Cervical disk replacement (CDR) surgery may be an option for you if you have degenerative disk disease in your neck. It involves replacing the damaged disk with an artificial one. CDR surgery can help maintain the range of motion in your neck and relieve nerve pain. As with all surgeries, it comes with possible risks and complications.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
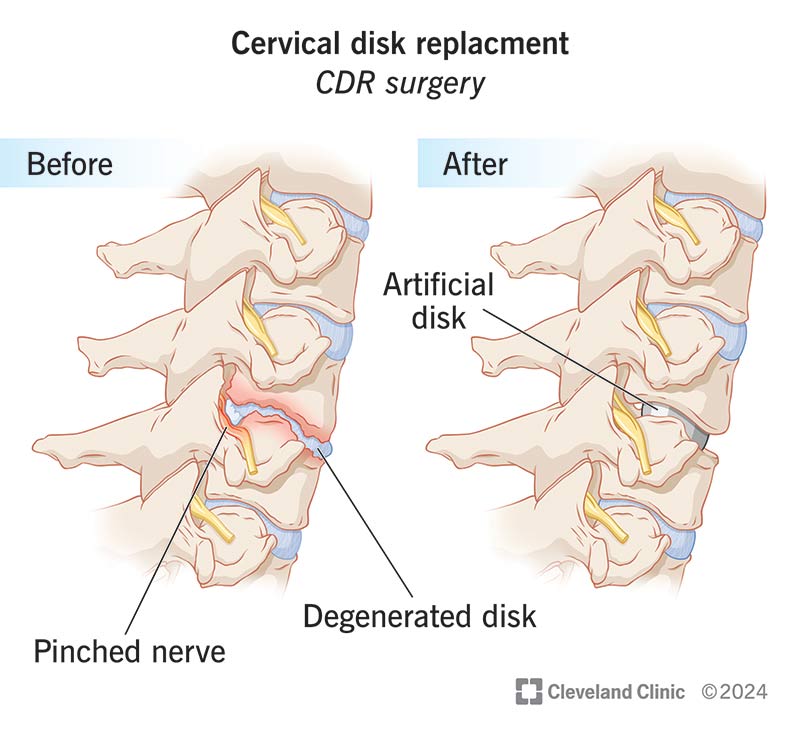
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/cervical-artificial-disk-replacement)
Cervical disk replacement (CDR) surgery involves replacing a damaged spinal disk in your neck (cervical spine) with an artificial (prosthetic) disk.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Spinal disks are rubbery cushions between your vertebrae (bones in your spinal column). They act as shock absorbers and help you move, bend and twist comfortably. The goal of CDR surgery is to restore the height of a worn down (degenerated), collapsed disk space. This maintains the range of motion in your neck and may decompress nerve roots, which may help relieve pain.
There are several types of artificial cervical disks. The three main material types for them are cobalt, titanium and stainless steel.
You may have a lot of questions and concerns about needing neck surgery. While CDR is a newer type of surgery compared to other cervical spine procedures, several studies have shown that it’s effective and safe. Your surgeon will walk you through the process of CDR surgery and what you can expect.
Cervical disk replacement surgery is mainly for people who have cervical degenerative disk disease with pinched nerves (radiculopathy) or myelopathy. Your provider may recommend CDR surgery if conservative (nonsurgical) treatment hasn’t worked to manage your symptoms for at least six weeks.
Certain factors may disqualify you from being a good candidate for this surgery, like having:
Advertisement
Together, you and your healthcare provider will decide if cervical disk replacement surgery is right for you. Providers most often compare CDR surgery to anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) because they can treat many of the same issues. Your provider may compare and contrast CDR and ACDF when discussing your options.
You'll meet with your surgeon (either an orthopaedic surgeon or neurosurgeon) before your cervical disk replacement surgery. You can expect your surgeon to:
Let your healthcare provider know if you use tobacco products. Nicotine in tobacco products can interfere with your healing. Your provider may ask you to quit using these products at least four weeks before your surgery.
Your surgeon will also explain any risks or side effects and give you information about how you can prepare. If you have any questions or concerns, make sure to ask your surgeon before the date of your surgery.
Your surgeon will go over the steps of CDR before the surgery. In general, the steps include:
After CDR surgery, your care team will move you to a recovery room where they’ll monitor your vital signs as you wake up from anesthesia. You may need to stay overnight in the hospital. Your healthcare provider will let you know when it’s safe for you to go home. You’ll need someone else to drive you home after surgery.
Your surgeon will give you instructions to help your body heal. This may include:
Advertisement
Several studies show that cervical disk replacement surgery provides significant short-term and long-term pain relief for many people. It can also help maintain the range of motion in your neck.
The majority of people who have cervical disk replacement surgery get symptomatic relief and can resume full activity after six months. But as with any treatment, it’s not guaranteed to relieve your symptoms.
Short-term complications of cervical disk replacement surgery are rare but can include:
Possible long-term complications of CDR include:
Your healthcare provider will go over all the possible risks and complications of CDR before your surgery.
It may take up to six months to fully recover from CDR surgery. Your surgeon will give you a timeline of certain activities you can build up to over time after surgery. In general, most people can:
Advertisement
Be sure to ask your surgeon for a complete list of activity restrictions.
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience the following after cervical disk replacement surgery:
You’ll need to have follow-up appointments with your provider after surgery to make sure you’re healing well and that the artificial disk is functioning as it should. Your provider will let you know how many appointments this will be and when to schedule them.
Having surgery can be scary, especially a major surgery like cervical disk replacement (CDR). But know that this surgery is often effective and safe. Talk to your care team if you have any questions about the surgery or your recovery. Following your provider’s instructions can help you get back to the activities you enjoy without pain or complications.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Everyday things like turning your head shouldn’t be a pain in the neck. Cleveland Clinic medical spine experts can find ways to ease your cervical neck pain.
