursitis, or pes anserinus bursitis (pronounced “ber-CY-tuss”), occurs when the bursa next to your knee joint becomes irritated and produces too much fluid. The bursa then swells, causing knee pain and tenderness.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A bursa is a fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion and lubricant. Bursae (plural form of bursa) allow your tendons and muscles to glide smoothly along your bones.
Your pes anserinus bursa is located between three conjoined tendons (your sartorius, gracilis and semitendinosus) and your shin bone (tibia). The term “pes anserinus” means “goose’s foot” in Latin. As the conjoined tendons attach to your tibia, it looks like a goose’s footprint.
People with pes anserine bursitis usually develop one or more warning signs. Pes anserine symptoms may include:
Your pain level can vary depending on how advanced your condition is. In general, people with pes anserine bursitis experience more discomfort when kneeling, standing up from a chair or walking up and down stairs. Typically, pain improves with enough rest.
Bursitis most often occurs due to overuse or stress on your bursae. Some of the most common pes anserine bursitis causes include:
Advertisement
Pes anserine bursitis is most common among athletes. The condition also predominantly affects females and people:
Your healthcare provider will examine your knee and discuss your symptoms with you. Because pes anserine bursitis can have the same symptoms as a stress fracture, you may need a knee X-ray to rule out a broken bone. Ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may also be necessary to determine the extent of your injury.
There are several ways to reduce discomfort and begin your road to recovery. Pes anserine bursitis treatment includes:
Any time you develop persistent knee pain, you should schedule a visit with your healthcare provider. If you don’t experience pain relief after a few months of at-home treatment, or you begin to feel worse, you should follow up with your provider. They may recommend other treatment options for you.
Questions you may want to ask your provider include:
Most people with pes anserine bursitis heal in about six to eight weeks. It could take longer for more severe cases. You’re likely to recover faster if you rest and seek proper treatment.
You can usually return to work immediately following pes anserine bursitis treatment, especially if you have a desk job. But if your job is physically demanding, you may need to take a few weeks off. Ask your healthcare provider when it’s safe for you to return to work or school.
To reduce your risk for pes anserine bursitis, ask your healthcare provider to recommend exercises you can do at home. These exercises can help stretch and strengthen the muscles in your knees, thighs and abdomen — and in many cases, they can prevent a recurrence.
Advertisement
If you have overweight or obesity, talk to your healthcare provider about how you can reach and maintain a healthy weight for you. This can help take pressure off your pes anserinus bursae.
Pes anserine bursitis can be debilitating and interfere with your quality of life. Fortunately, there are effective treatment options, especially when you get an early diagnosis. Your healthcare provider can determine a personalized treatment plan to ease your painful symptoms and help you get moving again. You don’t have to live with the pain. Make an appointment with your provider so you can get on with your life.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Knee pain can keep you from doing the things you love. Cleveland Clinic experts can craft a treatment plan to get you back to the regular pace of your life.
