A carotid endarterectomy removes plaque (fat and cholesterol) buildup from inside your carotid artery, improving blood flow to your brain. This surgery can help prevent a stroke. You can help prevent future plaque buildup by changing what you eat and being physically active.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
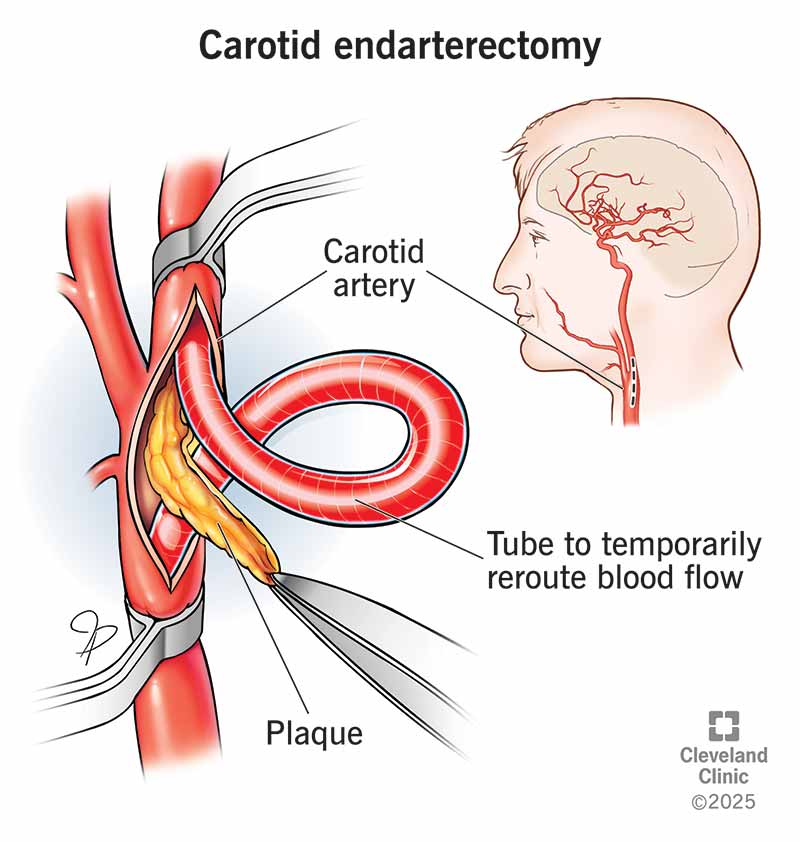
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/carotid-endarterectomy.jpg)
A carotid endarterectomy is a surgery to remove plaque (fat and cholesterol buildup) from inside your carotid artery. A carotid artery on each side of your neck supplies blood to your brain, neck and face. You may have an endarterectomy on the left or right side of your neck.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Healthcare providers remove plaque from carotid artery walls so you can get better blood flow to your brain. Plaque can slow down or stop blood flow. If enough blood can’t reach your brain, you can have a stroke.
Carotid endarterectomy is a common carotid artery disease treatment. This helps prevent a stroke, which is the fifth leading cause of death in the U.S.
If you have a stroke, it’s important to get to an emergency room for treatment within three to six hours to get the care you need.
A surgeon will evaluate you and your medical history and test results. They may recommend a carotid endarterectomy procedure if you:
Before a carotid endarterectomy, you may need to:
Advertisement
A surgeon performs this procedure in a hospital. A carotid endarterectomy normally takes about one or two hours.
A healthcare provider will give you general anesthesia (like being asleep) or local anesthesia, which means you’re awake but the area to be operated on is numbed. If you get local anesthesia, you’ll also receive medicine to help you relax.
The surgeon takes these carotid endarterectomy steps:
In a variation of this, a surgeon flips the carotid artery inside out (eversion) to remove the plaque. This may take less time and avoid the need for a patch.
A carotid artery endarterectomy can help prevent future strokes. Most people tolerate the procedure well. In a study of people over 80 who had this procedure, most were alive five years later. Most of those who didn’t live five years died from an unrelated illness.
With an experienced surgeon, there’s minimal risk. But as with any surgery, there’s a risk of complications from a carotid endarterectomy, including:
You can consider a carotid endarterectomy a major surgery because of the possibility of life-threatening complications. But the risks vary, depending on:
You’ll need to stay overnight in the hospital so your care team can monitor you after the surgery. You’ll probably be able to eat and drink several hours after surgery.
You may have a temporary drain in your neck to remove fluid from your cut (incision). This drain will usually only stay in for one day. It’s a common complication to have some neck pain for about two weeks afterward. But you can take standard, over-the-counter pain medications to relieve it.
You may need to start or resume taking aspirin, clopidogrel or other medicines to prevent blood clots.
Advertisement
Your healthcare provider will discuss the results of your procedure with you. For most people, this procedure helps prevent further brain damage and reduces the risk of stroke. But you may need to change some daily habits to prevent plaque buildup, clot formation and other problems in your carotid arteries.
Even with a successful procedure, your healthcare provider might recommend:
These steps can help keep plaque from building up again.
Carotid endarterectomy recovery is rapid. Most people go home the day after the procedure. After you get home, it’s OK to shower. Just don’t scrub the surgical glue on the cut or let the stream of water hit it.
Check your incision daily and avoid putting any lotions on it. Avoid wearing clothes that rub against your incision.
You can go back to most of your normal activities (like working) in one or two weeks. You can drive after your incision heals and it doesn’t feel uncomfortable to turn your head. Before you fully recover, the area near your jawline and earlobe may feel numb for six months to a year.
Advertisement
Your provider will want to see you one month after your carotid endarterectomy surgery. After that, you should have follow-up visits every six months for two years and then once a year. They’ll want to make sure your carotid artery doesn’t get narrow again. They’ll use ultrasound to check for this in both carotid arteries (even the one where you didn’t have a procedure).
The success rate of carotid endarterectomy is high. People usually don’t have narrowing in the same artery again.
You can expect to have a carotid endarterectomy scar about 4 inches long on your neck. It will likely be less noticeable in a few months.
Contact your healthcare provider if you have:
A carotid endarterectomy removes plaque buildup from your carotid artery. A stent (mesh tube) keeps your carotid artery open. A provider puts in a stent after an angioplasty procedure that pushes plaque against your carotid artery walls. All of these improve blood flow in your carotid artery.
Advertisement
Our brains control so much of what we do — even things we don’t have to think about. So, it’s understandable to feel frightened about blood having trouble reaching your brain. But a carotid endarterectomy can improve blood flow to your brain and help prevent a future stroke. Ask your provider questions about anything that isn’t clear. They can draw on their experience to explain more.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When the carotid arteries in your neck are blocked, you’re at risk for a stroke. Cleveland Clinic’s experts are world renowned in treating this condition.
