Having 20/20 vision means you see the world with normal clarity and sharpness. If you don’t have 20/20 vision, corrections like eyeglasses or contact lenses are usually all it takes to see the world this clearly.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
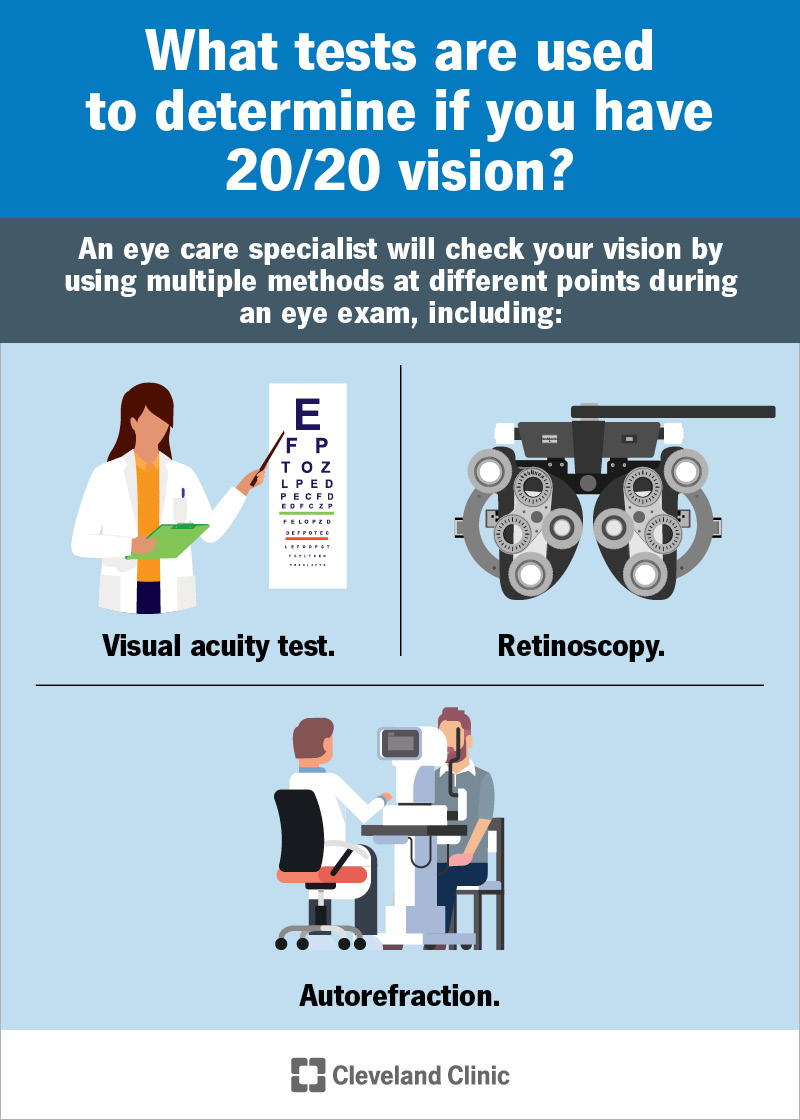
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/20-20-vision-infograph)
20/20 vision is “normal” vision. It’s a measure of the clarity or sharpness of your eyesight when you’re 20 feet away from an object. Eye care specialists call this visual acuity. Having 20/20 vision means your vision is typical — it doesn’t mean your vision is perfect. And while 20/20 vision is considered “normal” vision, only 35% of people in the world have it without glasses, contact lenses or eye surgery.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
When you take a visual acuity test, the first number is how far away you are from the object. In vision tests, this number will always be 20. That’s because this test places you 20 feet away from a target. The second number is how far away a person with normal visual acuity would have to be to see the object with the same clarity and sharpness as you.
For example, if you have 20/15 vision, you see an object that’s 20 feet away as clearly as most people would see it if they stood 15 feet away. This means your vision is better than normal. If you have 20/40 vision, what you see 20 feet away from an object is what someone with normal vision could see from 40 feet away. This means your vision is worse than normal since you need to be closer to the object to see it. If you have less than 20/20 vision without corrective lenses, there are many options available that can help you see things more clearly.
In places around the world that use the metric system, 20/20 vision is known as 6/6 vision. This is because they measure your ability to see an object clearly from 6 meters away rather than 20 feet.
Having 20/20 vision is important for seeing the world clearly, but other parts of vision are important, too. Those include:
Advertisement
Having good eyesight is important for your safety. It also plays a big role in your quality of life, helping with work, social activities, hobbies and much more. And good vision can mean that you wear glasses or contacts. What’s important is that you see clearly enough — with or without correction — to interact with the environment and people around you.
Vision does more than help you void sharp corners. It helps keep your mind sharp so you can keep up with your everyday activities. It helps you read recipes when you cook, instructions on your medications or cleaning products, and signs on the road as you drive.
An eye care specialist will check your vision by giving you an eye exam. They commonly use multiple methods at different points during an eye exam, including:
The most common causes of vision that’s less than 20/20 are refractive errors. These are issues with the shape of your eyes that make your vision blurry, including:
Other eye conditions can also impact how well you see, including:
It’s also possible — though less common — for your vision to be better than normal.
Many possible vision correction treatments are available if you have refractive errors. These treatments alter your vision to bring it as close to 20/20 as possible. They include:
Other conditions may require surgical or medical treatment plus eyeglasses or contacts. Even then, you may not have 20/20 vision.
There are several things you can do to maintain your eye health and reduce your risk of having decreased visual acuity. They include:
Advertisement
Your eyes are the windows to the world around you, regardless of how you score on a visual acuity test. It’s important to take good care of them. Doing so reduces your risk of vision loss.
Advertisement

Sign up for our Health Essentials emails for expert guidance on nutrition, fitness, sleep, skin care and more.
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability and up-to-date clinical standards.
Getting an annual eye exam at Cleveland Clinic can help you catch vision problems early and keep your eyes healthy for years to come.
