Dilated pupils (mydriasis) are when the black center of your eyes are larger than normal. The condition may be caused by dilating eye drops from an eye exam, the side effects from a drug/medication or traumatic injury. Pupils naturally dilate due to changes in light and emotional events, but unusual pupil dilation could be the result of a medical condition.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
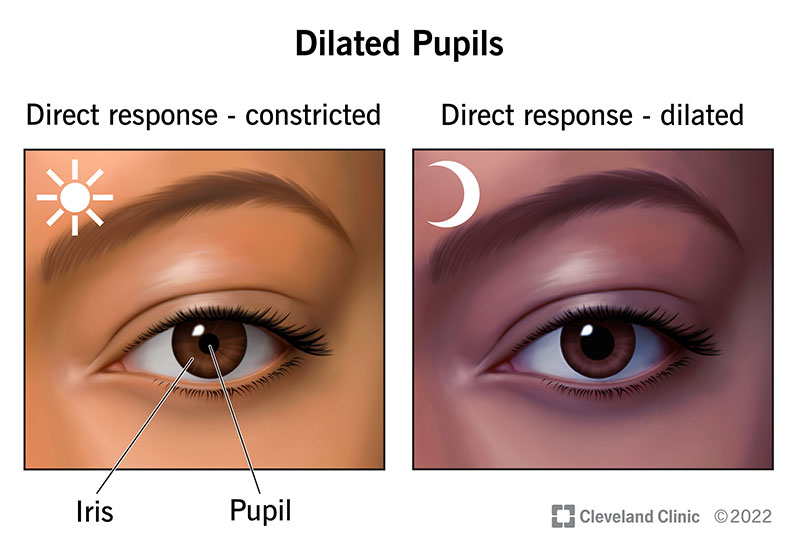
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/-/scassets/images/org/health/articles/22238-dilated-pupils.jpg)
If your pupils are dilated, the black center of your eyes (pupils) are larger than usual. Pupils are typically the same size in both eyes.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Pupils change in size to control how much light enters your eye. The colorful part of your eye (iris) controls the size of your pupil with tiny muscles. In bright light, your pupils will get smaller to prevent light from entering. In the dark, pupils get larger to allow more light in. These changes are called direct responses.
Pupils also shrink when you focused on a close object. This is called an accommodative response. If a pupil does not get smaller in bright light or expand in the dark, the pupil is not functioning normally.
Mydriasis is when the pupil is dilated and doesn’t respond to light. Another term for mydriasis is “fixed pupil.”
A pupil’s normal size is 2 to 4 millimeters in bright light and 4 to 8 millimeters in dim light (dilated).
Pupils are dilated when the center black portion of your eyes takes up more space than the colorful portion of your eyes (iris).
Pupils are supposed to dilate under normal circumstances due to light changes and emotional variables. Most of the time, dilated pupils will go back to normal size on their own. If pupils dilate suddenly, occur after a traumatic injury or cause headaches and confusion, seek medical attention immediately.
Yes, when one pupil is more dilated than the other it is called anisocoria. This common condition occurs when both pupils react normally to light but vary in size by more than half a millimeter. Anisocoria affects about 20% of the population.
Advertisement
The most common causes of dilated pupils are:
Certain recreational drugs can dilate pupils, including:
Certain over-the-counter and prescription medications can also lead to dilated pupils, including:
Some medical conditions or injuries also dilate pupils, including:
Often, dilated pupils will cause symptoms based on how light reaches the eye. These include:
Most of the time, dilated pupils will return to normal on their own without treatment, especially if they are the result of eye drops. For more serious cases of mydriasis, further treatment is required, including:
If you received dilating eye drops from an ophthalmologist, your eyes could be dilated between four and 24 hours. The length of time is dependent on the type of drop used and how your body responds to it.
If pupil dilation is the side effect of a medication or drug, the duration may vary based on the type of drug and the dosage taken.
Pupil dilation that's a reaction to an emotional factor (adrenaline, attraction, stress) could have a shorter duration, and the pupil could return to normal size in as little as two to three minutes.
Although it is normal for dilation to occur based on changes in light, mydriasis could be a sign of an eye injury or problem within the brain, like a head injury, tumor or stroke. Contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
Advertisement
Pupil dilation can be attributed to an increase in the hormone and neurotransmitter oxytocin, which acts as a chemical messenger during sexual arousal. Oxytocin also plays a role in controlling key aspects of the reproductive system, including sperm transportation and production, childbirth and breastfeeding.
In some cases, anxiety can cause pupils to dilate as a result of adrenaline. The hormones and chemicals released from the adrenal glands send nerve impulses to organs, leading the body to react in a “fight or flight” mode. Stress can stimulate adrenaline hormones to react, resulting in dilated pupils, increased heart rate, high blood pressure and excessive sweating.
Similar to how your body reacts in a “fight or flight” adrenaline situation, lying can cause hormones and chemicals associated with stress to trigger eye dilation.
Pupils are supposed to change in size as a reaction to light and normal events in your life. The range of time that pupils dilate varies for each person, but the majority of cases will go back to normal on their own. If you notice your pupils are unusually dilated, reach out to a healthcare professional for treatment.
Advertisement
Learn more about the Health Library and our editorial process.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic's health articles are based on evidence-backed information and review by medical professionals to ensure accuracy, reliability, and up-to-date clinical standards.
Cleveland Clinic’s primary care providers offer lifelong medical care. From sinus infections and high blood pressure to preventive screening, we’re here for you.
