A vaginal ring is a small, flexible ring worn inside your vagina for birth control. It releases the hormones estrogen and progestin through your vaginal lining to prevent pregnancy. It’s worn for three weeks and then removed for one week.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
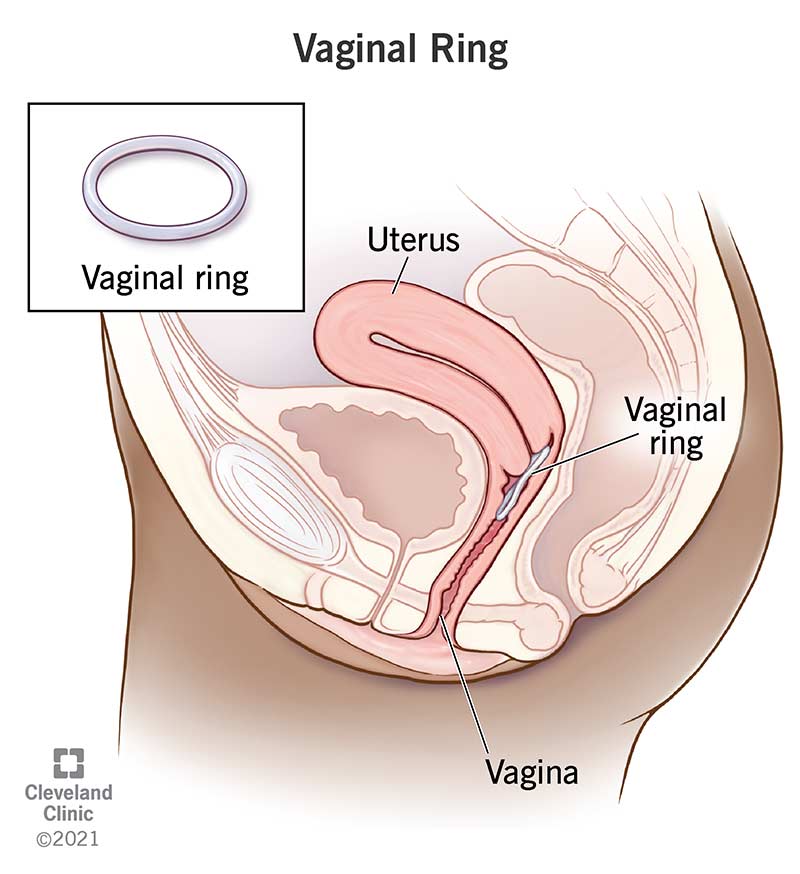
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/24157-vaginal-ring)
A vaginal ring, or birth control ring, is a hormonal birth control method to prevent pregnancy. It’s a small, flexible ring that’s worn inside your vagina. The ring releases estrogen and progestin into your body through your vaginal lining. These two hormones work together to prevent pregnancy by:
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A vaginal ring is worn for three weeks, then removed for one week to allow bleeding to occur. When used properly, it’s a highly effective form of birth control.
There are three vaginal rings approved for use as hormonal contraceptives in the United States. You’ll need a prescription from a healthcare provider to use these products:
A birth control ring works by slowly releasing estrogen and progestin into your body. You wear the ring inside your vagina and absorb the hormones through your vaginal lining. Estrogen prevents ovulation, which means you don’t release an egg for sperm to fertilize. Progestin thickens the mucus around your cervix which makes it harder for sperm to get inside. It also thins the lining of your uterus, so a fertilized egg can’t implant itself.
You will place the ring in your vagina for 21 days (three weeks and then take it out for one week). Once the week is over (seven days), you insert a new vaginal ring and a new cycle begins.
Advertisement
A healthcare provider must prescribe a vaginal ring.
Using a vaginal ring can carry some health risks. You should avoid using the ring if you:
Share your medical history with your healthcare provider so they can determine if the birth control ring is safe for you.
The birth control ring is one of the most effective forms of contraception when used correctly. A lot of people choose to use a vaginal ring for birth control because it’s easy to use and effective. Unlike a daily birth control pill, you don’t have to remember to take it. There are many forms of birth control available. Talk with your healthcare provider about what method will work best for you.
There are two hormonal vaginal rings approved for use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Both vaginal rings work by releasing estrogen and progestin into your vagina. They’re both worn for 21 days (or three weeks), then removed for seven days (one week). There are a few distinct differences between the two vaginal rings:
Speak with your healthcare provider before getting started to make sure you understand how and when to insert and remove your vaginal ring. Hormonal birth control rings will only be effective if they’re worn properly.
Advertisement
Before getting a prescription for a vaginal ring, your healthcare provider will most likely conduct a medical evaluation and pelvic exam. You’ll discuss your medical history and any concerns you have about the vaginal ring and make sure you know how to insert and remove the ring.
