Cold sores are painful bumps that form on or around your lips when you have an oral herpes infection. Once you catch oral herpes, the virus stays in your body for life. From time to time, it may reactivate, causing a cold sore outbreak. Cold sores are very contagious. Avoid touching others with the affected area of skin until it’s fully healed.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
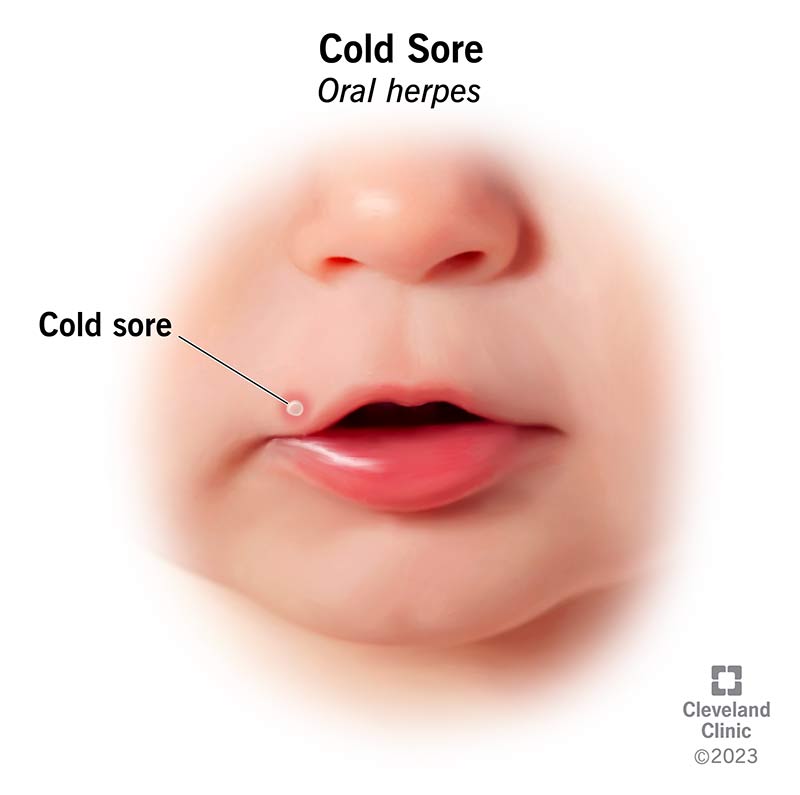
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/21136-cold-sore)
A cold sore (also called a fever blister) is a skin blister associated with a herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection. Cold sores typically form on your lips or the skin around your mouth. But they can also develop on other areas of your face, including your nose, cheeks or chin.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Cold sores themselves are a symptom of an oral herpes infection. This means the herpes simplex virus (HSV) entered your body at some point in your life and took up residence in your nerve cells. HSV stays dormant (latent, or “asleep”) in the nerves in your head and periodically reactivates, leading to cold sores.
The first time HSV infects you (primary infection), there may be other symptoms besides cold sores. These include:
These symptoms may make it hard for you to eat or drink. Usually, you won’t have these symptoms later on when the virus reactivates. Instead, you’ll just have cold sores.
Primary oral herpes infections often happen during childhood, particularly in children between the ages of 1 and 5 years old. It’s important to watch for signs of dehydration if your child has trouble drinking enough fluids.
It’s also possible for your child to get another type of HSV infection on their fingers (herpetic whitlow) if they suck their thumb or touch their sores.
Cold sores develop and go away over the course of one to two weeks. Here’s what you can expect for a typical cold sore outbreak:
Advertisement
Cold sores usually last one to two weeks. Symptoms may be more severe and sores may take longer to heal if you’re immunocompromised.
A herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection causes cold sores. There are two types of HSV (HSV-1 and HSV-2). HSV-1 causes most cases of oral herpes, the infection that leads to cold sores. But HSV-2 can also cause oral herpes and related cold sores.
Many different things can trigger cold sores. Sickness, stress, sun exposure, trauma to your mouth area and hormonal changes (like during menstruation or pregnancy) are just a few examples. Knowing your triggers can help you avoid some outbreaks. But outbreaks can also happen unpredictably.
Yes, they’re very contagious. Contact with someone else’s cold sore can cause you to develop an HSV infection. The location of the infection depends on which part of your body touches the cold sore.
For example:
Advertisement
A person with a cold sore can spread HSV through skin-to-skin contact and also through their saliva. This means if someone you know has a cold sore, you should avoid:
Cold sores are contagious from when you first notice tingling or other skin symptoms (prodromal stage) until they completely heal. You’ll know the cold sore has healed when the scab falls off and the skin underneath looks back to normal.
Cold sores are most infectious within 24 hours of when they first form. “Infectious” refers to how much of a germ (in this case, HSV) you need to be exposed to in order to get sick. When a virus or other germ is highly infectious, it just takes a little bit to make you sick.
So, the first day you have a cold sore, it’s super easy for HSV to spread from the sore to someone else — for example, through kissing or sharing a straw. But HSV can still spread before and after that point, too, for the duration of the outbreak. This means as soon as you feel those warning signs that a sore might form, you should take precautions around others.
Advertisement
Treatment options for getting rid of cold sores include:
Topical anesthetics don’t affect healing. Antiviral medications help speed up the healing process. They’re most effective when started within 48 hours of the cold sore forming.
If you get frequent or severe cold sore outbreaks, your provider may recommend daily antiviral medications (chronic suppressive therapy). This form of treatment may help you have fewer and less severe cold sore outbreaks. Your provider can tell you more about what this involves and whether it’s right for you.
Advertisement
Contact a healthcare provider about your cold sores if any of the following are true:
Call a pediatrician if your child develops a cold sore and any of the above scenarios apply.
Newborns exposed to HSV won’t just get a cold sore — instead, they may develop a life-threatening condition called neonatal herpes. If you believe your newborn was exposed to HSV (for example, if an adult with a cold sore kissed them) or they have symptoms like skin blisters, call your pediatrician right away. Babies with neonatal herpes need immediate medical care.
Cold sores and canker sores are both small, round sores that affect your mouth area. They have several important differences, including:
Cold sores sometimes develop inside your mouth. This may happen when you first get infected with HSV. Later on, when the virus reactivates, you’ll likely only get cold sores on your lips and face. It’s different if you’re immunocompromised, though. In this case, you might get sores inside your mouth as part of oral herpes outbreaks.
Yes, cold sores are always a sign of a herpes simplex infection. But keep in mind that not every bump or irritation on your lip is a cold sore. For example, you might think you have a cold sore when really you have a pimple on your lip.
Talk to a healthcare provider if you’re not sure about any sores or blisters you notice. Your provider can help you determine if they’re cold sores or something else.
Cold sores affect everyone a little differently. Maybe your friend only gets cold sores when they’re under the weather. But maybe you feel like you get these painful sores all the time, and they take forever to heal. If cold sores are disrupting your life, talk to a healthcare provider. Treatments are available to help outbreaks go away faster. Your provider may also recommend daily medications to help you have fewer outbreaks. Cold sores are a common issue many people deal with, but they don’t have to be a common part of your daily routine.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
