When providers use the informal term “soft tissue,” they’re describing something that isn’t bones. But that means this term can refer to many things, like skin, muscle and more. Providers often use “soft tissue” to mean they’ve ruled out injuries or conditions affecting your bones.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
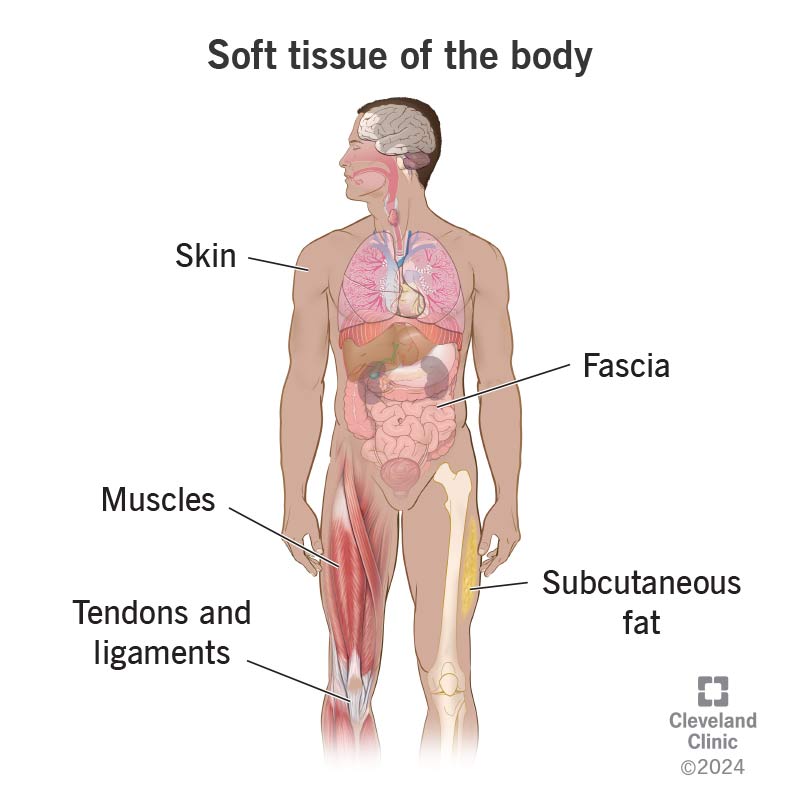
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/soft-tissue-body.jpg)
Soft tissue is an umbrella term for many forms of nonhardened tissue throughout your body. It’s common for healthcare providers to use this term to differentiate softer tissues from nearby bones.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Soft tissue isn’t one of the four true types of tissues (epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous). But this term is common among healthcare professionals and laypersons alike.
Soft tissue surrounds your bones and other internal structures throughout your body. It can refer to:
Hard tissue happens in one of two ways:
Different types of soft tissues have different jobs.
Advertisement
“Soft tissue” and “connective tissue” aren’t interchangeable. There’s a lot of overlap between them, since ligaments and tendons are both soft and connective. But bones are both hard and connective tissue. So, don't hesitate to ask if you're unclear on what someone — especially your provider — means when they talk about soft or connective tissue.
Experts use the term “soft tissue injury” to distinguish them from bone injuries like fractures. Some injuries that they might describe as soft tissue injuries include:
Soft tissue is a general term, so it can apply to many tissues and injuries to them. If you aren’t sure what kind of soft tissue injury a healthcare provider is talking about, don’t feel bad about asking for clarification. Your understanding can make a difference in your treatment and recovery.
Many medical conditions (which can happen without injuries) can also affect soft tissues. They include:
Soft tissue conditions and injuries can cause one or more of the following symptoms:
Soft tissue injuries and conditions are often diagnosed with a physical exam and imaging scans. Imaging tests like X-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans are especially useful because they can rule out bone injuries. If it’s not your bones, it’s more likely the soft tissues nearby.
Other imaging scans like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may help diagnose soft tissue conditions. Other types of lab tests are also possible. Your healthcare provider is the best source of information about these. Your provider can recommend tests and explain how they might help.
Soft tissue injuries can benefit from a variety of treatments. One of the most important approaches is the RICE method:
Advertisement
Depending on the injury, other treatments may help, too. They include:
Soft tissue conditions may need very different treatments than injuries do. The treatments depend mainly on the underlying cause, but other factors like your health history can play a role, too. Your healthcare provider is the best person to tell you about treatment options for soft tissue injuries.
Soft tissues can benefit from many of the same things that take care of your body overall. They include:
Advertisement
“Soft tissue” is a straightforward term when it describes something to blow your nose with. But when used to describe part of your body, it’s easy to feel confused about what that term means. But that’s partly because soft tissue isn’t a formal term.
Maybe you rolled your ankle stepping off a curb, or you have some recurring pain in your knee or wrist. You don’t have a broken bone, but your provider is now calling it a soft tissue injury. And that could still mean a lot of things. So, if you have any questions or aren’t sure you understand what the issue is, tell your provider. Part of their job is to help you understand what’s happening with your body.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
From sudden injuries to chronic conditions, Cleveland Clinic’s orthopaedic providers can guide you through testing, treatment and beyond.
