Inguinal lymph nodes are lymph nodes in your groin. Like all lymph nodes, inguinal lymph nodes are a part of your lymphatic system and work with your immune system to fight disease and infection. Swollen Inguinal lymph nodes generally mean your body is working to fight an infection or illness. Rarely, swollen inguinal lymph nodes indicate cancer.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Inguinal lymph nodes are lymph nodes located in your groin. Your groin is the area of your body where your thighs meet your belly (abdomen).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Lymph nodes are part of your lymphatic system. Your lymphatic system includes lymph fluid, lymph vessels, bone marrow and lymphatic organs. These organs include your adenoids, spleen and tonsils. Lymphatic structures are part of your body’s immune system. They create and transport cells that fight against infections and other diseases.
Lymph nodes are small, oval-shaped glands that produce disease-fighting cells. They also act as filters for your lymph vessels. Your lymph vessels are a network of thin tubes that collect lymph fluid and circulate it throughout your body.
In your upper inner thighs, you have about 10 superficial inguinal lymph nodes. Superficial means close to the surface of your skin. These lymph nodes drain into your deep inguinal lymph nodes. Deep inguinal lymph nodes are deep within the connective tissue of your upper thighs. Then the lymph fluid drains into other lymph nodes in your pelvic region.
Your inguinal lymph nodes help your body fight off infection. As lymph fluid passes through these lymph nodes, immune cells within each node filter out bacteria, viruses and other harmful material. Your inguinal lymph nodes form a major drainage pathway for your legs, genitals and pelvic region.
Advertisement
Your inguinal lymph nodes are located in your groin. Specifically, they’re in the inner upper thigh area. Your superficial inguinal lymph nodes sit near the surface of your skin just below your inguinal ligament. Your deep inguinal lymph nodes are deeper within your body.
Normal inguinal lymph nodes are small, oval-shaped glands. They look kind of like beans. The shape of an abnormal inguinal lymph node is more round than oval.
A normal inguinal lymph node is about 1/4 inch in width. The length of an inguinal lymph node should be at least two times its width. When the width of an inguinal lymph node is more than 1/2 inch, it’s considered abnormal. If you have enlarged inguinal lymph nodes, your body may be trying to fight a disease or infection in your lower body area.
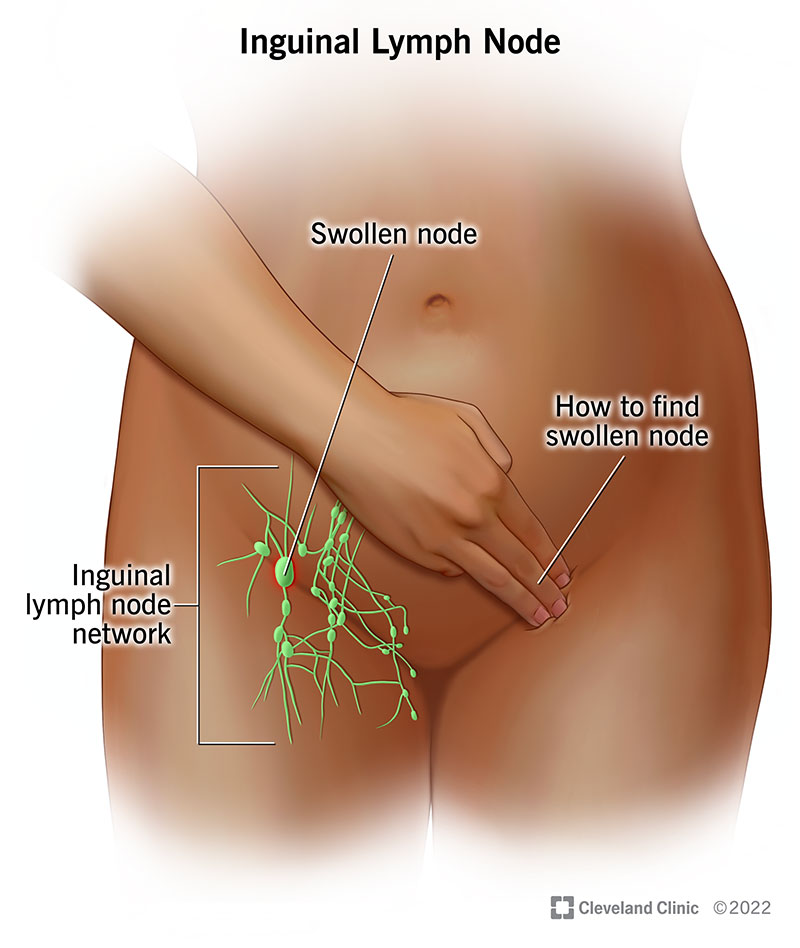
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/23218-inguinal-lymph-node)
Swollen lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy) usually mean your body is fighting an infection or an illness. Swollen inguinal lymph nodes could indicate you have an infection in your groin area. When your lymph nodes are at work trying to fight an infection, they may become enlarged. Enlarged inguinal lymph nodes may cause pain and tenderness. Infections that may cause swollen inguinal lymph nodes include:
Rarely, swollen inguinal lymph nodes are a sign of cancer in your groin area. Cancer cells travel through lymph fluid from the point where cancer begins into your lymph nodes. Types of cancer that can be found in inguinal lymph nodes include:
Advertisement
You normally won’t notice your inguinal lymph nodes. They can be hard to feel unless they’re swollen. When they’re busy fighting an infection, they may become enlarged and sensitive to the touch. To check them:
Most swollen lymph nodes aren’t a cause for concern and will go away on their own. However, if your inguinal lymph nodes are swollen for no clear reason, be sure to check in with your healthcare provider.
Inguinal lymph node dissection is used to look for cancer in your inguinal lymph nodes. During an inguinal lymph node dissection, a surgeon cuts into your groin and removes any inguinal lymph nodes that may contain cancer. The lymph nodes are sent to a lab.
At the lab, a doctor who specializes in the causes and nature of diseases (pathologist) examines the lymph nodes. The pathologist puts together a report that includes the type of cancer and the number of lymph nodes that have cancer cells. Your healthcare provider will use this report to make treatment decisions.
Advertisement
Inguinal lymph nodes are lymph nodes in your groin. Like all lymph nodes, inguinal lymph nodes are a part of your lymphatic system and work with your immune system to fight disease and infection. Once in a while, your inguinal lymph nodes may become swollen. Most of the time, swollen inguinal lymph nodes mean your body is at work fighting an infection. If they become swollen or enlarged for no known reason, reach out to your healthcare provider to make sure there’s not a more serious cause.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
