A myelogram is an imaging test that uses a contrast material and X-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans to get detailed pictures of your spine. Healthcare providers might recommend a myelogram if you have chronic back pain.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A myelogram is an imaging test that takes detailed pictures of your spine. It uses a contrast material to highlight issues in your spinal cord and the areas around it, like your nerves and soft tissues. A myelogram also looks at the relationship between your vertebrae (the small bones that make up your backbone) and the disks that cushion them.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A regular spine X-ray gives a clear picture of just your bones because it doesn’t use contrast material. The contrast material providers use in a myelogram shows up white on an X-ray or computed tomography (CT) scan, giving a detailed view of your spinal canal, spinal cord and nerves. Myelography is a type of fluoroscopy, which means your radiologist can see the contrast material moving through your spinal column in real time.
You might hear healthcare providers refer to specific types of myelograms, like cervical or lumbar. These aren’t different tests. They’re just names that reflect which area of your spine needs imaging. For example, if you need images of your neck (the cervical section of your spine), then your provider will take a cervical myelogram. If you need images of your lower back (the lumbar section of your spine), then your provider will take a lumbar myelogram.
If you have chronic back pain, your healthcare provider will likely suggest either a computed tomography (CT) scan or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) first. If neither test can explain the issue, your provider may recommend a myelogram to get more information.
A myelogram can help diagnose conditions like:
Advertisement
Your provider may also recommend a myelogram test if you’ve had recent surgery — especially if you’ve developed any new, lingering pain or weakness since the procedure.
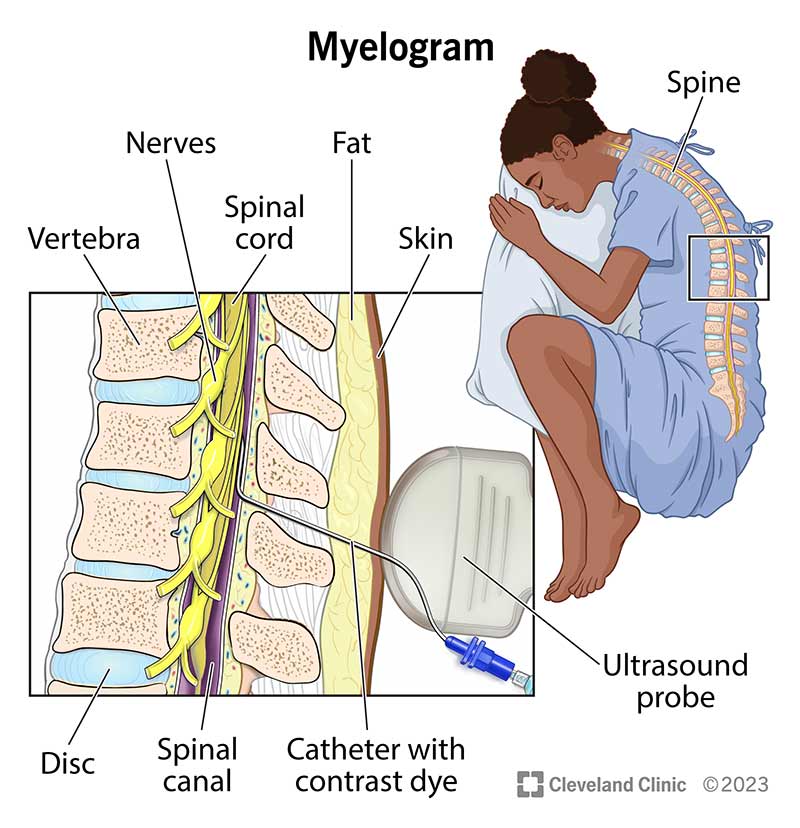
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/4892-myelogram)
A myelogram can reveal certain issues that providers can’t see with a conventional CT scan or MRI. It’s particularly useful for getting a clear view of the bones, disks and other tissues surrounding your spinal canal that may be pressing on your nerves or spinal cord.
When your radiologist injects the contrast material into your spinal column, the dye will move through the space around your spinal cord. As this happens, the nerves and spinal cord in your spine will show up as a silhouette on the X-ray or CT images. This allows your provider to see issues they can’t see with a traditional X-ray.
Your healthcare provider will give you a list of specific instructions to follow before your myelogram. In the meantime, here are some general guidelines:
If you have diabetes:
You usually don’t need lab tests before a myelogram unless you have a history of blood disorders or conditions like dehydration or chronic kidney disease (CKD).
You won’t be asleep during your myelogram, but your provider may give you sedative medications to help you relax. A radiologist and technologist will be in the room with you the whole time.
During the myelogram test, they’ll:
This procedure typically takes about an hour and may cause some discomfort or a minor headache.
Your provider will monitor you for about one hour after your test and make sure you’re ready to leave the hospital. They’ll give you written instructions to follow once you get back home. Your radiologist will send a detailed report to your primary care physician (PCP).
Advertisement
Up to 10% of people experience side effects after a myelogram. Normal side effects that’ll go away in a day or two include:
Call your healthcare provider immediately if you develop a headache that doesn’t go away or other worrisome symptoms like:
On average, it takes about 24 hours. You’ll need to sit still or lie down for several hours after your myelogram test. Resting reduces your risk of a cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) leak. You can go back to normal routines after one full day. But be sure to let your provider know if you have lingering headaches or if you develop fever, stiff neck, numbness in your legs or other concerning symptoms.
Here are some things you can do at home to help your recovery:
Your primary care physician will review the results of your test once they receive a report from your radiologist. This usually takes a few days. Then, they’ll call you to explain the results and tell you what comes next.
Advertisement
After your myelogram, call your healthcare provider right away if you develop:
The answer to this question is different for everyone. While you shouldn’t feel unbearable pain, you might feel some discomfort during your test, including:
The contrast material can also cause:
Your provider will do everything they can to keep you as comfortable as possible and complete the test quickly.
Chronic back pain can disrupt your quality of life and keep you from doing the things you love. And when conventional imaging tests haven’t given you the answers you seek, it might be time for a myelogram. A myelogram can help your provider figure out what’s causing your discomfort and help you find a solution.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When you need a clear picture of what’s happening inside your body, the Cleveland Clinic imaging team is here for you.
