Atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition that causes skin discoloration and itchy rashes. It usually starts in childhood, and flare-ups can continue through adulthood. There’s no cure, but you can manage it with creams and medications or other available treatment options.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
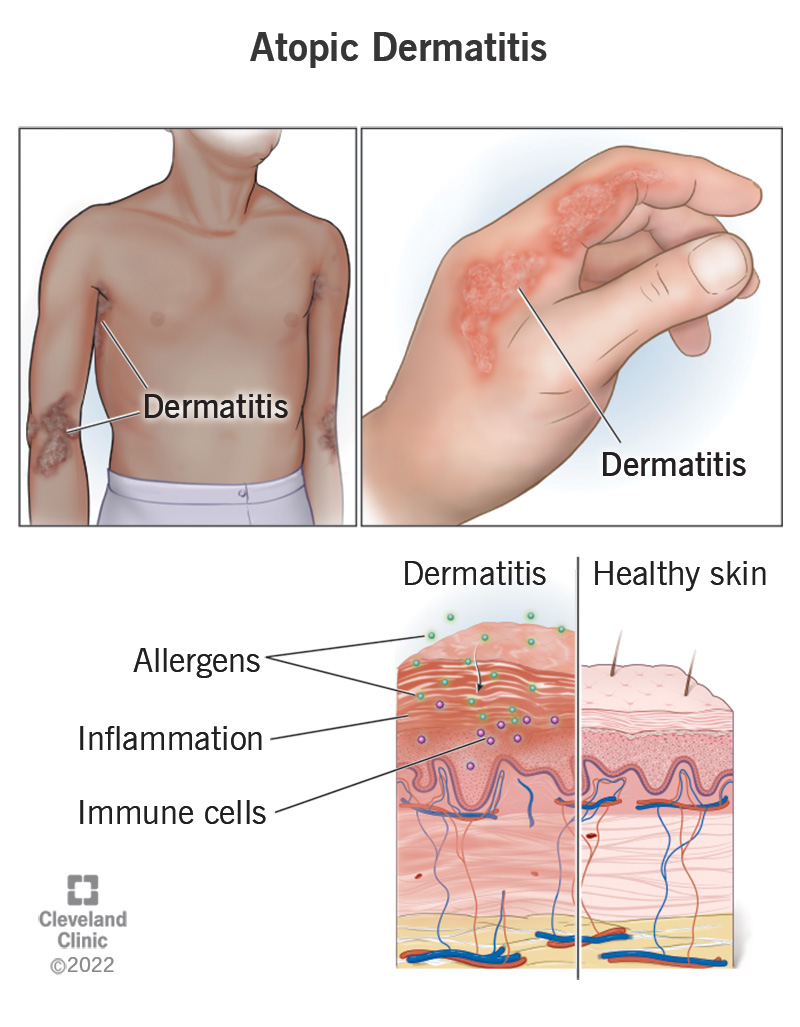
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/24299-atopic-dermatitis)
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic (long-lasting) condition that causes dry, itchy and discolored patches of skin. It affects both children and adults and can flare up or come and go throughout your life.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
When an atopic dermatitis rash develops, it can be uncomfortable and itchy. Your immediate reaction may be to scratch it. This can cause swelling, cracking, crusting and scaling. The rash might “weep” a clear fluid.
Dermatitis and eczema both refer to skin inflammation. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema. Eczema is a term describing a group of skin conditions that result from inflammation.
Treatment options are available to help you manage symptoms.
Atopic dermatitis refers to a group of skin conditions related to underlying allergies. Its appearance can vary and change over time like the following types:
Your provider may refer to atopic dermatitis by its location:
Advertisement
Common atopic dermatitis symptoms may include:
Symptoms can vary significantly from person to person. It’s common for atopic dermatitis to develop in areas where your skin bends or flexes, like behind your knees or on the inside of your elbow. But rashes can occur anywhere on your skin. Symptoms range from mild to severe.
Atopic dermatitis will have the features of a skin rash. But those features will look slightly different based on your skin tone. For example, if you have a light skin tone, the rash may look red. If you have a dark skin tone, it may be darker than your natural tone, brown, purple or gray.
It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider if you notice changes to your skin. They can pinpoint what’s going on and help you manage it.
A change in how well your skin’s protective barrier and immune system function causes atopic dermatitis.
Your immune system usually protects your body from things that can harm it, like irritants, allergens and illnesses. If you have atopic dermatitis, you may have a genetic variant that prevents your skin from creating a strong barrier against allergens and irritants. When your skin gets irritated, it inflames and feels itchy. This causes it to break down even further.
Triggers of atopic dermatitis may include:
When you come into contact with an allergen or irritant that triggers symptoms, it’s called contact dermatitis. Common allergens and irritants may include but aren’t limited to the following:
Sometimes, it’s difficult to figure out what’s causing symptoms to flare up, but your provider can try to help.
You may be more at risk of atopic dermatitis if you:
Itching your skin may cause a rash to break open. It may bleed or turn into an infection. Signs and symptoms of an infection may include:
No. Atopic dermatitis isn’t contagious. The rash doesn’t spread from person to person through physical contact.
A healthcare provider will diagnose atopic dermatitis after reviewing your symptoms during a physical examination. They’ll look closely at your skin. They may ask you questions about your symptoms, like when they started and what it feels like. Your provider will also review your medical history and known family medical history.
Advertisement
In some cases, your provider may recommend a skin biopsy. This is a test to look at a sample of your skin more closely in a lab under a microscope.
Your healthcare provider may recommend different options to treat your atopic dermatitis symptoms. This may include:
Two medications that your provider may prescribe to treat atopic dermatitis include:
Topical medications are creams or ointments that you rub on your affected skin in the same way you apply a lotion. You should use these medications as directed. They may have side effects if you overuse them.
To soothe mild, itchy, dry and cracked skin from atopic dermatitis, you can:
Advertisement
The timeline varies from person to person after you start treatment. For example, you may notice itch relief shortly after applying a prescription medication to your skin. The rash may start to fade within days to weeks.
Since there isn’t a cure for atopic dermatitis, the rash generally comes back after treatment. This is why it’s important to pay attention to your triggers and make sure you’re avoiding them, if possible.
If you have any questions about what you can expect, talk to your provider.
Contact a provider if you notice changes to your skin that cause pain and discomfort. If you’re constantly scratching your skin and develop an infection (with swelling, pain and pus), your provider will help you treat it.
Atopic dermatitis symptoms may come and go throughout your life. But the condition doesn’t go away completely.
You may be able to reduce your symptoms by using a moisturizer at least twice daily. Even if you’re diligent in your skincare routine, you can still experience flare-ups. That’s why it’s important to know how to manage your symptoms when they come back. Your healthcare provider can help you do this.
While atopic dermatitis isn’t typically dangerous, it can wreak havoc on your comfort and quality of life. Fortunately, there are several treatments available to help keep your symptoms in check. Most people experience a dramatic improvement once they find a skincare regimen that works for them. You may need to try different management techniques until you find the routine that works best for your skin. Let your care team know if you have any questions about your treatment plan or how to manage this condition.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Every day, people see your skin, hair and nails. At Cleveland Clinic, our expert and caring dermatology team will make sure they’re healthy and strong.
