The limbic system is a group of structures in your brain that regulate your emotions, behavior, motivation and memory. While small in size, your limbic system has a big job to help you interact with the world around you.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
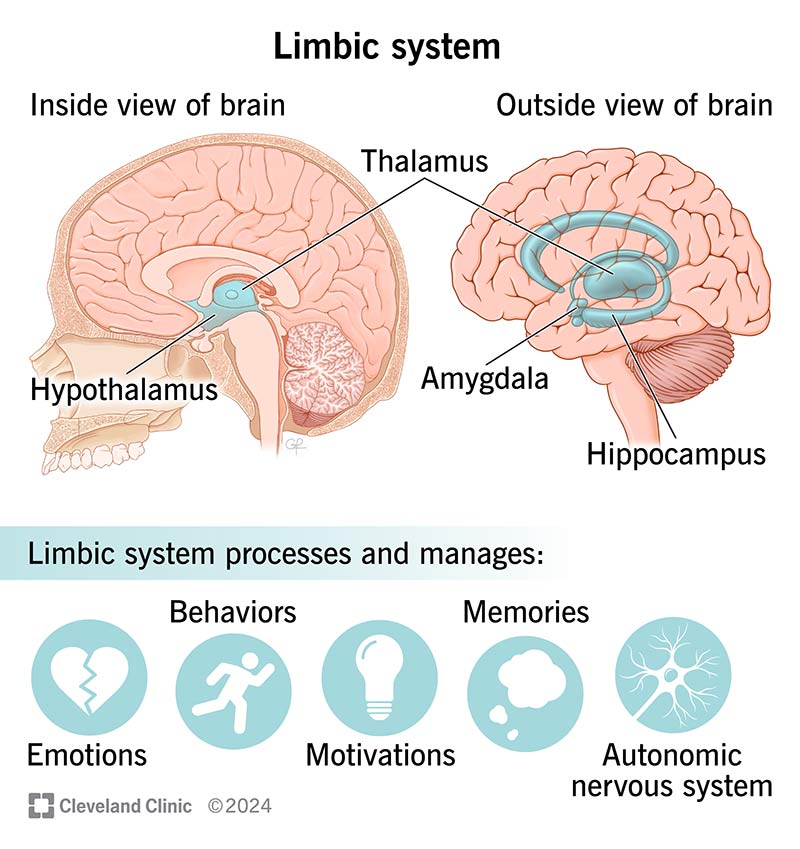
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/limbic-system)
The limbic system is a group of interconnected brain structures that help regulate your emotions and behavior. The structures (also known as components or parts) of the limbic system work together with other brain regions by processing your memory, thoughts and motivations, then tell your body how to respond.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The limbic system is one of the oldest structures of your brain. It produces natural instincts that your ancestors used to survive by triggering behaviors needed to:
There are many components to your limbic system that give it a lot of responsibilities. For example, it helps manage your memories and helps you learn from them. It also helps keep you stimulated and motivated.
The connection between your physical and emotional well-being is why the limbic system is also known as your emotional nervous system.
For example, the limbic system is involved when you need to eat. You’ll recognize your limbic system in action when you feel pleasure while eat certain foods. The limbic system is also responsible for increasing your blood pressure when you feel emotional stress.
Higher mental function occurs when multiple components of your brain work together to help you complete a task. You use higher mental functioning when you speak, remember, control your emotions, plan or make decisions, for example. The components of your limbic system work together with other brain regions so you can attain higher mental functioning every day.
Advertisement
The main functions of the limbic system include processing and managing your:
The limbic system helps control your emotions and behaviors. It manages your actions based on what it learns from your environment. It takes in information, processes it, learns from it and reacts. It can help you regulate:
The limbic system is located deep within your brain. It contains several parts (structures or components) that take the shape of a closed fist in the middle of your forebrain (the largest region of your brain).
The word “limbic” comes from the Latin word “limbus,” which means “border.” When referencing the limbic system, this refers to the location of the components that sit on the border above your brainstem and underneath your cerebral cortex (the outer layer on the top of your brain).
There are four main structures of the limbic system:
Your sense of smell comes from your olfactory bulb, which isn’t part of your limbic system. Many of your other senses are processed through signals to your limbic system so your body can react to them. Your sense of smell causes you to recall memories and certain emotions related to the smell, which directly contributes to the function of your limbic system.
Almost all mental health conditions and conditions that affect your memory involve your limbic system. Common conditions that affect your limbic system include, but aren’t limited to, the following:
The following symptoms may happen as a result of a condition affecting part of your limbic system:
Depending on what symptoms you experience, a healthcare provider may offer the following to confirm a diagnosis:
Treatment varies based on your diagnosis but could include:
Advertisement
Your limbic system connects your physical and emotional health. To keep your limbic system in top shape, you can:
Some researchers identify additional components within the limbic system beyond the four main structures, which may include the:
Advertisement
There’s disagreement in the science community as to whether these components fit within the limbic system based on its current definition.
There’s also conflict in whether the term “limbic system” accurately describes this area’s complete function. Many providers are phasing this word out and prefer to use the individual names of each part of the brain involved.
The limbic system plays an important role in your body. It has a lot of responsibilities that revolve around the link between your emotions, memory and behavior. Researchers are still learning about the details of the limbic system and how it functions within your brain. If you have any questions about these components and how to maintain their health, talk to a healthcare provider to learn more.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have a neurological condition, you want expert advice. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll work to create a treatment plan that’s right for you.
