Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is an inner ear disorder. A person with BPPV experiences a sudden spinning sensation whenever they move their head. BPPV isn’t a sign of a serious problem. If it doesn’t disappear on its own within six weeks, a simple in-office procedure can help ease your symptoms.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
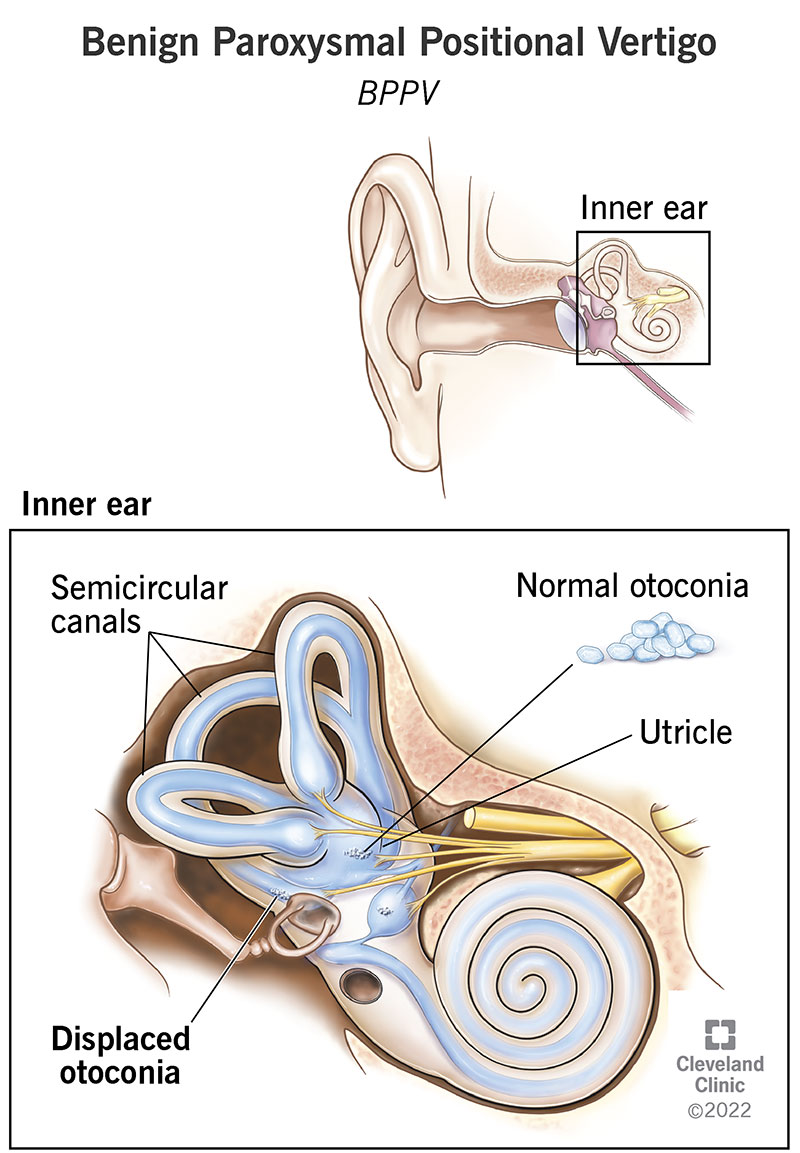
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/Images/org/health/articles/11858-benign-paroxysmal-positional-vertigo)
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a common inner ear disorder. With BPPV, changes in your head position — such as tipping your head backward or sitting up in bed — lead to sudden vertigo (a feeling that the room is spinning).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
BPPV isn’t a sign of a serious problem, and it usually disappears on its own within a few days of the first episode. (It could take several weeks for some people.) However, the symptoms of BPPV can be very frightening and may be dangerous, especially in adults over the age of 65. The unsteadiness of BPPV can lead to falls, which are a leading cause of fractures.
BPPV can affect people of all ages, but it’s most common in adults over the age of 50. About half of all people in this age range experience at least one episode of BPPV in their lifetime.
