The elbow joint is where your humerus (your upper arm bone) meets your radius and ulna (the two bones in your forearm). It joins your upper arm to your forearm. Your elbow also contains cartilage, ligaments, muscles, nerves and blood vessels. Your elbow moves in two main directions. You use it almost any time you move your arm.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
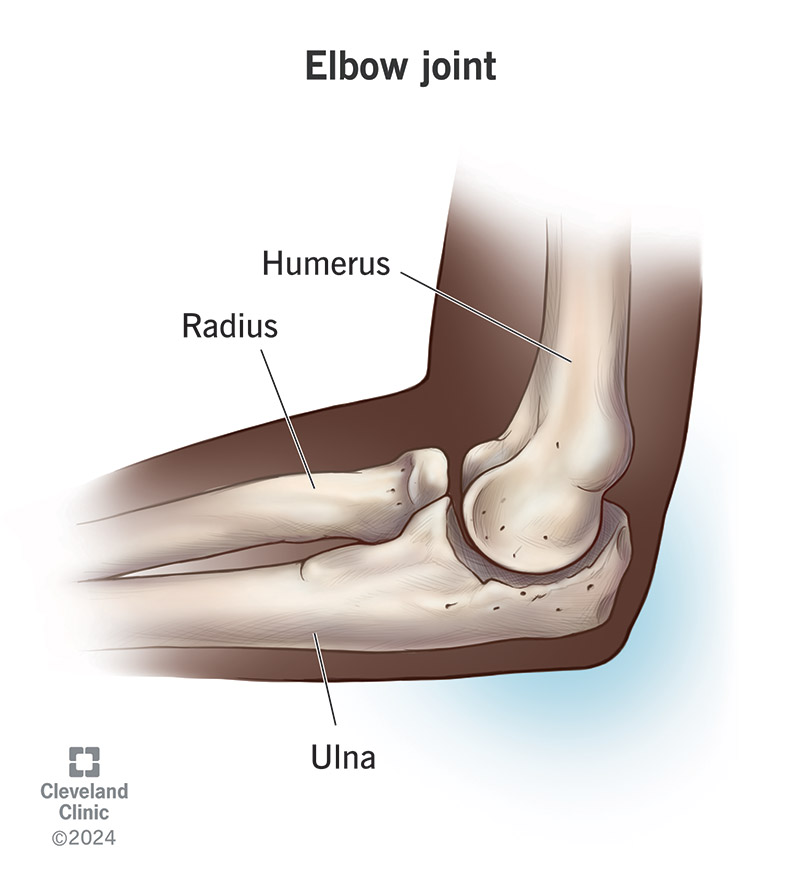
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/elbow-joint)
The elbow is the joint that connects your upper arm to your forearm.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Like all your joints, your elbows are part of your skeletal system. Your elbows also contain cartilage, muscles, ligaments, nerves and blood vessels.
Visit a healthcare provider if you’re experiencing elbow pain or other symptoms that make it hard to use your elbow. They’ll diagnose the cause and suggest treatments to help you get back to your usual routine and activities.
Your elbow flexes to bend your arm. It can move in four directions:
The elbow joint is in the middle of your arm — the part that bends where your upper arm and forearm meet.
Healthcare providers classify joints based on:
The elbow is a synovial joint. Synovial joints have the most freedom to move. They’re made of a cavity in one bone that another bone fits into. Slippery hyaline cartilage covers the ends of bones that make up a synovial joint. A synovial membrane — a fluid-filled sac that lubricates and protects the joint — lines the space between the bones. This extra cushioning helps synovial joints move with as little friction as possible.
Advertisement
Functionally, the elbow is both a hinge joint and a pivot joint (a trochoginglymus joint). Hinge joints move just like the hinges that hold a door in place. They have a few parts that don’t move, but other pieces travel a specific distance to open and close. Your elbow hinges to bend and straighten your arm.
It’s also a pivot joint. Pivot joints rotate in place without moving out of their original position. Your elbow pivoting is what lets you turn your forearm over to move your palm up and down.
Your elbow joints are made of:
Three bones make up your elbow joint:
Cartilage is a strong, flexible tissue that protects your joints. It acts as a shock absorber throughout your body. Your elbows are lined with hyaline cartilage. Hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage in your body. Some healthcare providers call it articular cartilage.
Hyaline cartilage is slippery and smooth, which helps bones in your joints move smoothly past each other. The surfaces of your humerus, ulna and radius that touch each other have a hyaline cartilage lining.
Ligaments are like cords that connect bones together.
There are three main ligaments in your elbows:
Muscles are soft tissue made of stretchy fibers. They tense up (flex) to pull and move parts of your body. Muscles attached to your arm bones help move your elbow.
Muscles that control flexion let you flex your lower arm in, toward your body. They include the:
Two extensor muscles let you move your lower arm out, away from your body:
Muscles that control supination let you move your palm up:
Pronator muscles help you move your palm down:
Nerves are like cables that carry electrical impulses between your brain and the rest of your body. These impulses help you feel sensations and move your muscles. Nerves that give your elbow feeling include the:
Advertisement
Blood vessels are channels that carry blood throughout your body. They form a closed loop, like a circuit, that begins and ends at your heart. Three arteries carry blood to and from your elbow, including the:
Your elbows can be affected by anything that damages your bones or connective tissue, including:
Sports injuries are some of the most common elbow injuries:
The symptoms you experience will depend on which elbow injury or issue you have. Some common elbow symptoms include:
Visit a healthcare provider as soon as you notice changes or pain in your elbow, especially if you experience an injury like a fall. Some of the most common tests providers use to diagnose issues include:
Advertisement
Which treatments you’ll need depend on the injury or health condition you have. You might only need at-home treatment. You may need to wear a sling, brace or cast. If you need surgery, your surgeon will probably perform a minimally invasive elbow arthroscopy. Your healthcare provider or surgeon will tell you which treatments you’ll need and what to expect.
Visit a healthcare provider if you’re feeling elbow pain or experiencing other symptoms that last more than a few days. You can usually manage minor symptoms at home with the RICE method:
Don’t play sports or do intense physical activity that can put more stress on your elbow until a healthcare provider says it’s safe.
You might only think about your elbows when you bang one on the counter or someone uses theirs to foul you during a pickup basketball game. But you use your elbow joints almost constantly to move and turn your arms. They’re a complex joint, but they’re also one of your strongest.
Advertisement
You can probably manage most injuries with at-home treatments like icing and rest, but don’t ignore pain that lasts for more than a week. Visit a healthcare provider if you have pain, swelling or other symptoms that make it hard to move and use your elbow. They’ll suggest ways to help your elbow heal.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
We diagnose and treat conditions that cause wrist pain and elbow pain. Learn how Cleveland Clinic experts use minimally invasive treatments to relieve your discomfort.
