An ultrasound technologist, or a diagnostic medical sonographer, creates images called ultrasounds or sonograms. Sonography uses sound waves to produce images of the inside of your body. Healthcare providers use the images to diagnose or monitor many different health conditions.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
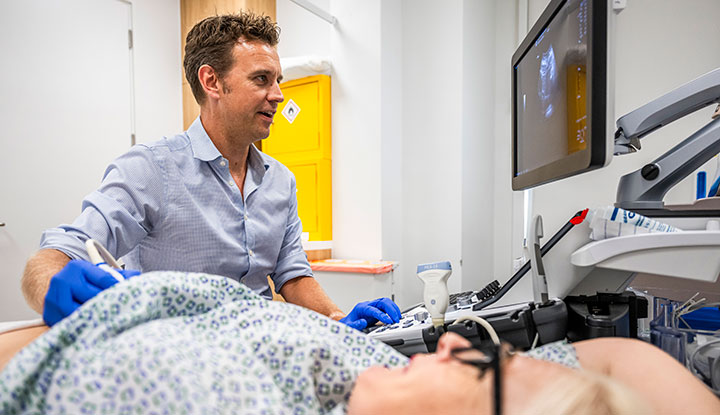
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/24877-ultrasound-technician-diagnostic-medical-sonographer)
An ultrasound technologist, or diagnostic medical sonographer, is a healthcare provider who uses ultrasound technology to create images of the inside of your body. Medical sonographers work closely with physicians to diagnose and monitor many medical conditions. They’re sometimes called ultrasound technicians.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Ultrasound technologists specialize in creating images called ultrasounds or sonograms. Sonography uses sound waves to produce images of your body’s organs and tissues. A sonographer scans parts of your body with a wand called a transducer. The transducer sends out pulses of sound that bounce back, causing echoes. The echoes form an image of the inside of your body on the sonographer’s computer screen.
Ultrasound technologists have many other responsibilities, like:
Diagnostic medical sonographers can specialize in specific parts of your body. The different types of medical sonographers include:
Advertisement
When you think of the word “ultrasound,” you might picture someone who’s pregnant looking at images on a screen. That’s one of the more familiar uses of ultrasound. But it’s much more than that. Ultrasound technologists play a key role in healthcare by capturing detailed images of various parts of your body. They work closely with doctors and other healthcare providers, and play a key role in your medical care.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
When you need a clear picture of what’s happening inside your body, the Cleveland Clinic imaging team is here for you.
