The Ross procedure for aortic valve repair can help you live an excellent quality of life. It replaces a nonfunctioning aortic valve with the pulmonary valve. A healthy donor valve replaces the original pulmonary valve. After recovering, many people live a healthy, active lifestyle for decades.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
This complex heart surgery is for adults and children with aortic valve disease. It is also known as a pulmonary autograft procedure and is a type of aortic valve replacement.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
It involves:
The aortic valve plays a critical role in your health. It opens to release oxygen-rich blood from your heart out to your body and prevents blood from going back into your heart between beats. Aortic valve disease, including stenosis (narrowing) and regurgitation (leaking), can affect valve function, making you feel sick. These issues raise your risk of severe complications, like heart failure and infections.
With severe heart valve disease, it’s necessary to replace the non-functioning valve. Using your own tissue maximizes long-term valve function.
People who undergo a successful Ross procedure maintain a quality of life similar to people without heart disease. There are no restrictions on physical activity. You are also far less likely to experience heart failure.
The Ross procedure involves using a healthy pulmonary valve to repair the aortic valve. This approach is uncommon but ideal because:
Advertisement
You may benefit from a Ross procedure if you are younger than 60 years old and have:
People with certain conditions are not good candidates for this procedure. These conditions include:
The Ross procedure takes many hours to complete. Here’s what happens:
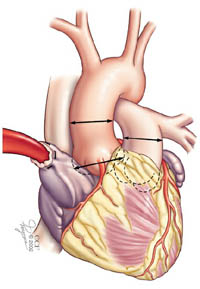
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/16744-aortic-valve-ross-procedure-1.jpg)
The Ross procedure begins with the measurement of the aortic and pulmonic valves.
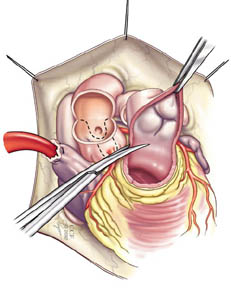
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/16744-aortic-valve-ross-procedure-2.jpg)
The next step in the Ross procedure is to open your aorta and pulmonary artery. Your surgeon carefully inspects the valves to determine if the Ross procedure is appropriate.
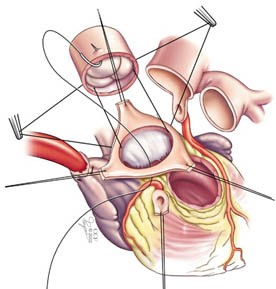
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/16744-aortic-valve-ross-procedure-3.jpg)
In the Ross procedure, your surgeon removes your diseased aortic valve. Then, they remove the pulmonary valve and move it over to the aortic position.
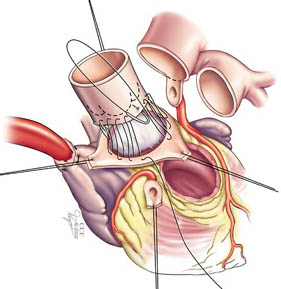
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/16744-aortic-valve-ross-procedure-4.jpg)
Next in the Ross procedure, your surgeon sutures the pulmonary valve in its new place and reattaches your coronary arteries.
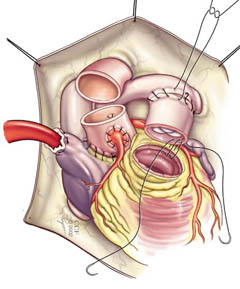
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/16744-aortic-valve-ross-procedure-5.jpg)
Your surgeon attaches a pulmonary homograft (donor tissue) to the outflow tract of your right ventricle as part of the Ross procedure.
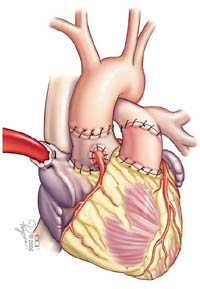
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/16744-aortic-valve-ross-procedure-6.jpg)
Finally, the surgeon performing your Ross procedure attaches your aorta to the autograft (formerly your pulmonary valve) and the pulmonary artery to the homograft (donor tissue) and your procedure is complete.
This procedure offers many benefits, such as:
Advertisement
This complex surgery has many risks. Receiving care from an experienced heart surgeon who performs a high volume of Ross procedures lowers the likelihood of complications.
Ross procedure complications may include:
After surgery, you wake up in the cardiac intensive care unit (ICU). You may need a ventilator to help you breathe. A heart monitor provides real-time assessments of heart function. You can expect to stay in the ICU for up to five days.
Your recovery continues at home and can last several months. During this time, it’s common to experience:
After a Ross procedure, you’ll need lifelong monitoring to test valve function.
A replacement pulmonary valve isn’t meant to last a lifetime and typically needs replacing within 15 to 20 years. Regular monitoring ensures you receive a timely replacement. Healthcare providers often use minimally invasive techniques for this procedure so that you can expect a quick recovery.
Advertisement
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience signs of complications, such as:
The Ross procedure offers a lifeline to people with severe aortic valve disease. It replaces the aortic valve with your pulmonary valve. A healthy donor valve replaces the pulmonary valve. After a successful procedure, many people enjoy a renewed sense of health and hardly any activity restrictions. For the best results, it’s important to receive care from an experienced heart surgeon who has performed a high volume of Ross procedures.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When you have aortic heart valve disease, you want the best care. Cleveland Clinic is number one in the nation for heart health. We’re ready to help you.
