Thumb arthritis is osteoarthritis in the basal joint at the base of your thumb. Healthcare providers may call this your thumb carpometacarpal (CMC) joint. Thumb arthritis symptoms include pain, swelling and loss of strength and motion in your thumb. Treatments include placing ice or heating pads on your thumb, medication, splints and surgery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
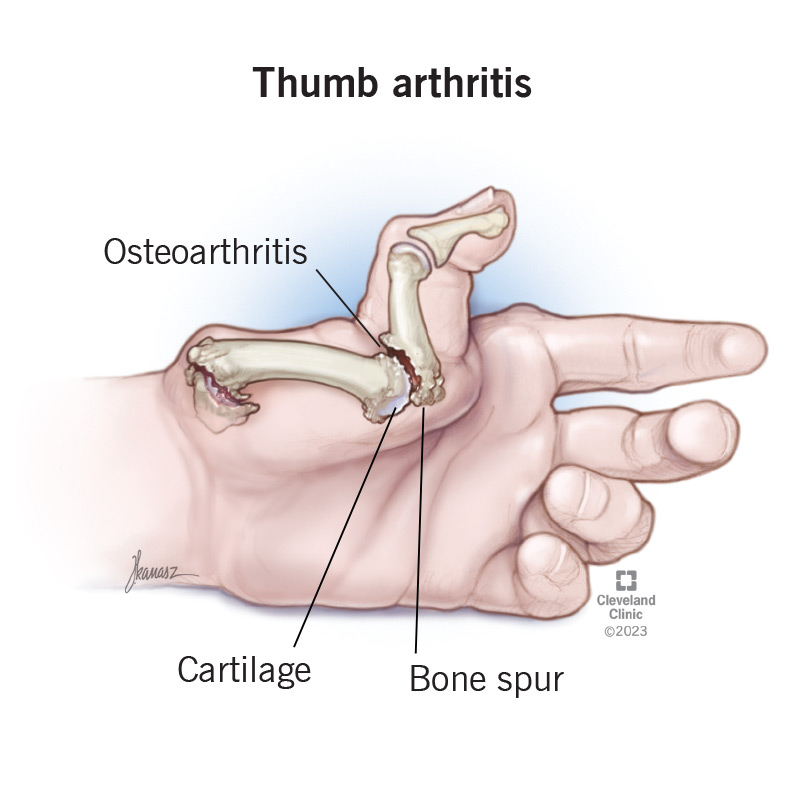
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/thumb-arthritis)
Arthritis in your thumb happens when the protective cartilage that cushions your thumb joints starts to wear out and deteriorate (osteoarthritis).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Osteoarthritis in your thumb usually develops in the carpometacarpal (CMC or basal) joint. This is the joint near your wrist at the fleshy part of your thumb. It helps your thumb move around in different directions so you can grip things in your hand. Healthcare providers may use the term CMC arthritis for arthritis in your thumb.
Thumb arthritis is the second-most common kind of arthritis that affects your hand, after arthritis in the last joint in your fingers.
CMC arthritis symptoms may include:
Arthritis in your thumb happens when the cartilage that cushions your thumb joints breaks down (degenerate). Cartilage helps your bones to glide easily in your joints. Age and use can make cartilage break down. That can cause your bones to rub against each other, which causes friction and damage.
Thumb arthritis risk factors include:
Advertisement
A healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms. They may ask if your thumb hurts all the time or if certain activities cause pain. They’ll ask if you’ve ever injured your thumb.
They’ll examine your hand and thumb. They may see what happens when you move your thumb. They do that by holding your thumb joint while moving your thumb. They may suspect thumb arthritis if:
Your provider may also request an X-ray to confirm the diagnosis.
Thumb arthritis treatment varies based on the severity of your symptoms. If you have mild symptoms, a healthcare provider may recommend at-home treatments like:
Your provider may recommend steroid injections if your symptoms are severe or get worse. They’ll inject a steroid solution into your thumb joint. This typically provides pain relief for several months. But injections become less effective over time. At that point, your provider may recommend surgery.
Options for surgery include:
Thumb arthritis is a very treatable condition. Nonsurgical treatments often ease symptoms. But surgery is an option when other treatments don’t relieve symptoms. Your healthcare provider may recommend physical therapy or occupational therapy. For example, a certified hand therapist can help you regain strength and movement in your hand and thumb.
Advertisement
We rely on our thumbs for everyday tasks — turning keys, holding books, swiping on a tablet and more. But when thumb arthritis sets in, even the simplest motions can become painful. It's more common than you think, and it can seriously affect your daily life. If you notice pain, swelling or stiffness in your thumb joint, talk to a healthcare provider. They can help you find relief and learn how to make everyday tasks easier.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Stiff, painful joints can make daily life challenging. Cleveland Clinic orthopaedic specialists can help you find relief from osteoarthritis and get you moving again.
