The ampulla of Vater is an important landmark in your biliary system. It’s the place where your common bile duct and pancreatic duct merge to enter your small intestine. The ampulla is a reservoir that holds bile and pancreatic enzymes and releases them into your intestine to help digest food. Rarely, it can be the site of a biliary obstruction or cancer.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
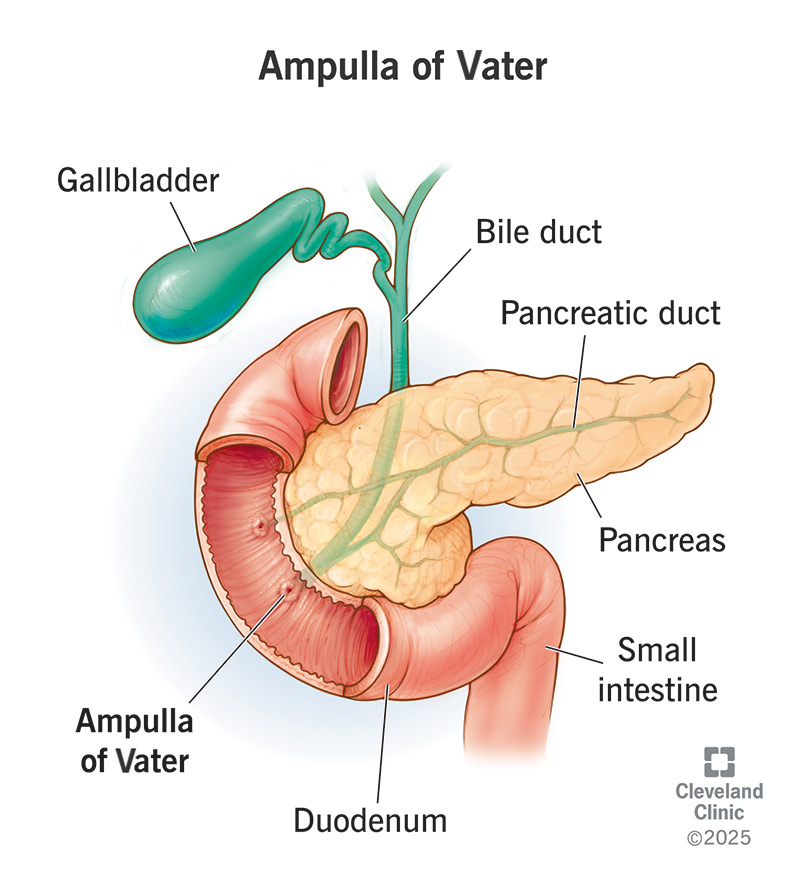
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/24209-ampulla-of-vater.jpg)
The ampulla of Vater is the place where your common bile duct and pancreatic duct empty into your duodenum (first part of your small intestine). Here, bile (from your liver) and enzymes (from your pancreas) merge before entering your duodenum. These substances help to break down the food in your intestine for digestion.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
An ampulla is a rounded flask from Roman times. In your body, an ampulla usually describes a pouch-like reservoir where two ducts converge. An anatomist named Abraham Vater first described this ampulla, and it was later named for him. Other names for it include the hepatopancreatic ampulla and the biliopancreatic ampulla.
Your biliary system plays an important role in your digestion. The ampulla of Vater is the place where your biliary tract contributes its digestive juices to your gastrointestinal tract. Bile from your liver and digestive enzymes from your pancreas reach the end of their journey through your bile duct and pancreatic duct and merge here.
The ampulla of Vater is within the wall of your duodenum, which is about 10 inches long. Healthcare providers subdivide the duodenum into four parts. The ampulla of Vater is halfway along the second or “descending” part, about 4 inches in. This is the transition point between your foregut, which breaks down food, and midgut, which absorbs it.
Traditionally, the ampulla of Vater has a bulbous appearance that resembles the spherical Roman flask. The neck of the flask is where the two ducts feed into the wider reservoir. However, this anatomy can vary. In fact, as often as 38% of the time, the two ducts remain distinct, and they empty into your duodenum through a double-barreled opening.
Advertisement
The rounded body of the ampulla contains a system of circular muscles (sphincters) that open and close to control the flow of bile and enzymes. Like most of the muscles in your digestive system, these are smooth muscles, which function automatically. They respond to signals from your nervous system. These signals tell the sphincters when to open or close.
The main parts of the ampulla of Vater include the sphincter of Oddi (the valve system at the entrance) and the papilla of Vater (the opening into your duodenum). Sphincter of Oddi is a composite term for a valve system that includes the sphincter of the pancreatic duct, the sphincters of the bile duct and the sphincter of the ampulla.
Conditions that can affect the ampulla of Vater include:
If a tumor, gallstone or other issue in your ampulla of Vater prevents bile and enzymes from passing through it, the blockage can cause your whole biliary system to back up. This causes symptoms like:
An obstruction in your biliary system can happen anywhere. Your ampulla of Vater is just one place your healthcare provider will look for it. Wherever it occurs, the obstruction affects the whole system.
Advertisement
Healthcare providers can often examine and treat your ampulla of Vater through endoscopy, without the need for surgery. They do this by passing a tiny camera on the end of a thin tube down your throat and all the way into your duodenum. They can pass tools through the endoscope to remove tumors and relieve obstructions. This procedure is called ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography).
Your ampulla of Vater is a small landmark in your biliary system with surprising importance. It’s the place where digestive juices enter your intestine. It’s also the place where a healthcare provider can enter and examine your bile ducts and pancreatic duct. You might never hear about your ampulla until your provider discovers a problem with it. If they do, it’s likely they can treat it when they find it.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have issues with your digestive system, you need a team of experts you can trust. Our gastroenterology specialists at Cleveland Clinic can help.
