Hepatitis C is a liver disease caused by the HCV virus. You can get the virus through contact with infected blood. You might not have symptoms, but screening tests can detect the infection. New medications can cure it. But without treatment, it can cause chronic liver disease and lead to cirrhosis, liver failure or liver cancer.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
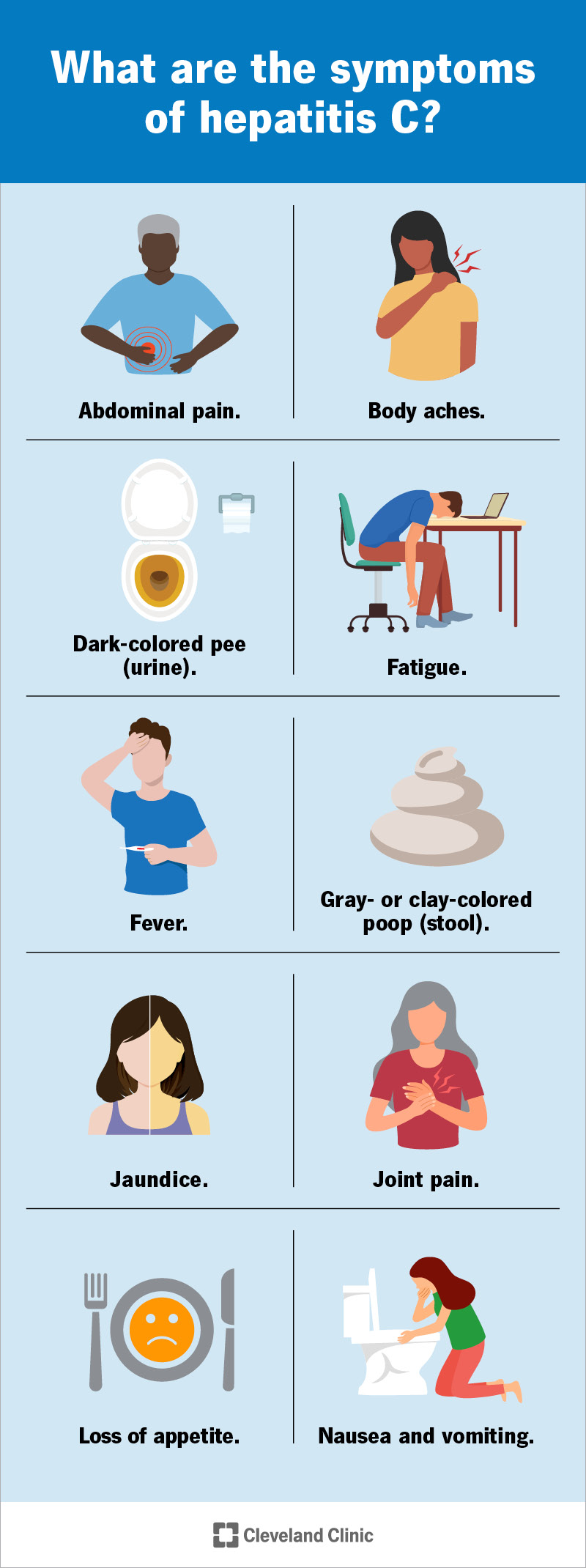
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/15664-hepatitis-c.jpg)
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes inflammation that damages your liver. It usually doesn’t go away without treatment, and it can cause serious liver damage over time. New medications can now cure hepatitis C infection. But many people don’t have symptoms and don’t know they have it.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Hepatitis C spreads primarily through blood. You get it by coming into contact with blood from someone infected with the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Transmission often occurs when people share needles for injecting drugs. Researchers estimate between 2 and 4 million people in the U.S. have hepatitis C.
Most people don’t have any symptoms of hepatitis C. If you do have symptoms, you might have them when your body first begins to recognize and fight the virus. This is the “acute” phase of the infection.
It can cause:
If you don’t have acute symptoms, you might begin to have symptoms after many years of chronic (long-term) hepatitis C infection. These are signs that the infection is starting to affect your liver function.
You might have all the symptoms above, and also:
You can get hepatitis C if you have contact with blood from someone else who has the virus. In the U.S., the most common cause of hepatitis C transmission is sharing needles to inject intravenous drugs.
Advertisement
Other possible causes of transmission include:
It’s important to know that hepatitis C is contagious even if you don’t have symptoms or know that you have it. However, it only spreads through blood, not through other bodily fluids or casual contact.
Up to 30% of people who get hepatitis C may be able to fight it off naturally when it’s still new (acute). It can take several months for your body to defeat the virus. Most people who get hepatitis C can’t fight it off naturally. When your body surrenders after months of fighting, it becomes a chronic infection.
Chronic hepatitis C infection means long-term, ongoing inflammation in your liver (hepatitis). This is a form of chronic liver disease. Inflammation slowly damages your liver over many years, causing scarring that interferes with its functioning (cirrhosis). The end-stage of this process is chronic liver failure.
Cirrhosis and liver failure bring risks of other complications, including:
If you think you might have hepatitis, or you have symptoms of liver disease, a healthcare provider will examine you to look for physical signs. These may include swelling in your body or yellowing in your eyes.
They’ll follow up with blood tests. These may include:
If blood tests show your liver is struggling, your provider might want to do other tests to check for liver damage. A transient elastography is a type of ultrasound that measures the scarring in your liver.
Direct-acting antiviral (DAA) medications are the primary treatment for hepatitis C. These are tablets that you swallow. There are at least a dozen DAAs that treat different strains (genotypes) of the virus.
Commonly prescribed medications include:
Advertisement
If you’ve had hepatitis C for a long time and have a lot of liver damage, you may need other treatments. Some damage is reversible, but some isn’t. You might need treatment for the effects of liver disease.
Most people take DAAs for two to six months, but some people might need to take them for longer.
Common DAA side effects include:
When you have liver disease, it’s important to do what you can to protect your liver from further harm. That might mean:
Some people who get hepatitis C can fight it off naturally during the acute phase. But for most people, it becomes a chronic infection. Chronic hepatitis C will continue to damage your liver over time, even if you don’t have symptoms and don’t know you have it. This is why routine screenings are important.
Once you know that you have it, you can treat it with antivirals. Research shows these medications cure most cases of hepatitis C, no matter how long you’ve had it. But even after curing hepatitis C, some people have irreversible liver damage (cirrhosis). This happens in about 20% of people after 20 to 30 years.
Advertisement
The only way to prevent infection is to avoid contact with infected blood. There’s no vaccine yet for hepatitis C, although scientists continue to work on one. The virus has many variations and mutates very quickly. That makes it challenging to develop a vaccine that’s effective against all the variations.
You might be surprised and upset to learn you have hepatitis C. You may not feel sick, and you may not know when or how you got it. But finding out puts you in a much better position than not knowing. Hepatitis C is curable, and by catching it sooner rather than later, you can prevent it from causing lasting harm.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Untreated hepatitis can cause liver damage or failure. Cleveland Clinic’s expert providers offer you the latest treatments and caring support.
