A male yeast infection is a fungal infection caused by a yeast called Candida. It's also known as Candida balanitis. Candida balanitis causes a red, itchy rash on the head of your penis. Candida grow and thrive in warm, moist environments such as the foreskin of uncircumcised men. Treatment typically includes an antifungal cream.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
You may think of yeast infections as something that only occurs in women. But men can get yeast infections too. A male yeast infection is a yeast infection that affects your penis. The medical term for yeast infections that affect men is Candida balanitis. Candida is a type of yeast that causes yeast infections. Balanitis is inflammation or an infection of the head of your penis (glans penis).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Your skin has many forms of yeast that live on it, including Candida. In healthy people, this ordinarily doesn’t cause any problems. But when there’s an overgrowth of Candida, it can dig below the surface of your skin. This can cause a rash or skin infection. Candida grows and thrive in moist, warm environments. It’s commonly found in damp, creased areas such the foreskin of your penis.
Candida balanitis can affect people of any age. About 1 in every 25 men will develop Candida balanitis in their lifetime. The condition will affect 1 in every 30 uncircumcised men.
Children under age 4 and uncircumcised people have the highest risk of being diagnosed with the condition. Candida balanitis is more likely to occur if you have a condition called phimosis. Phimosis means you can’t pull back (retract) your foreskin over your penis. Once children reach age 5, their foreskin usually becomes easier to retract and their risk level falls.
Male yeast infections are fairly common. About 3% to 11% of men will have a yeast infection in their lifetime.
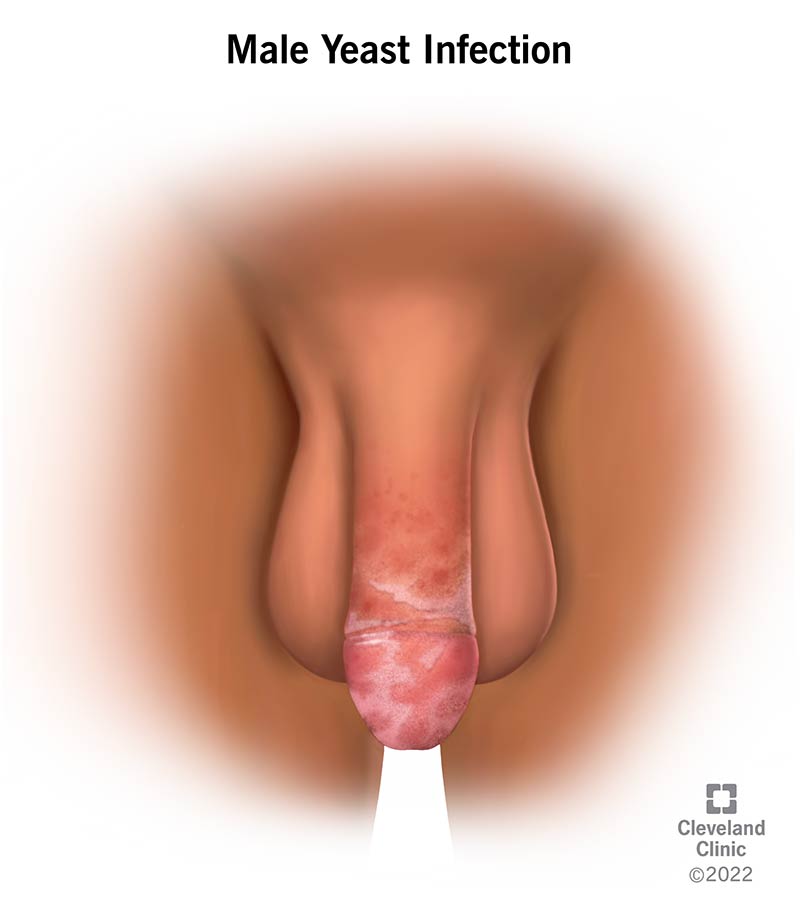
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/23199-male-yeast-infection)
Symptoms of a male yeast infection include pain, swelling and redness in your groin area. The redness is usually in patches. Other symptoms may include:
Advertisement
After having a yeast infection, you may notice your skin peeling. The infection makes your skin more vulnerable. This can make it flaky or crusty and eventually it may start peeling.
A yeast called Candida causes male yeast infections. Candida grows and thrives in warm, moist environments. Candida balanitis most commonly occurs in uncircumcised men. Other conditions and risk factors that allow Candida to grow include:
Yeast infections are more common in certain groups of people. This includes people who:
Your healthcare provider will perform a physical examination. They may be able to diagnose a yeast infection by looking at your penis and foreskin. If you have a red rash, they may be able to tell you have a yeast infection.
Your healthcare provider may want to collect a sample of the infected area for testing. They’ll use a scalpel or tongue depressor to gently scrape some of the skin from the infected area. A pathologist will examine the sample under a microscope to identify the fungus.
Treatment for male yeast infections may include an antifungal medication. Your healthcare provider may recommend an antifungal cream, lotion or ointment. You can apply the antifungal directly onto the infected area of your skin. You can buy many antifungal medications over the counter. Your healthcare provider may need to prescribe you a stronger antifungal medication if the infection doesn’t go away. Topical antifungal medications include:
In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend an antifungal medication taken by mouth. This includes medications such as fluconazole (Diflucan®). Your healthcare provider may also recommend using a steroid cream as well to help with your symptoms.
It’s important to keep your groin area clean and dry to help get rid of your yeast infection. This can also help prevent a yeast infection from returning.
Advertisement
If antifungal medications don’t help or you have frequent yeast infections, you may want to consider circumcision. In addition, if you can’t pull back your foreskin to clean it thoroughly, your healthcare provider may recommend circumcision as well.
You may be able to get rid of a yeast infection fast at home with over-the-counter antifungal medication. But if the infection persists and doesn’t go away within a couple of weeks, call your healthcare provider. You may need a prescription treatment option.
A male yeast infection may take some time to get rid of. After you start antifungal treatment, the infection should start to clear up within one to three weeks. But yeast infections aren’t easy to control. They frequently come back in uncircumcised people. If your symptoms persist, call your healthcare provider.
You may be embarrassed, but it’s important to have your yeast infection checked out by your healthcare provider. An untreated yeast infection can cause many complications which may include:
Advertisement
You can prevent a yeast infection by keeping your groin area clean and dry. Other steps you can take to prevent yeast infections include:
A yeast infection may be the last thing you want to talk to your healthcare provider about, but it’s important that you do. There are treatments available to help relieve the pain and itchiness that come with a male yeast infection. With the help of an antifungal medication such as a cream or an ointment, you should be good to go. But if not, your healthcare provider is there to help you. Reach out to your healthcare provider today to find the best option for you.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Need care fast? Cleveland Clinic’s Express Care and Urgent Care locations treat everything from sprains to sinus infections — no appointment needed.
