Birthmarks are marks on your skin that are present at birth or shortly after. They cosmetically change the appearance of your skin. Some birthmarks fade over time and others stay with you. In rare cases, changes to a birthmark can be a sign of skin cancer. Talk to a provider if you notice changes to your skin.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A birthmark is a spot or patch on your skin that looks different from the skin around it. Birthmarks are very common and come in many different shapes and sizes. Most birthmarks are present at birth, which is where they get their name. Some birthmarks fade as you age while others will be with you for your entire life, unless you choose to remove them.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Birthmarks are mostly harmless and painless. Some birthmarks can increase your risk of developing skin cancer, like certain types of moles (congenital nevi). If you notice changes to your birthmarks, contact a healthcare provider.
There are two main categories of birthmarks — vascular birthmarks and pigmented birthmarks:
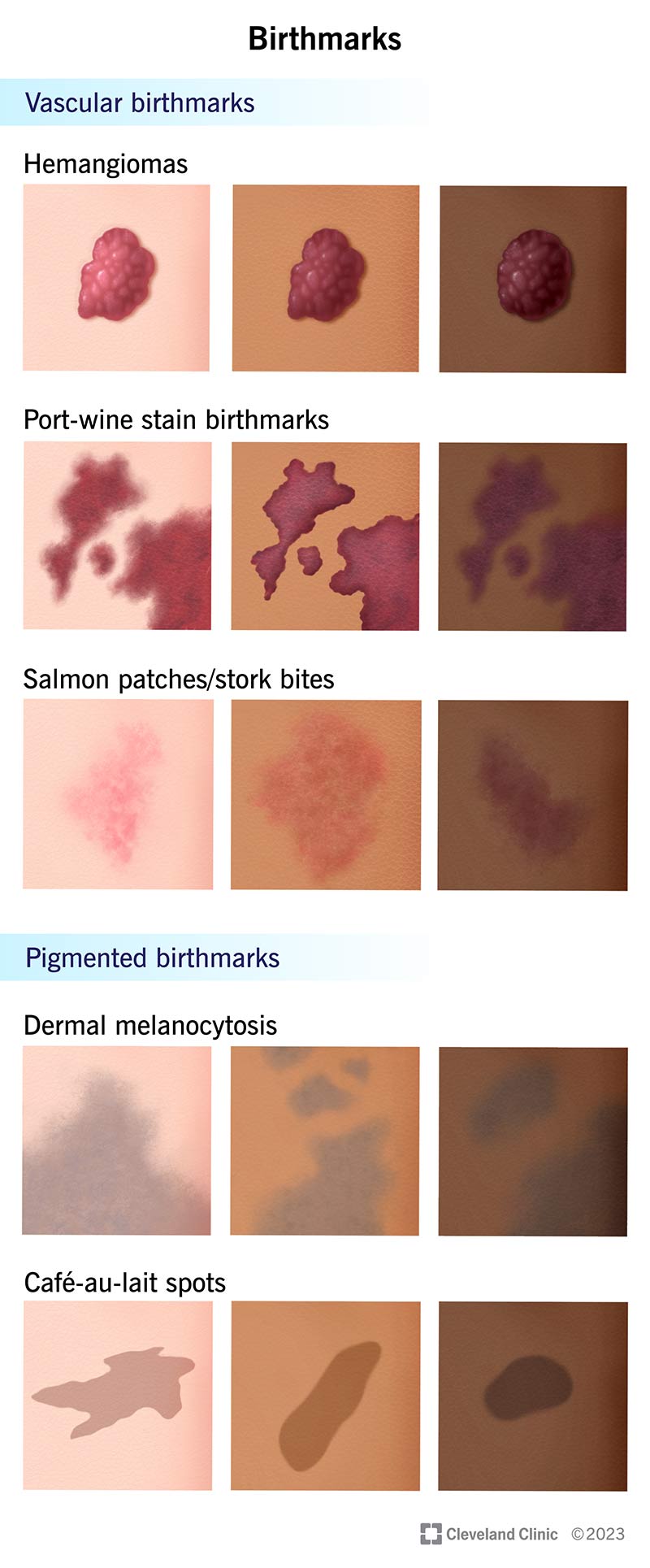
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/12159-birthmarks.jpg)
A birthmark is a mark on your skin that looks different from the skin around it. Birthmarks come in many different shapes and sizes.
