An NSTEMI is a type of heart attack that happens when there’s a partial blockage in a coronary artery. This reduces blood flow to your heart muscle and can quickly lead to heart damage. An NSTEMI is a life-threatening medical emergency. Seek care immediately. Providers will do procedures and give you medicine to restore blood flow to your heart.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
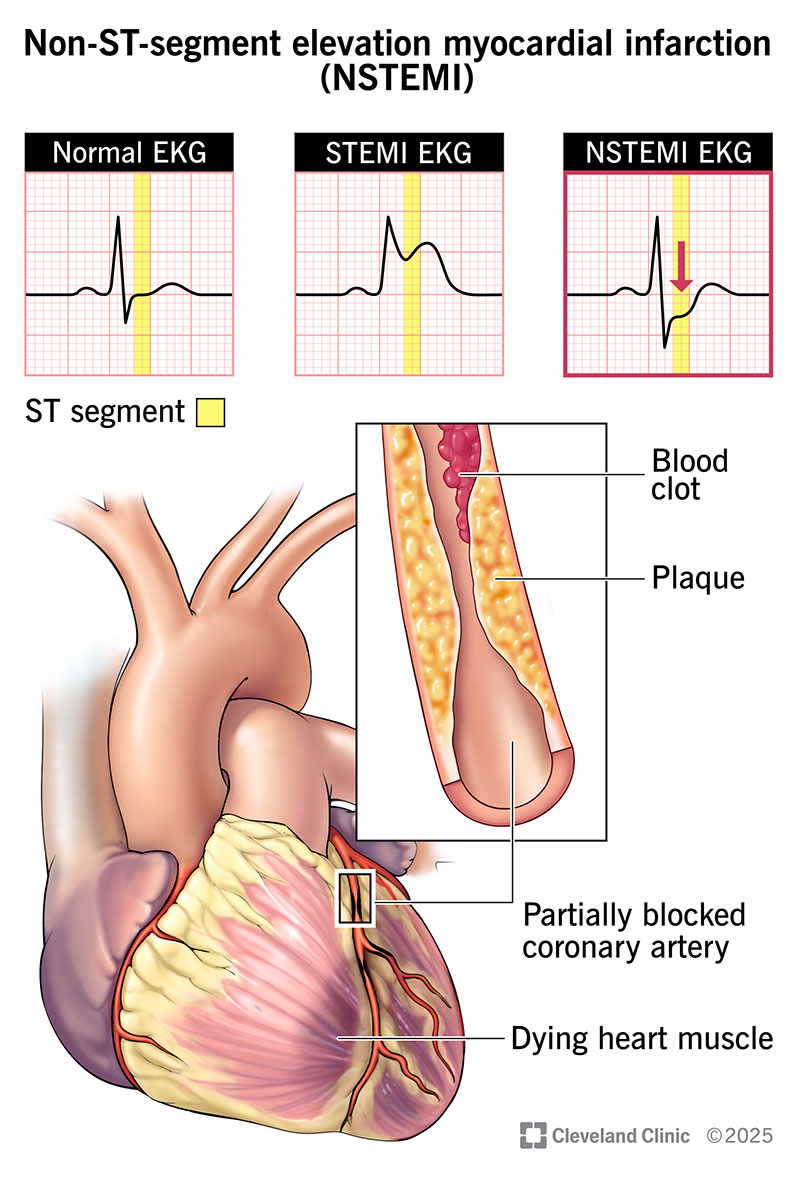
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22233-nstemi-heart-attack-illustration)
A non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI, or non-STEMI) is a common type of heart attack. It occurs when a blood clot in one of your coronary arteries partly blocks blood flow. This condition gets its name because it doesn’t cause a specific electrical pattern called ST-segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) test. This makes it different from a STEMI.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Call 911 or your local emergency services number if you or someone you’re with has chest pain/discomfort or other heart attack symptoms. Delaying medical care can lead to permanent heart damage or death.
NSTEMI symptoms are the same as those for any heart attack and include:
An NSTEMI happens when a blood clot forms over plaque in your coronary artery, causing a partial blockage. This can happen if you have coronary artery disease (plaque buildup in your heart’s arteries).
The plaque may build up over many years without causing problems. But if part of its surface wears away or breaks open, blood clots are drawn to that spot. The clots can quickly (over minutes to hours) narrow the space where blood can flow.
An NSTEMI means there’s still some room for blood to get through. But if the clotting continues, it can cause a total blockage. This means an NSTEMI can turn into a STEMI. And it’s a big reason why you need treatment right away for any heart attack symptoms.
These things raise your risk for an NSTEMI or any type of heart attack:
Advertisement
The reduced blood flow during an NSTEMI damages your heart muscle. The affected part of your heart can start dying. Your heart muscle can’t grow back or repair itself. That means the damage will be permanent unless blood flow is quickly restored.
Possible complications of an NSTEMI include:
Without treatment, an NSTEMI can also be fatal.
Healthcare providers diagnose an NSTEMI by doing a physical exam and running tests. They need to quickly learn if you’re having a heart attack, and if so, if it’s a STEMI or an NSTEMI. The exact type you’re having helps them plan treatment.
An EKG is one of the most important tests they’ll do. It shows your heart’s electrical activity as a wave on a graph. A heart attack can cause changes in the pattern that providers interpret. One part of the wave is called an ST-segment. A STEMI makes that part consistently taller than expected. But an NSTEMI doesn’t do that.
Instead, signs of an NSTEMI on an EKG may include:
Blood tests are also important for diagnosing NSTEMIs and other heart attacks. Your provider looks for raised levels of a chemical called troponin, which is a sign of heart muscle damage. You may also need imaging tests, like an echocardiogram, heart CT scan or heart MRI. These make detailed pictures of your heart and, depending on the specific test, can show things like blockages and heart damage.
Healthcare providers use procedures and medicines to open your blocked coronary artery. They also give you medicines to help your heart work better and lower your risk of complications. Treatment of all heart attacks, including NSTEMIs, is time-sensitive. That means the faster blood flow is restored, the better.
Possible NSTEMI treatments include:
Advertisement
Your symptoms should start going away while you’re receiving treatment. Many people feel tired or weak for several days after a heart attack. It’s important to take things slow and let your body heal.
Cardiac rehab can help you strengthen your heart, feel better sooner and improve your chances of survival.
Your provider will tell you how often you need follow-up visits. These are vital for your recovery and long-term health. They give your provider a chance to check your heart function and talk with you about how you’re feeling.
Call your provider any time you have new or changing symptoms, side effects from medicines or questions about your treatment plan.
If chest discomfort or other NSTEMI symptoms return, call 911 or your local emergency services number right away.
The outlook for an NSTEMI depends on several things, including how much of your heart muscle is damaged. And if you’ve had any type of heart attack, your odds for having another go up.
Follow-up care and preventive measures are very important. This means taking your prescribed medicines and going to all of your check-ups. Your healthcare provider will explain what you can expect and how you can protect your heart.
Symptoms of a heart attack can be frightening and confusing. The good news is that we know a lot more about how to diagnose and treat these issues than we did in the past. And we keep learning. That means your chances of a good outcome are always getting better.
Advertisement
If you’ve had an NSTEMI, lean on your healthcare provider for guidance. Stick with your treatment plan. Ask any questions that come to mind, and know that your provider is there to listen and support you.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When your heart needs some help, the cardiology experts at Cleveland Clinic are here for you. We diagnose and treat the full spectrum of cardiovascular diseases.
