Knee replacement surgery (knee arthroplasty) is surgery to replace all or some of your knee joint. Your surgeon will replace damaged cartilage and bone with prosthetic implants. It can take up to a year to recover fully after a knee replacement, but you’ll be able to resume some of your usual activities gradually as you heal.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
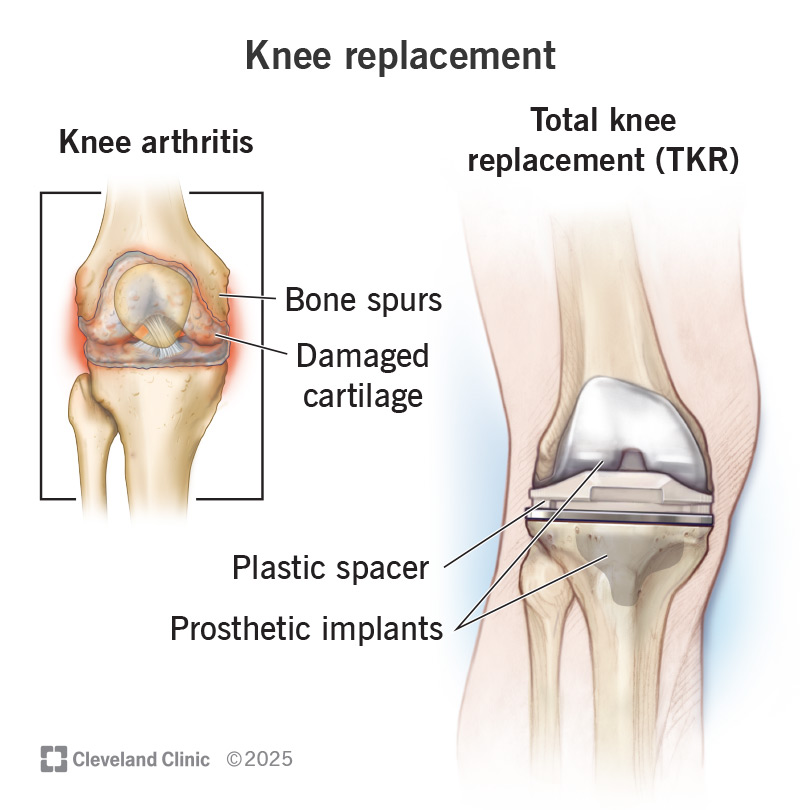
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/knee-replacement)
A knee replacement is surgery to replace all or some of your knee joint. It’s a type of procedure called an arthroplasty (joint replacement).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
An orthopedic surgeon will remove damaged parts of your natural knee joint and replace them with an artificial joint (a prosthesis) made of metal and plastic.
A healthcare provider might recommend knee replacement if you have severe symptoms that make it hard to move or use your knee. Knee pain, stiffness and swelling that don’t get better after trying other treatments can all be signs a knee replacement may be right for you.
Knee arthritis is the most common condition that causes people to need knee replacement surgery. It's rare, but your provider might suggest a knee replacement if you develop post-traumatic arthritis after breaking a bone in your knee joint.
Your surgeon will recommend either a total or partial knee replacement:
Advertisement
Video content: This video is available to watch online.
View video online (https://cdnapisec.kaltura.com/p/2207941/sp/220794100/playManifest/entryId/1_93poszpq/flavorId/1_5f3sgelj/format/url/protocol/https/a.mp4)
Learn what happens during a total knee replacement from Michael Erossy, MD.
Your surgeon will tell you what you’ll need to do before surgery. In general, you’ll need:
Tell your provider and surgeon which medications and over-the-counter supplements you take. You may have to stop taking some medications or supplements before your surgery.
Your surgeon will tell you when you should stop eating and drinking (fast) the day before your surgery. You’ll probably need to fast for 12 hours before the surgery.
No matter which type of knee arthroplasty you need, the surgery will follow these steps:
Knee replacements usually take an hour or two. It depends on the type of arthroplasty you need and how damaged your natural knee joint is.
Your surgeon can give you an estimate of how long the surgery will take while you’re doing your surgery prep.
Knee arthroplasty is a safe, effective procedure that can relieve long-term pain and help you regain your mobility. Most people who have a knee replacement have reduced pain, increased ability to move and use their knee, and an improved quality of life. If you’ve been avoiding certain activities you used to love, you may be able to get back to them once your knee heals.
Like all surgeries, there’s a small risk of complications after a knee replacement. Complications are rare, but can include:
After surgery, you’ll be moved to a recovery room. Your surgery team will keep an eye on you for a few hours to make sure you wake up from the anesthesia without complications. They’ll also monitor your vital signs and pain level.
Advertisement
Some people who have knee replacement surgery go home the same day. You might need to stay in the hospital overnight. Your surgeon will tell you when it’s safe for you to go home.
It usually takes around a year to recover fully after a knee replacement. But you should be able to resume most of your usual activities in six weeks.
Your recovery time will depend on several factors, including your:
Your surgeon will give you a customized recovery plan, but in general, you should:
Advertisement
Your recovery will be easier and safer if you prepare your home ahead of time, including:
After surgery, you’ll feel pain, especially in the first few weeks of your recovery. You’ll feel pain from the surgery itself and as your body begins to heal.
Your surgeon will suggest a combination of prescription pain medication, over-the-counter NSAIDs (if it’s safe for you to take them) and acetaminophen. They’ll tell you how much of each medication you can take every day or in a certain amount of time.
Talk to your surgeon if you feel like you’re experiencing too much pain or if you’re worried about any complications from taking pain medication.
A knee replacement usually lasts a long time. In fact, almost everyone who has a knee replacement has improved knee function for at least 10 to 15 years. You may live with the prosthetic implants for the rest of your life.
Call your surgeon or healthcare provider right away if you experience any of the following symptoms:
Advertisement
Choosing to have knee replacement surgery is a big decision, and it’s completely normal to feel anxious and have lots of questions. Talk to your healthcare provider and surgeon about anything that’s on your mind before or after your surgery.
Recovering from a knee replacement is hard work and can take months, but it’s worth it. Most people who have a knee arthroplasty have significantly less day-to-day pain and are able to move better than they could before the surgery. Ask your surgeon what to expect during your recovery and when it’s safe to return to your usual routine.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Constant knee pain isn’t fun — or comfortable. At Cleveland Clinic, we do total knee replacement surgery every day to help people move better and enjoy life again.