If you can insert a tampon, you shouldn’t have a problem inserting a vaginal ring. Follow these steps for inserting a vaginal ring:
You’ll leave a vaginal ring in for three weeks (21 days). After three weeks, remove the ring for one week (seven days). If you decide you want to become pregnant, it’s easy to stop using the vaginal ring to try and conceive.
You’ll remove the vaginal ring by inserting a clean finger into your vagina (usually your index finger). Once you find the ring, hook your finger through it and then gently pull it out.
Most people have mild side effects that go away after a few months of use. The most common side effects are:
Advertisement
If you use a vaginal ring, you might be at increased risk for the following problems:
A lot of people choose to get a vaginal ring because it offers benefits over oral pills or other hormonal forms of birth control. Some of the greatest advantages of a vaginal ring are:
Like most medications, the vaginal ring can have side effects. It also doesn’t protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and can be ineffective if not used correctly.
No, you can’t leave a vaginal ring in as long as you want. Vaginal rings are prescribed to be worn for three weeks and removed for one week. The NuvaRing and EluRyng deliver enough hormones to last five weeks. The Annovera ring has enough hormones to last an entire year. This gives people the false idea that they can delay menstruation. Speak with your healthcare provider before skipping your period or deciding not to use the vaginal ring as directed.
Advertisement
Vaginal rings are 91% to 99% effective. The effectiveness can be reduced if you don’t use it the correct way.
The amount of time it takes for the vaginal ring to begin preventing pregnancy depends on if you were previously on birth control.
If you haven’t been using hormonal birth control and start using a vaginal ring:
If you’re switching to a vaginal ring from birth control pills or a patch:
If you’re switching from progestin-only birth control, including a minipill, implant, injection or intrauterine device (IUD):
Several factors can make the vaginal ring less effective:
Follow the instructions you are given with your prescription to make sure you are using the vaginal ring correctly.
Your vaginal ring may fall out of your vagina on its own. Having sex, taking out a tampon or straining to have a bowel movement are common reasons a vaginal ring slips out. You should rinse it off with lukewarm water and reinsert it as soon as you can.
If the ring is out for more than two hours (Annovera) or three hours (NuvaRing and EluRyng) between days seven to 14 of your cycle:
If the ring is out for more than two hours (Annovera) or three hours (NuvaRing and EluRyng) between days 15 and 21 of your cycle, there are two options:
Your vaginal ring should feel comfortable inside of your vagina — you should eventually forget it’s there. If it feels uncomfortable to you, try pushing it up higher into your vagina. If you experience too many side effects from a vaginal ring, it might mean that it isn’t the right birth control method for you.
Using a vaginal ring shouldn’t impact any plans you have for pregnancy. You should begin ovulating regularly after removing the ring. It takes some people a few months to have a normal cycle because their bodies are still adjusting. Speak with your healthcare provider if you don’t get your period within three months.
There are risks and side effects of using a vaginal ring. You should contact your healthcare provider right away if you have:
There are three birth control rings approved for use in the U.S. They all contain similar hormones and are worn inside the vagina for three weeks, then removed for one week. The Annovera ring is washed and reused for one year. The NuvaRing and EluRyng are one-time use (you will throw it away and open a new one each cycle).
Your partner may be able to feel your vaginal ring, but not always. If your partner has a negative reaction to your vaginal ring, speak with your healthcare provider about other birth control options. If you remove your ring for sexual intercourse, it needs to be put back in within two (Annovera) or three (NuvaRing and EluRyng) hours or it loses its effectiveness.
The method of birth control you use is a decision between you and your healthcare provider. All forms of birth control are only effective if used correctly. Both methods can follow a cycle of three weeks of hormones and one week of menstruation. Birth control pills can be hard to take at the same time each day. Some people feel more comfortable taking oral birth control instead of having something inside their vaginas.
An IUD (intrauterine device) is a T-shaped device worn in your uterus. Some of the biggest differences between an IUD and a vaginal ring are:
No, a vaginal ring doesn’t protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). A condom offers the best protection from most STIs.
Yes, you can take your vaginal ring out for sex. The ring is still effective for up to three hours (NuvaRing and EluRyng) or two hours (Annovera) if left outside your vagina. Be sure to set it down in a safe spot and rinse it off with lukewarm water before putting it back in.
Vaginal rings are an effective form of birth control when you use them correctly. Speak with your healthcare provider about using a vaginal ring to prevent pregnancy. Share any concerns you have about inserting or removing the ring. They can make sure you understand how to use it as well as the side effects to watch for.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Your birth control needs to work for you. At Cleveland Clinic, we help you find the right birth control option to fit your goals and lifestyle.
