Bowman’s capsule is part of a nephron, a filter in your kidney. One million nephrons in each kidney clean your blood. A Bowman’s capsule in each nephron plays a part in the filtering process. After filtering, nutrients stay in your blood, and waste goes out through urine.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
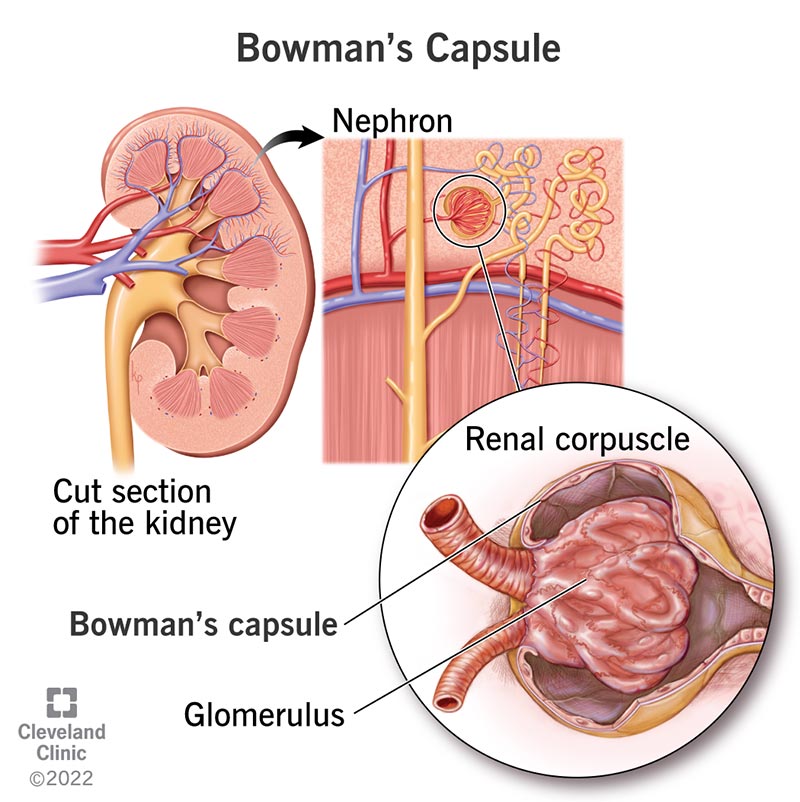
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22964-bowmans-capsule)
Bowman’s capsule is a part of each filtering unit (nephron) in your kidney. You have about 1 million nephrons that filter blood in each of your two kidneys. Kidneys clean blood and return it to your body.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Every nephron has a glomerulus. A two-walled pouch, Bowman’s capsule covers the glomerulus. This group of tiny blood vessels is the starting point for filtering waste products out of your blood. Bowman’s capsule and the glomerulus make up the renal corpuscle.
You may hear other names for Bowman’s capsule, like:
The space in between the walls (layers) of Bowman’s capsule is called Bowman’s space. You may hear healthcare providers refer to Bowman’s space as:
The function of Bowman’s capsule is to help the glomerulus filter blood. Small molecules from your blood pass freely into Bowman’s space. Cells and large proteins stay in your blood.
The glomerular capsule also protects cells called podocytes by keeping white blood cells from getting in. White blood cells can’t pass through Bowman’s capsule. Podocytes in a kidney capsule have pedicels that manage what stays and what goes. Finger-like pedicels link together like they’re holding hands. The way they join creates slits that only let certain things go through. When you’re healthy, protein and cell content can’t get through.
The small molecules then pass through tubes in your kidney. Your kidney regulates which molecules your blood absorbs and which leave your body in pee (urine).
Advertisement
Waste materials go out of your body as urine through tubules (tiny tubes). The blood pressure in the glomerulus helps move the blood along. As the fluids leave, water and nutrients go back into your blood.
Two arterioles go into the Bowman’s capsule. One brings blood into the glomerulus. The other lets blood out.
Bowman’s capsule is in the renal cortex, part of your kidney. Your kidneys are in your back, below your rib cage. Usually, you have one kidney on either side of your spine. Your kidneys are between your intestines and diaphragm. Each kidney connects to your bladder by a tube called a ureter.
Bowman’s capsule looks like a pouch, sac or cup. You can only see it under a microscope. Bowman’s capsule contains fluid like blood plasma, but with no red or white blood cells or platelets.
The glomerular capsule has two layers. A type of body tissue, simple squamous epithelium, makes up the outer (parietal) layer. These parietal cells give structure to Bowman’s capsule. Cells called podocytes form the inner (visceral) layer.
Diseases and conditions that affect your kidneys also affect Bowman’s capsule. This glomerular capsule is especially at risk of diseases of the glomeruli. These are the small blood vessels that Bowman’s capsule surrounds.
Glomerular diseases can damage glomeruli. They don’t work well when they’re inflamed, swollen, scarred or hardened. Without treatment, these diseases can result in kidney failure.
Contact your healthcare provider if you’re having signs and symptoms of kidney issues, like:
Providers use several tests to measure kidney function and diagnose kidney problems. Tests may include:
You need all the parts of your kidney to work well, including Bowman’s capsule. If a glomerular capsule fails, that affects its ability to filter blood.
Advertisement
You can help keep Bowman’s capsule healthy by taking care of your kidneys. It’s important to have regular checkups and blood and urine tests to monitor your kidney health. This is especially true if you have high blood pressure, obesity and/or diabetes.
You can reduce your risk of developing a kidney problem by:
It’s easy to forget about your hardworking kidneys and their parts. When they work well, they filter blood without a problem. If they aren’t working right, you might start having symptoms. That’s a sign to check with your healthcare provider. They’ll work with you to find out what’s happening and what you can do about it.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
