Hip replacement surgery replaces your natural hip joint with prosthetic implants. It takes an hour or two to complete. The recovery time can take up to 12 weeks, and most people who’ve had a hip replacement live with it for the rest of their lives.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
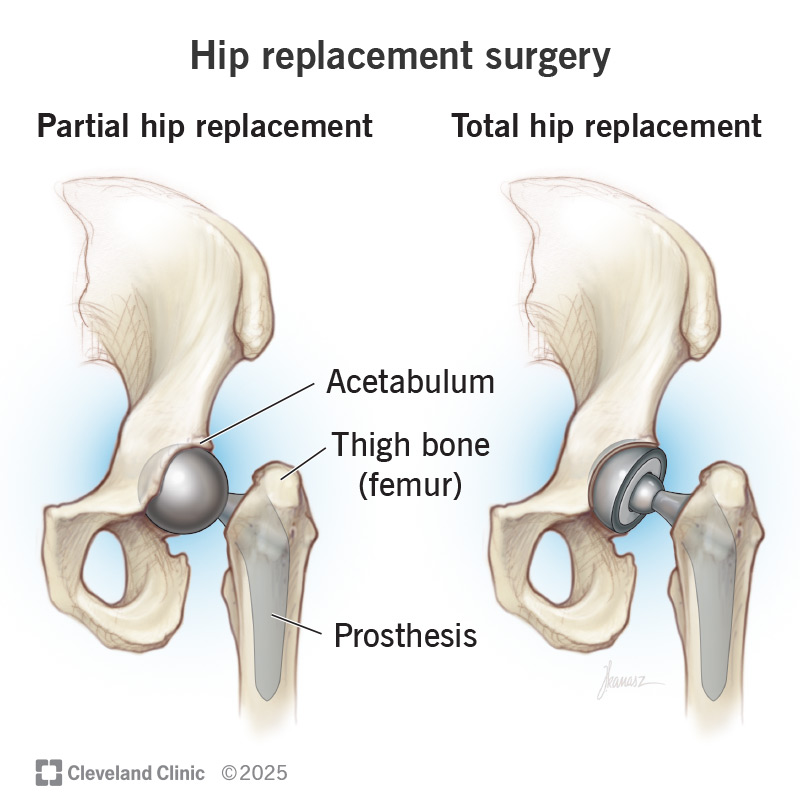
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/hip-replacement-surgery)
Hip replacement surgery is a procedure to replace your natural hip joint with an artificial implant. It’s a type of joint replacement surgery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
You may need hip replacement surgery if symptoms in your hip make it hard (or unsafe) to do all your usual activities. Severe hip pain, stiffness and loss of range of motion (how far you can move your hip) are the most common symptoms that might make you choose a hip replacement.
Any condition or injury that damages your hip can cause these symptoms. But hip arthritis is the most common one.
Your healthcare provider will probably suggest other treatments like medication, physical therapy or using a cane or walker before surgery.
An orthopedic surgeon will replace some or all of your hip joint:
Your surgeon will perform a physical exam and some tests before your hip replacement surgery. They’ll ask you about your symptoms and check your current range of motion. Tell your surgeon which medications and supplements you take.
Advertisement
Your surgeon will compare the hip that needs replacing with your other hip. They’ll have you move your hip in different directions. These motions will help them check the muscles that support your hip and leg.
You’ll probably need several tests before a hip replacement, including:
You might need other imaging tests in addition to X-rays, including:
Hip replacement surgery usually follows these steps:
Hip replacements usually take one to two hours. Your surgeon will tell you how long your surgery will take based on the type you need.
Hip replacement surgeries are usually very successful. Most people who have a hip replacement experience a dramatic decrease in their symptoms — especially pain and stiffness.
Once you’re fully recovered, you should have increased mobility. A hip replacement surgery usually makes it easier to walk, climb stairs and do other physical activities.
Like all surgeries, there are some risks to having a hip replacement. Complications are rare, but can include:
Your anesthesiologist will make sure you wake up from anesthesia correctly and don’t experience any immediate complications from your surgery.
Most hip replacements are outpatient surgeries. That means you can go home the same day. You might need to stay in the hospital overnight (outpatient extended recovery).
Your surgeon or a physical therapist will give you stretches and exercises to start as soon as 24 hours after surgery. They’ll monitor the strength and flexibility in your leg and hip. And they’ll keep an eye on your ability to stand and sit.
Ask your surgeon or physical therapist for tips on moving through your home safely after your surgery. They can show you how to:
Advertisement
It will probably take you several months to recover from a hip replacement. You’ll need physical therapy for a few months.
It might be six to 12 weeks before you’re able to use your hip with no restrictions. During that time, you’ll need to do exercises that strengthen and stretch the muscles around your hip joint. You’ll slowly return to climbing stairs, bending and walking. Over time, your range of motion and strength will come back.
People over 70 can sometimes take longer to recover. But there’s no way to know ahead of time how long your body will take to heal. Your age doesn’t necessarily mean your recovery will be faster or slower than anyone else’s.
The most important part of your recovery is how you feel. As you progress through physical therapy and your body heals, you should notice that it’s easier to move and use your hip than it was before your surgery.
Your care team will give you a list of dos and don’ts after your surgery. In general, don’t:
Everyone’s recovery is unique. These restrictions won’t be permanent. Your surgeon will tell you what you can or can’t do, and when it’s safe to drive and move in certain ways again.
Advertisement
Prosthetic hip implants used in hip replacements usually last a long time. Lots of people who have hip replacements keep the implants for the rest of their lives.
It’s rare, but you might need more surgeries on your hip in the future. Your surgeon will tell you what to expect.
Contact your surgeon right away if you notice any of the following after a hip replacement:
Having any surgery can be scary, especially when it’s to replace a part of your body with a prosthesis. But hip replacements are extremely safe, effective and successful surgeries. If you’re experiencing symptoms like pain, stiffness and trouble moving your hip, ask your provider if a hip replacement could be a good option for you.
After your surgery, you’ll need time to strengthen your muscles and heal your body. Take your recovery slow and don’t rush yourself. Talk to your surgeon or physical therapist about your movement goals and which activities you’d like to participate in after your hip replacement.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Stiff, painful joints don’t have to slow you down for good. Cleveland Clinic’s joint replacement surgery experts can help you get back to doing what you love.