Types of vascular birthmarks include:
Advertisement
Types of pigmented birthmarks include:
Birthmarks are very common but not everyone has one. An estimated 10% of all babies born around the world have a specific birthmark called a hemangioma.
Birthmarks look different on each person and vary in size, shape and color. Features of a birthmark include:
Pigmented birthmarks might increase in size as you age and change colors, especially after sun exposure and during times of hormone changes. They can become itchy and might occasionally bleed when injured.
The exact cause of why birthmarks develop is unknown. In some cases, birthmarks form because:
Complications of pigmented birthmarks can include psychological effects when the birthmark is located in a prominent area of your body, like on your face. This can affect your self-esteem and how you feel about your appearance.
Advertisement
Pigmented birthmarks also can pose an increased risk of skin cancer. A healthcare provider should check any changes that occur in the color, size or texture of a mole. See a provider right away if you have any pain, bleeding, itching or swelling of a birthmark.
A healthcare provider can diagnose a birthmark after a physical exam to get a closer look at the mark on your skin. If your birthmark is deep within your skin, a provider can confirm it with an imaging test like an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), ultrasound or CT (computed tomography) scan. A skin biopsy might be necessary if you have a birthmark that changes in size or shape and may be a sign of skin cancer.
If you don’t like how a birthmark looks on your skin, you can talk to a healthcare provider about removing it. You shouldn’t attempt to remove a birthmark at home. A healthcare provider will recommend the removal of certain birthmarks if you’re at a higher risk of developing skin cancer.
Treatment to remove a birthmark may include:
A healthcare provider can review your birthmark and let you know what your best treatment options would be. Providers usually treat childhood birthmarks after a child reaches 6 years old. They might treat them earlier if they affect the function of your child’s organs, like their vision or breathing.
Advertisement
You may be at risk of scarring if you have a birthmark surgically removed. Surgeons take extra precautions during procedures to reduce your risk of scarring. You may also be at risk of developing an infection after a removal procedure. To avoid these risks, talk to your surgeon or provider about how you can take care of your skin as it heals after treatment.
Birthmarks are usually harmless and are only cosmetic. Sometimes they complement your appearance and are called beauty marks. In most cases, you don’t need to treat birthmarks. Salmon patches and strawberry hemangiomas will fade over time. Other types of birthmarks will stay with you throughout your life unless you choose to remove them.
Sometimes, large birthmarks can affect your self-esteem, especially if they’re located in a prominent place on your body. If you feel uncomfortable in your own skin, you can:
There’s no way to prevent the development of birthmarks. You can reduce your risk of birthmarks changing color or developing into skin cancer from sunlight exposure by protecting your skin from the sun’s ultraviolet rays. Wear sunscreen and protective clothing when you’re outside to reduce your risk. You can also avoid sun exposure during the daytime when the sun is at its brightest, between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
Advertisement
Visit a healthcare provider if you have changes to your existing birthmarks or develop new marks on your skin. Some changes to look out for include:
Questions you may want to ask your healthcare provider include:
Birthmarks are harmless markings on your skin. They’re not caused by something a parent did or didn’t do during pregnancy. Rather, they’re natural additions to your appearance and may or may not be noticeable. If you don’t like how your birthmark looks on your skin, you can talk to a healthcare provider about removing it. Some birthmarks change over time and some can develop into skin cancer, in rare cases. If you notice changes to your birthmarks, contact a healthcare provider.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
As your child grows, you need healthcare providers by your side to guide you through each step. Cleveland Clinic Children’s is there with care you can trust.
