Calcific tendonitis develops when calcium deposits build up in your tendons or muscles. These deposits can become inflamed and cause pain. Calcific tendonitis can occur anywhere in the body, but it most often affects the shoulder joint.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
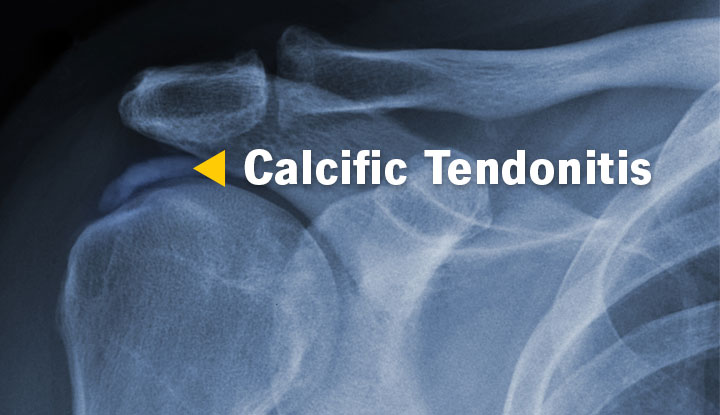
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/21638-Calcific-Tendonitis)
Calcific tendonitis is caused by calcium buildup in your tendons. These calcium deposits can accumulate in one area or may occur in more than one location. If the deposits grow bigger or become irritated, they can cause severe pain. Calcific tendonitis most often affects the shoulder — or rotator cuff — though it can occur anywhere in the body.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Rotator cuff tendonitis — also called tendonosis — is associated with inflammation of bursae and damage of the shoulder tendon. A bursa is a thin, membrane-lined sack that helps the tendons move across other structures. Calcific tendonitis doesn’t affect bursae directly but the bursae can become inflamed.
While calcific tendonitis refers to the calcification of your tendons, frozen shoulder is a condition characterized by pain and stiffness. In some cases, calcific tendonitis is associated with frozen shoulder.
People between the ages of 40 and 60 have a higher risk for calcific tendonitis. Women are also slightly more likely to be affected than men. Calcific tendonitis can happen to anyone and is not associated with any particular activity.
Calcific tendonitis is not very common. The condition occurs in less than 10% of people being treated for shoulder pain.
Some people with calcific tendonitis don’t develop pain. However, if the calcium deposits in your tendons become inflamed, it can cause severe discomfort. For some patients, this eventually leads to pain and stiffness.
Calcific tendonitis occurs in three stages, including:
Advertisement
No. Calcific tendonitis is inflammation of the tendons while arthritis is inflammation and damage of the joint itself. Calcific tendonitis may be confused with calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease (CPPD, or pseudogout) — a type of arthritis in which calcium phosphate crystals form in the joints.
Aging and wear and tear can eventually lead to calcific tendonitis. But healthcare experts really aren’t sure why some people develop the condition and others don’t.
People with calcific tendonitis may develop a number of different symptoms. These include:
Your healthcare provider will examine your shoulder, ask about your symptoms and review your medical history. You may be referred to an orthopedic specialist for further testing.
After checking your shoulder’s range of motion, your healthcare provider may order imaging tests. These may include:
Most cases of calcific tendonitis can be treated with steroid injections, physical therapy and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other calcific tendonitis treatments include:
Side effects depend on the treatment that is performed. Most non-surgical options have minimal side effects that may include temporary discomfort and swelling. Patients who undergo surgery for calcific tendonitis have a small risk of:
In most cases, recovery after calcific tendonitis surgery takes about six weeks. You may need to wear a sling to keep your shoulder from moving too much.
Advertisement
Calcific tendonitis may be accompanied by mild or severe pain. You can manage most mild symptoms with:
Most of the time, calcific tendonitis can be addressed and resolved quickly. But periodic checks by your healthcare provider are recommended — especially if you’ve had the condition before.
Calcific tendonitis can also be associated with frozen shoulder or rotator cuff tears. If you have pain that doesn’t improve with treatment, be sure to let your healthcare provider know.
Though calcific tendonitis can’t be prevented altogether, there are steps you can take that may reduce your risk. For example, if you develop pain in your shoulder, don’t participate in any strenuous activities until you have it checked out by your healthcare provider.
If you experience sudden or intense shoulder pain, stiffness of your shoulder joint or discomfort that interrupts sleep, schedule a consultation with your healthcare provider. They can identify the root cause of your pain and determine an appropriate treatment plan.
Sometimes calcium deposits can lead to shoulder impingement syndrome. This occurs when the deposits cause your tendon to grow larger and it rubs against the bone. Many people also report significant pain during the reabsorption stage.
Advertisement
In most cases, calcific tendonitis eventually goes away on its own. However, if you think you have calcific tendonitis, call your healthcare provider so they can rule out other issues.
Calcific tendonitis symptoms can wax and wane. Some people go months or years without experiencing issues. If you’ve had the condition in the past, it’s a good idea to schedule periodic checkups with your healthcare provider.
Calcific tendonitis is usually resolved quickly. However, this condition can also be associated with other issues affecting the shoulder, such as bursitis, frozen shoulder and rotator cuff tendonitis. Therefore, if you develop calcific tendonitis symptoms, such as sudden pain, tenderness or reduced range of motion, contact your healthcare provider. Prompt diagnosis and treatment gives you the best chance for a quick, successful recovery.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic experts are here to treat your tendinopathy (tendon pain) and get you back to doing the things you love.
