Scalp psoriasis is an autoimmune condition. It causes raised, discolored plaques on your scalp or on the skin around your scalp that may be dry, itchy and irritating. Prescription and over-the-counter medications can alleviate your symptoms.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
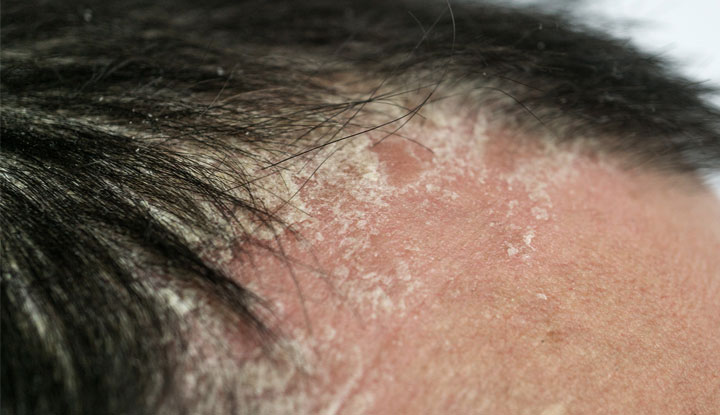
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22828-scalp-psoriasis-1127052066)
Scalp psoriasis (sore-eye-uh-sis) is a long-lasting (chronic) autoimmune disease (caused by your own immune system) that causes your skin cells to reproduce too quickly. It creates thick, discolored patches of skin (plaques) on your scalp and other areas around your scalp. These areas may include:
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Scalp psoriasis can affect anyone. But you may be more likely to have scalp psoriasis if you:
Psoriasis affects about 7.5 million people in the United States. About half of those have scalp psoriasis at any given time; though most people with psoriasis have at least one flare of scalp psoriasis, and 80% to 90% of people with psoriasis have plaque psoriasis.
Scalp psoriasis causes thick, rough, scaly, dry, discolored plaques to develop on your scalp and the skin around your scalp. The plaques can be itchy or painful. Scalp psoriasis can cause hair loss (alopecia), and scratching your plaques may worsen that hair loss.
Scalp psoriasis can make you worry about how others look at you. It can also affect your behavior and how you think about yourself. You may become self-conscious or experience stress, anxiety and depression.
Symptoms of scalp psoriasis vary.
Mild scalp psoriasis symptoms may involve only small, thin scales or flaking that looks like dandruff.
Moderate or severe scalp psoriasis symptoms include:
Advertisement
Scalp psoriasis is an immune system disease. Your immune system overreacts, causing inflammation, which leads to new skin cells growing too fast.
Typically, new skin cells grow every 28 to 30 days. But in people with scalp psoriasis, new skin cells grow and move to the skin surface every three to four days. The buildup of new cells replacing old cells creates thick patches of skin.
Scalp psoriasis can runs in families, but the actual triggers are complex. Parents may pass it down to their children, and environmental exposures can include skin trauma, sunburn, medications, stress and other inflammatory or autoimmune health conditions.
No, scalp psoriasis isn’t contagious. You can’t spread scalp psoriasis to another person through skin-to-skin contact.
Your healthcare provider will examine your scalp and the remainder of your skin to look for signs of psoriasis. They’ll also ask about your symptoms, your family history and if you’ve recently started or stopped using a medication or hair product just before your flare-up.
Your healthcare provider may perform several tests to rule out other conditions that could cause your symptoms, such as scalp fungal infection, eczema or seborrheic dermatitis (dandruff). The tests may include:
There isn’t a cure for scalp psoriasis. You may have flare-ups and times where the plaques go away (remission). Treatment can provide relief for your symptoms and can include UV light or medications that can be directly applied to the lesions, injected into the lesions or taken by mouth.
Certain foods or drinks may contribute to scalp psoriasis flare-ups. If you have scalp psoriasis, it’s a good idea to keep track of what you eat and drink in a food journal. Keeping track of what you eat and drink can help you and your healthcare provider determine any causes of your flare-ups.
An anti-inflammatory diet may limit your scalp psoriasis flare-ups. Foods that have anti-inflammatory properties include:
Foods and drinks that may cause flare-ups include:
Advertisement
Your healthcare provider may prescribe the following as a cream, lotion or gel to treat mild cases of scalp psoriasis:
In more severe or widespread cases of scalp psoriasis, your healthcare provider may prescribe:
Treating scalp psoriasis may be difficult. Your body is unique, and it might not respond to certain treatments. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best treatment for you.
While home remedies are safe for most people, it’s a good idea to check with your healthcare provider before trying some of the following options. You may be at risk of developing an allergic reaction.
Advertisement
Advertisement
It may take up to eight weeks or longer for your symptoms to start going away. It’s important to use any medications or treatments as directed by your healthcare provider, even if your plaques go away.
Scalp psoriasis may flare up and go into remission throughout your life. However, it can be generally well managed with treatment.
If you have scalp psoriasis, it may come and go throughout your life and there isn’t any way to completely prevent it. Following a healthy anti-inflammatory lifestyle can help make it less severe or less frequent, though. Treatments can reduce symptoms, even in people with severe scalp psoriasis.
If you have scalp psoriasis, the best way to take care of yourself is to:
Contact your healthcare provider if:
Dandruff is a skin condition that affects your scalp. It’s itchy, white or yellow flakes on your scalp. Medical researchers aren’t sure of the exact cause of dandruff, but they think factors may include:
Scalp psoriasis is an autoimmune disease.
Scalp eczema and scalp psoriasis can look very similar. They’re both inflammatory skin conditions. Scalp psoriasis typically has well-defined plaques, while scalp eczema is much itchier, even before you see the rash.
Your healthcare provider can tell the difference between scalp eczema and scalp psoriasis during an examination.
Scalp psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that causes thick patches of skin to develop on your scalp or the skin around your scalp. You may feel self-conscious, and it can be unpleasant if it’s itchy or painful. However, it isn’t contagious, and treatments can help your symptoms improve. It’s important to pay attention to your skin, including your scalp. Contact your healthcare provider as soon as you notice any plaques developing on your scalp.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Coping with psoriasis can be frustrating and distressing. Cleveland Clinic experts offer personalized treatment to help you manage this chronic condition.
