The substantia nigra is a brain structure that is part of your basal ganglia. While it’s very small, this structure is essential in how your brain controls your body’s movements. It also plays a part in the chemical signaling in your brain, which affects learning, mood, judgment, decision-making and other processes.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
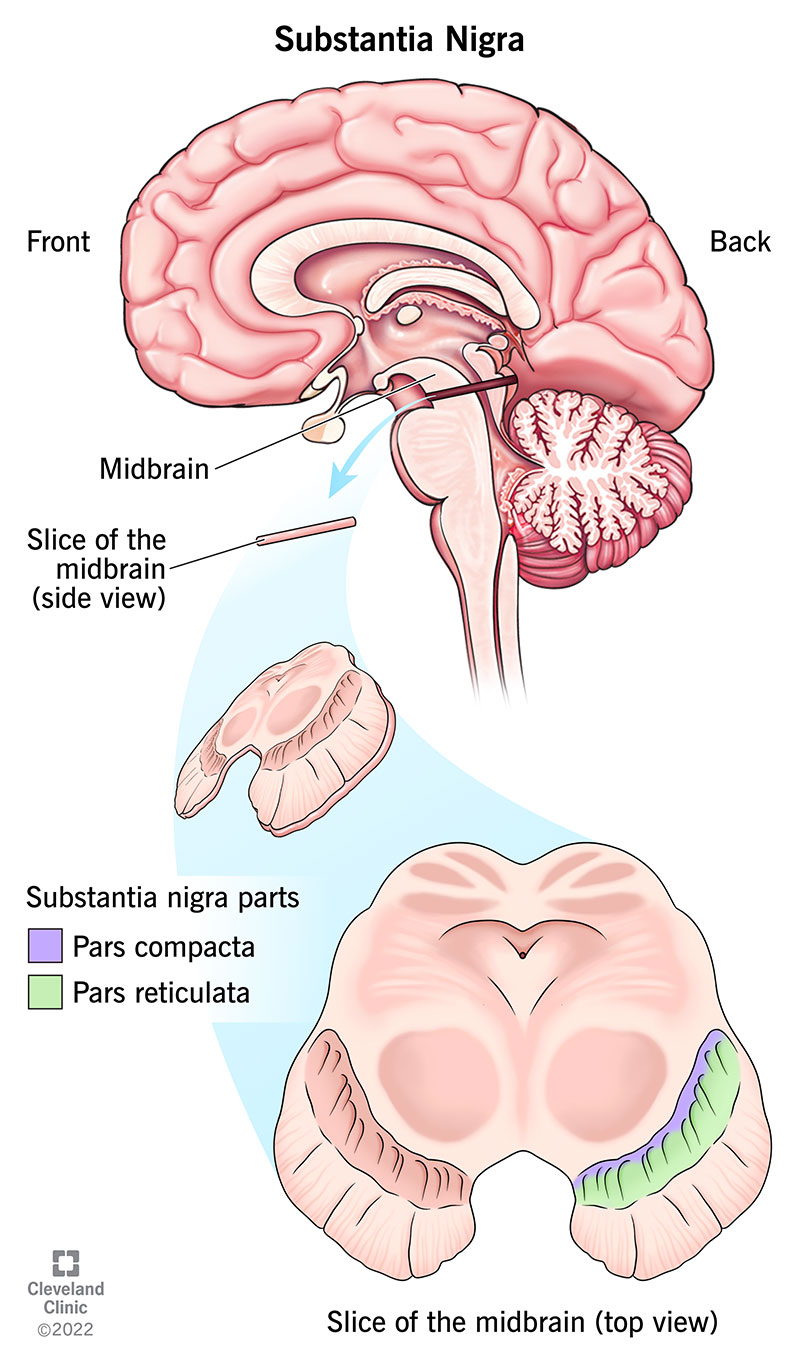
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/23010-substantia-nigra)
The substantia nigra (SN) is a part of your brain that helps control your movements. It’s part of the basal ganglia, a group of structures that form connections and circuits throughout your brain. The substantia nigra is important because of its role in your movements and how it influences your brain’s chemistry.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The substantia nigra (sub-stan-chee-uh ny-grah) is a part of your basal ganglia, forming connections with different parts of your brain. It produces dopamine, which controls movements and muscle tone.
The substantia nigra has two different sections, and they both have different roles and connections. The two sections are:
The SN is in your midbrain. As the name suggests, this section of your brain is at the center of your brain. It’s just above your brainstem, leading down to where your skull meets your neck and connects to your spinal cord.
Though the term “substantia nigra” refers to just one of these structures, you actually have two. They're on either side of your midbrain, and each has a pars reticulata and a pars compacta. The plural name is “substantiae nigrae.”
Advertisement
Though it's part of your basal ganglia, the SN is not a ganglion ("ganglia" refers to more than one ganglion). It's a nucleus, a type of nervous system structure made up of cells with the same job or connections.
The substantia nigra gets its name from Latin and means "black substance.” That’s because while most of your brain is a lighter shade of pinkish-gray, the substantia nigra is much darker, appearing as a band of black tissue surrounded by much lighter tissue. That’s because the brain cells here also contain melanin. That’s the chemical in your skin cells that makes them darken because of sun exposure, which causes your skin to tan.
The SN is very small. About 25 average-sized substantiae nigrae could fit into a golf ball.
Making up your basal ganglia, including the substantiae nigrae, are the following (with more information below):
Neurons are the cells that send and relay signals through your nervous system, using both electrical and chemical signals. Each neuron consists of the following:
Neuron connections are incredibly complex, and the dendrites on a single neuron may connect to thousands of other synapses. Some neurons are longer or shorter, depending on their location in your body and what they do.
Glial (pronounced glee-uhl) cells have many different purposes, helping develop and maintain neurons when you’re young, and managing how the neurons work throughout your entire life. They also protect your nervous system from infections, control the chemical balance in your nervous system and create the myelin coating on the neurons’ axons. Your nervous system has 10 times more glial cells than neurons.
Advertisement
Conditions that affect the substantia nigra include, but aren’t limited to:
The symptoms that can happen with conditions that affect the basal ganglia depend strongly on the type of condition.
Several tests can help diagnose conditions that affect your brain, including the substantia nigra. The most common tests used for this include:
Advertisement
A wide range of conditions can affect the substantia nigra, with an even wider variety of treatments for those conditions. The available treatments depend strongly on the condition. In some cases, these conditions are treatable with medication, while others may require surgery. Curing some of these conditions is also possible in some cases, but others may resist treatment. When curing a condition isn’t an option, treating the symptoms is usually the best option.
It’s possible to prevent — or at least delay — many conditions that affect your brain, including the substantia nigra. You can't prevent other conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease, because they happen unpredictably. Some of the most important things you can do include:
Advertisement
The substantia nigra is a tiny part of your brain, but it has an essential job. While experts still have much to learn about it, there’s much we already know. It’s a key part of your brain’s electrical and chemical signaling systems, and it helps coordinate your movements, vision and more. As technology and medical research advance, we'll continue to understand more about its inner workings and how to treat the conditions affecting it.

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
If you have a neurological condition, you want expert advice. At Cleveland Clinic, we’ll work to create a treatment plan that’s right for you.
