Blastocystis hominis is a single-celled parasite that can live in your intestines. Many people have the infection with no symptoms. Others develop gastrointestinal illness, but it’s not clear whether Blastocystis is the cause. Antibiotic or antiparasitic medications usually resolve symptoms.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
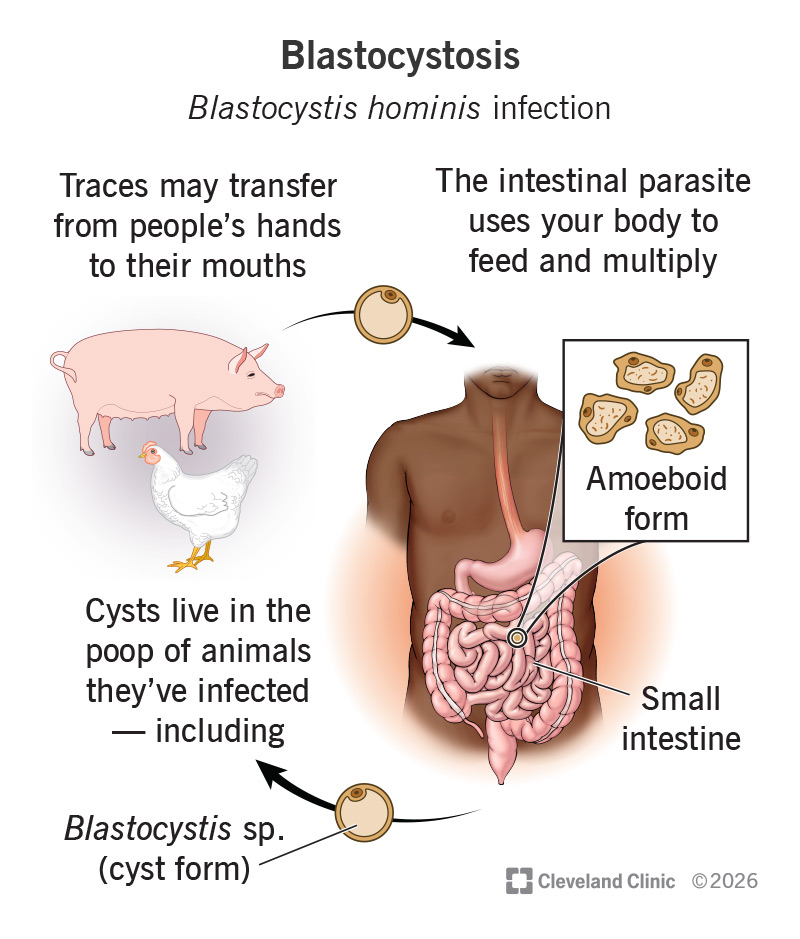
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22933-blastocystis-hominis-infection-blastocystosis.jpg)
Blastocystis hominis is a common intestinal parasite that infects people. It’s one of a group of parasites called Blastocystis sp. An infection with Blastocystis sp is called blastocystosis. Most people who have a Blastocystis infection don’t develop symptoms or even realize they’re infected. But for some, it can cause symptoms like stomach pain, nausea or diarrhea. These usually go away with antiparasitic treatment.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Most of the time, a Blastocystis infection doesn’t cause symptoms. But when it does, symptoms may include:
Some studies show a possible link between Blastocystis infection and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), but experts haven’t confirmed the connection.
Parasites like Blastocystis hominis use your body to feed and multiply. An intestinal parasite takes up residence in your small intestine and feeds off the nutrients there. This gives it the energy to multiply. After multiplying, some parasites may leave your body, but others may remain to repeat the cycle.
If an intestinal parasite stays with you for a long time and continues to grow and multiply, it may start to take too many of your nutrients. Some parasites also release toxins that make you ill. Your immune system may activate to try to remove the parasite. This may cause symptoms like nausea or diarrhea.
Blastocystis parasites most likely spread by the fecal-to-oral route. They live as cysts in the poop of animals they’ve infected — including humans. The poop and cysts may hide in the soil or in bodies of water where people pass through. Traces of it may transfer from people’s hands to their mouths.
Advertisement
You’re more likely to get a Blastocystis infection if you:
Experts are still debating this. Some don’t believe Blastocystis directly causes disease. Others think it does — but only under certain conditions, like:
Healthcare providers can diagnose blastocystosis with a stool test. They collect a sample and check it for Blastocystis cysts and other possible causes of your symptoms. If they don’t find another explanation, they may recommend treating Blastocystis.
There’s no specific treatment for a Blastocystis infection. But if you have symptoms, your healthcare provider may prescribe antiparasitic medications. In some cases, they may also prescribe antibiotics to treat bacterial infections.
These treatments often help, but not always. This might happen because:
You may also see natural treatments, special diets or herbal supplements marketed for blastocystosis. But studies haven’t confirmed their safety or effectiveness. Check with your provider before trying these approaches.
You might not need treatment if you don’t have symptoms. Blastocystosis often goes away on its own. If you want to confirm the infection is gone, you can take another stool test.
Most people with a Blastocystis hominis infection never develop symptoms. If you do, symptoms usually improve with treatment. If they don’t, your provider may check for other causes.
To lower your risk of blastocystosis and other infections:
Researchers continue to study Blastocystis to better understand how and when it causes illness in humans. Although it’s common worldwide, it usually isn’t a cause for concern. If symptoms develop, your provider can help you manage them.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Need care fast? Cleveland Clinic’s Express Care and Urgent Care locations treat everything from sprains to sinus infections — no appointment needed.
