Mouth breathing is when you constantly breathe through your mouth. You may do this when air can’t get in through your nose. Mouth breathing in children can change the shape of their face and affect their behavior. Treatment is medication or surgery to solve the issue that keeps you from breathing through your nose.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
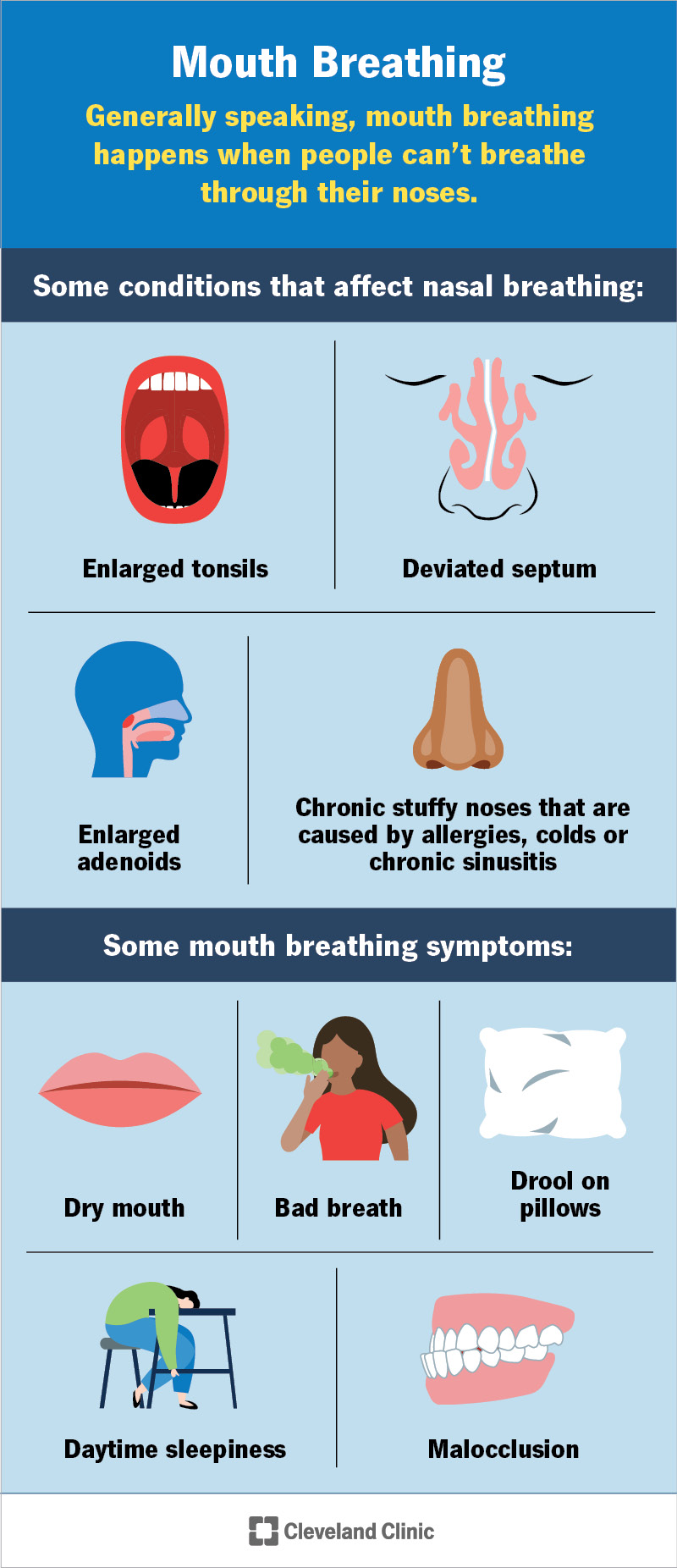
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/22734-mouth-breathing)
Mouth breathing — when you frequently take in air through your mouth instead of your nose — may make sense when you’re racing to catch a bus. But mouth breathing can be an issue when it’s the only way that you breathe. Mouth breathing in adults isn’t a serious health issue. But mouth breathing in children can affect their growth and behavior. It may even change the shape of their faces.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Mouth breathing affects children and grownups alike. Common symptoms include:
Mouth breathing in children may cause other symptoms, including:
Most people have mouth breathing because they can’t get air in through their nose. Conditions that may keep air from flowing through your nose include:
Advertisement
A healthcare provider will do a physical exam. They’ll look inside your nose and throat. They may do tests like:
A healthcare provider will treat the condition that makes it hard for you to breathe through your nose. They may recommend or prescribe the following treatments:
They may recommend you or your child have surgery, including:
Talk to a healthcare provider if you have mouth breathing symptoms like bad breath or drool on your pillow. Ask your child’s pediatrician to check your child’s nose and airway if you notice your child often breathes through their mouth or they have symptoms of mouth breathing.
Mouth breathing in children can become a harmful habit. You can help prevent that by:
Advertisement
Talk to a healthcare provider if you notice you’re breathing through your mouth more than your nose or think you’re mouth breathing while you sleep. (Your first clue may be the icky combination of a dry mouth, bad breath and drool on your pillow.) They’ll find out why you can’t get air in through your nose.
Mouth breathing may be why you wake up with a dry mouth and drool on your pillow. But a soggy pillow and parched pucker may be just some of the issues that mouth breathing may cause. It can also affect your sleep and make for serious morning breath. Mouth breathing in your child can change the shape of their face or lead to behavioral issues. Fortunately, healthcare providers can treat mouth breathing by diagnosing the condition that causes it.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