BPPV can affect children, but it’s rare.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is the most common inner ear disorder. In fact, approximately 20% of people who are evaluated for dizziness are diagnosed with BPPV.
BPPV usually goes away on its own. However, until it’s successfully treated, it can come back. In some cases, months — or even years — go by before another episode occurs.
Vertigo is the main symptom of BPPV. This vertigo sensation can range from mild to severe and may last seconds, or up to 1 minute. It may be accompanied by other benign paroxysmal positional vertigo symptoms, including:
Advertisement
While BPPV usually only affects one ear at a time, it can potentially affect both ears.
BPPV is almost always triggered by a change in your head’s position. Some people may notice symptoms when lying down or sitting up in bed. Others might notice symptoms when they tilt their head back or to the side. These symptoms often worsen with age due to normal wear and tear of the inner ear structures.
In some instances, BPPV may be a symptom of another inner ear condition, such as:
Additionally, BPPV may accompany migraines, or it may develop after a traumatic event — such as a fall, accident or sports injury.
BPPV develops when calcium carbonate particles (otoconia) move into your semicircular canals (inner ear structures that control balance) and become trapped. Normally, the otoconia are part of your utricle, a vestibular organ next to your semicircular canals.
In your utricle, the otoconia may become loose due to injury, infection or age. As your head position changes, the otoconia roll around and push on tiny hair-like structures (cilia) within your semicircular canals. Those cilia help transmit information about balance to your brain. Vertigo develops when the cilia are stimulated by the rolling otoconia.
Your healthcare provider can diagnose BPPV during an office visit. They’ll perform a physical examination and ask questions about your symptoms and medical history.
The most effective benign paroxysmal positional vertigo treatments involve physical therapy exercises. The goal of these exercises is to move the calcium carbonate particles out of your semicircular canals and back into your utricle. Here, the particles resorb more easily and don’t cause uncomfortable symptoms.
You can also take motion sickness medications to relieve your symptoms. However, you shouldn’t take these medications long term.
BPPV exercises — sometimes called canalith repositioning procedures — typically take about 15 minutes to complete. Particle repositioning involves a series of physical movements that change the position of your head and body. These actions shift the otoconia out of your semicircular canals and back into their proper location in your utricle.
A single particle repositioning procedure is effective in treating about 80% to 90% of cases of BPPV. Additional BPPV exercises may be needed if symptoms continue.
Your healthcare provider can perform this maneuver during an office visit. They can also demonstrate how to do these exercises at home to ease your BPPV symptoms.
Advertisement
In the meantime, here are some step-by-step instructions to try:
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/012585e5cf4a4564ba3faa8d66332e48.ashx)
Right position
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/15a4f3b230554fb8a46dbab2c92c2c78.ashx)
Left position
Yes. In many cases, BPPV goes away on its own eventually. But it can come back. If it does, your healthcare provider can tell you how to manage your symptoms when they occur.
The good news is that BPPV doesn’t indicate a serious health problem. Even so, dealing with your symptoms can be scary and frustrating. Your healthcare provider can teach you how to do BPPV exercises at home so you can manage your symptoms at the first sign of trouble.
Advertisement
In most cases, a BPPV episode lasts 1 to 2 minutes. Your symptoms may be mild, or they may be so severe that you throw up. You might even lose your balance when you try to stand or walk.
You can’t prevent BPPV, but you can manage it with particle repositioning exercises. To reduce your risk of trauma-related BPPV, be sure to wear a helmet when biking, playing contact sports or participating in other similar activities.
If you’ve experienced a BPPV episode, schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider. They can demonstrate physical therapy exercises to reduce your symptoms.
If you have dizziness combined with a severe headache, chest pain or an irregular heartbeat, call 911 right away.
Advertisement
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo isn’t life-threatening, but it can have a significant negative impact on your quality of life. If you’ve experienced sudden episodes of dizziness, vertigo, balance problems or other symptoms related to BPPV, call your healthcare provider. In most cases, physical therapy exercises and home treatments can keep your symptoms at bay.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Vertigo, dizziness and balance disorders can make you feel unsteady on your feet. Cleveland Clinic’s experts can craft a treatment plan that works for you.
